|
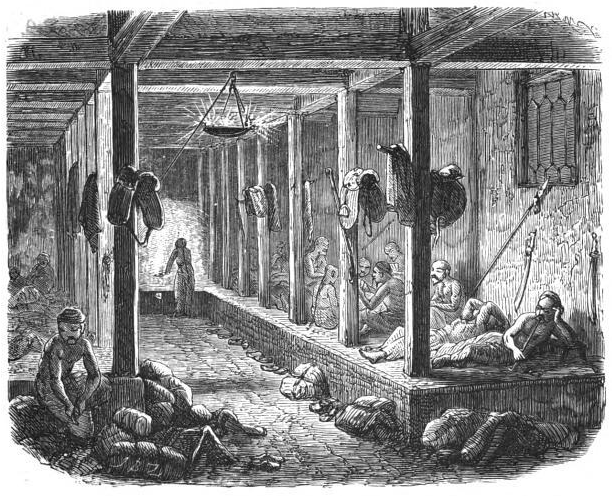
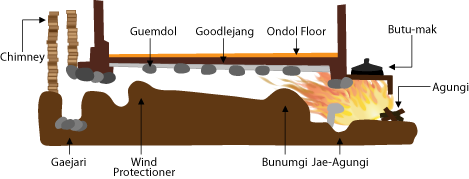
Ondol
(; , ; ) or ''gudeul'' (; ) in Korean traditional architecture is underfloor heating that uses direct heat transfer from wood smoke to heat the underside of a thick masonry floor. In modern usage, it refers to any type of underfloor heating, or to a hotel or a sleeping room in Korean (as opposed to Western) style. The main components of the traditional ondol are an '' agungi'' (; ), a '' firebox'' or '' stove'', accessible from an adjoining room (typically kitchen or master bedroom), a raised masonry floor underlain by horizontal smoke passages, and a vertical, freestanding chimney on the opposite exterior wall providing a draft. The heated floor, supported by stone piers or baffles to distribute the smoke, is covered by stone slabs, clay and an impervious layer such as oiled paper. History Origin Use of the has been found at archaeological sites in present-day North Korea. A Neolithic Age archaeological site, ''circa'' 5000 BC, discovered in Sonbong, Rason, in present-day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underfloor Heating
Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronics, hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by Conduction (heat), conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. History Underfloor heating has a long history back into the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. Archeological digs in Asia and the Aleutian islands of Alaska reveal how the inhabitants drafted smoke from fires through stone covered trenches which were excavated in the floors of their subterranea (geography), subterranean dwellings. The hot smoke heated the floor stones and the heat then radiated into the living spaces. These early forms have evolved into modern systems using fluid filled pipes or electrical cables and mats. Below is a chronological overview of under floor heating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agungi
An ''agungi'' () is a firebox found in traditional Korean kitchens which is used to burn firewood or other fuel for cooking. It is also a part of the traditional floor heating system, or ondol. The flat cooktop counter or hearth installed over the ''agungi'' is called a ''buttumak'' (). History Early ''buttumak'' have been dated to the 10th‒4th century BCE. Iron and ceramic ''buttumaks'', similar to their later forms, were excavated from Goguryeo 1st century BCE historical sites, such as Anak Tomb No. 3. Many Korean agrarian kitchens had ''buttumak'' with charcoal-fueled ''agungi'' until the early 1970s. File:Goguryeo buttumak 1.jpg, Iron ''buttumak'' from Goguryeo (37 BCE ‒ 668 CE) File:Agungi door 1.jpg, ''Agungi'' door from agrarian South Korea in the mid-20th century Structure ''Buttumaks'' in agrarian Korean kitchens were commonly made from brick or stone and then smoothed with clay. Above each ''agungi'' is an upward opening where '' gamasot'' (big pot o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocaust
A hypocaust