|
Ongon
Ongon (Mongolian; plural ongod) is a type of spirit in the shamanistic belief system of Mongolia. It is a common term in Mongol mythology. After death, all shamans become shamanic souls, ongod. Idols can be consecrated to them within three years of the shaman's death and can be placed in the home ("home ongon") or in another locale, such as a shelter out in the open ("field ongon"). The ongon is also the physical representation of that spirit, made by a shaman, which plays a central part in the ritual that invokes the protection of the spirit. One well-known such spirit is Dayan Deerh. The ongon is particularly important in black shamanism: the main function of the ''khar talynkh'' or black shaman is to bring people into contact with the ongon, whose spirit they call up "while drumming in a trance". In late-nineteenth century Mongolia, according to Otgony Purev, yellow shamanism revered ongon as well, and every three years yellow shamans gathered in Dayan Deerh monastery in Khöv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Shamanism
Mongolian shamanism, known as the ( ) in Mongolian language, Mongolian and more broadly called the Mongolian folk religion or occasionally Tengrism, Tengerism, refers to the animism, animistic and shamanism, shamanic ethnic religion that has been practiced in Mongolia and its surrounding areas (including Buryatia and Inner Mongolia) at least since the age of recorded history. In the earliest known stages it was intricately tied to all other aspects of social life and to the tribal organization of Mongolian society. Along the way, it has become influenced by and mingled with Buddhism. During the socialism, socialist years of the twentieth century, it was heavily repressed, but has since made a comeback. Yellow shamanism defines a distinct form of shamanism practiced in Mongolia and Siberia. The term "yellow" in "Yellow Shamanism" is derived from "Yellow Buddhist"; more commonly known as Tibetan Buddhism, this style of Shamanism integrated elements of ritual practice and traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population density, most sparsely populated sovereign state. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border an Endorheic basin, inland sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and List of cities in Mongolia, largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, the Second Turkic Khaganate, the Uyghur Khaganate and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest List of largest empires, contiguous land empire i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Mythology
The Mongol mythology is the traditional religion of the Mongols. Creation There are many Mongol creation myths. In one, the creation of the world is attributed to a Buddhist deity Lama. At the start of time, there was only water, and from the heavens, Lama came down to it holding an iron rod with which he began to stir. As he began to stir the water, the stirring brought about a wind and fire which caused a thickening at the centre of the waters to form the earth. Another narrative also attributes the creation of heaven and earth to a lama who is called Udan. Udan began by separating earth from heaven, and then dividing heaven and earth both into nine stories, and creating nine rivers. After the creation of the earth itself, the first male and female couple were created out of clay. They would become the progenitors of all humanity. In another example the world began as an agitating gas which grew increasingly warm and damp, precipitating a heavy rain that created the oceans. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dayan Deerh
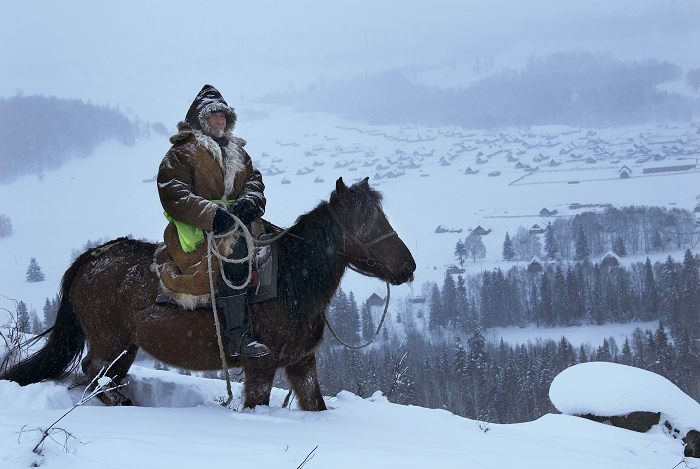
Dayan Deerh or Dayan Degereki is one of the most important divinities in the folk practices and shamanic invocations in Khövsgöl Province, Mongolia. His cult is linked to fertility rites which are practiced in yellow shamanism (which incorporates Buddhist ritual and belief) as well as in black shamanism (a less Buddhist-influenced type of shamanism). He is still venerated, especially on the eastern side of Lake Khövsgöl. Origin and cult Dayan Deerh is worshiped in both yellow shamanism and the less Buddhism-influenced black shamanism, though black shamans around Khövsgöl Nuur often do not accept him since he is popular among the yellow shamans. One explanation is that Dayan Deerh would have betrayed the black shamans by going over to the Buddhist side. Agnes Birtalan proposed that he began his career as a fertility god, then became a spirit particularly for shamans, and ended up as a protector. As a fertility god, he granted cattle and children to people, and was a shaman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Shamanism
Black shamanism () is a kind of shamanism practiced in Mongolia and Siberia. It is specifically opposed to yellow shamanism, which incorporates rituals and traditions from Buddhism. Black Shamans are usually perceived as working with evil spirits, while white Shamans with spirits of the upper world. Black shamans were thought to be able to stop demons by conversing with the spirits of human dead, turn into animals, fly, and go into trances. Buddhism entered Mongolia in the sixteenth century after the conversion of Altan Khan. In 1691, after Outer Mongolia had been annexed by the Qing Dynasty, Buddhism became the dominant religion of the entire area and shamanism began incorporating Buddhist elements. Violent resistance in the eighteenth century by the hunting tribes of Northern Mongolia against the (Buddhist) ruling group, the Khalka Mongols, led to the foundation of black shamanism. Spirit world and class Klaus Hesse described the complex spiritual hierarchy in clan-based Mongo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Shamanism
Yellow shamanism () is the term used to designate a particular version of shamanism practiced in Mongolia and Siberia which incorporates rituals and traditions from Buddhism. "Yellow" indicates Buddhism in Mongolia, since most Buddhists there belong to what is called the "Yellow sect" of Tibetan Buddhism, whose members wear yellow hats during services. The term also serves to distinguish it from a form of shamanism not influenced by Buddhism (according to its adherents), called " black shamanism". Terminology and background While the applicability of the term "yellow" (or any other term) is still somewhat disputed, scholars consider the variety of shamanism practiced by the Khalka Mongols, the largest population group of Mongolia, to be yellow shamanism; others refer to the shamanism practiced by the Buryats of Siberia as yellow shamanism. Mongolia Buddhism first entered Mongolia during the Yuan dynasty (thirteenth-fourteenth century) and was briefly established as a state relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
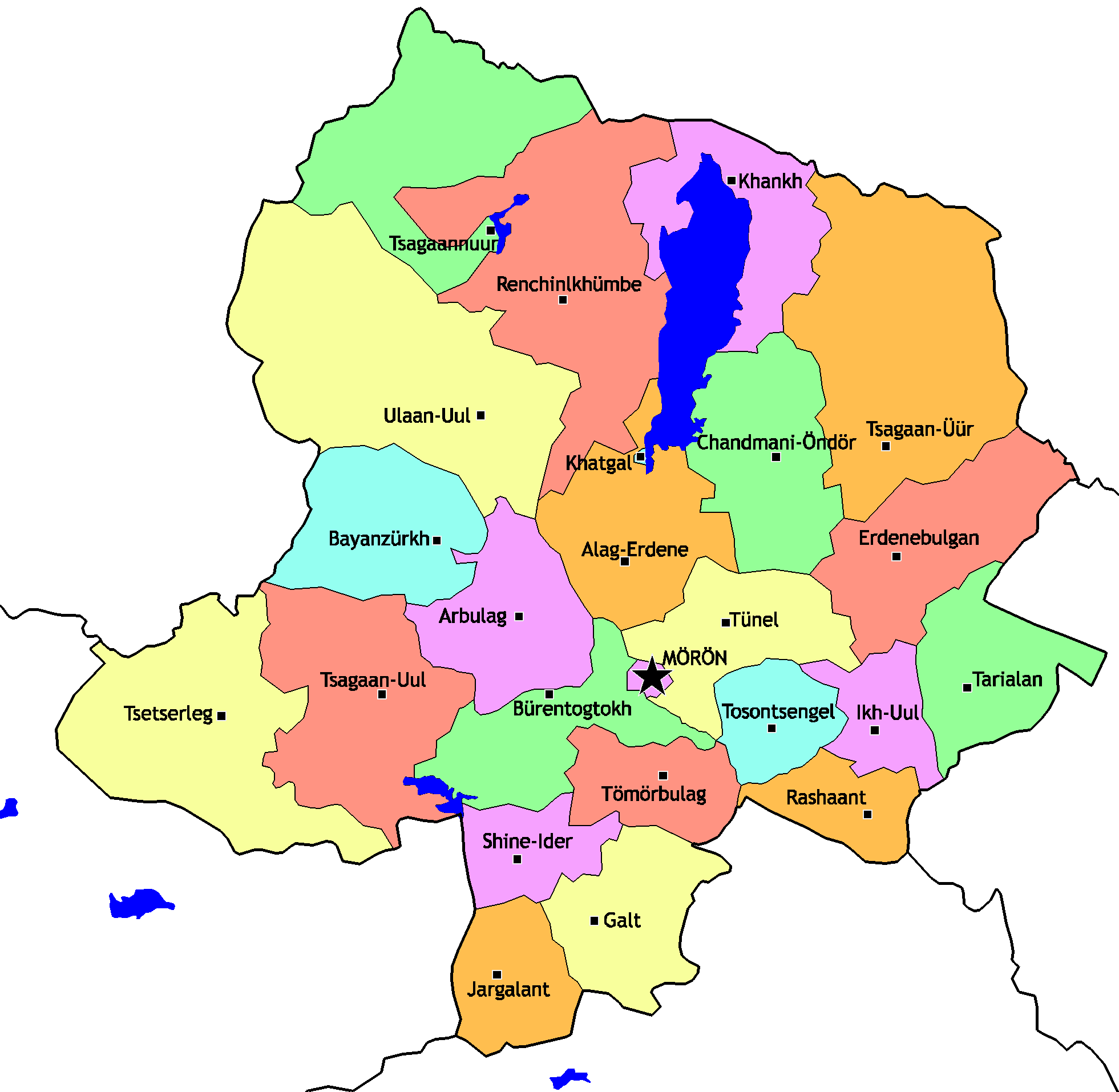
Khövsgöl Province
Khövsgöl () is the northernmost of the 21 Aimags of Mongolia, aimags (provinces) of Mongolia. The name is derived from Lake Khövsgöl. Geography and history The round-topped Tarvagatai (Khangai), Tarvagatai, Bulnain and Erchim sub-ranges of the Khangai Mountains, Khangai massif dominate the south and southwest of the largely mountainous province, and north and west of Lake Khövsgöl, lie the alpine Khoridol Saridag mountains, Khoridol Saridag, Ulaan Taiga, and Mönkh Saridag mountains. The center and eastern parts of the province are less mountainous, but still hilly. The region is well known in Mongolia for its natural environment, and Lake Khövsgöl is one of the country's major tourist attractions. The largest forests of Mongolia are located around and to the north of the lake, extending the South Siberian forest steppe, South Siberian taiga. The aimag was founded in 1931. Khatgal, Khövsgöl, Khatgal was the administrative center until 1933; since then it has been Mörö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuvans
The Tuvans (from Russian ) or Tyvans (from Tuvan ) are a Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Siberia that live in Tuva, Mongolia, and China. They speak the Tuvan language, a Siberian Turkic language. In Mongolia, they are regarded as one of the Uriankhai peoples. Tuvans have historically been livestock-herding nomads, tending to herds of goats, sheep, camels, reindeer, cattle, and yaks for the past thousands of years. (This is, in fact, evident in the Tuvan folk song " Tooruktug Dolgai Tangdym".) They have traditionally lived in yurts covered by felt or chums, layered with birch bark or hide that they relocate seasonally as they move to newer pastures. Traditionally, the Tuvans were divided into nine regions called ''khoshuun'', namely the Tozhu, Salchak, Oyunnar, Khemchik, Khaasuut, Shalyk, Nibazy, Daavan and Choodu, and Beezi. The first four were ruled by Uriankhai Mongol princes, while the rest were administered by Borjigin Mongol princes. History Besides pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darkhad
The Darkhad ( ) are a subgroup of the Mongols living mainly in northern Mongolia; particularly in the Bayanzürkh, Ulaan-Uul, Renchinlkhümbe, Tsagaannuur Districts of Khövsgöl Province. They speak a regional variant of Mongolian known as the Darkhad dialect. As of the 2000 census, 16,268 people identified themselves as Darkhad. The Darkhad were originally part of the Oirat or Khotgoid tribes. Between 1549 and 1686, they were subjects of Zasagt Khan aimag and the Khotgoid Altan Khan. In 1786 they became part of the Jebtsundamba Khutuktu's shabi otog. At roughly the same time they became known as ''Black Darkhad''. Many Darkhad practise shamanism. The Darkhad valley is named after them. History In 555 AD, the 3rd Khan of the Göktürks Kigin conquered the tribes of the Sayan Mountains. The Mongolian, Turkic, and Samoyedic tribes living in the taiga of southern Siberia were collectively referred to as "Forest People" Among these forest tribes, some lived in yurts, hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Shamanism
Asian may refer to: * Items from or related to the continent of Asia: ** Asian people, people in or Asian diaspora, descending from Asia ** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia ** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asia ** Asian (cat), a cat breed similar to the Burmese but in a range of different coat colors and patterns * Asii (also Asiani), a historic Central Asian ethnic group mentioned in Roman-era writings * Asian option, a type of option contract in finance * Asyan, a village in Iran See also * * * East Asia * South Asia * Southeast Asia * Asiatic (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |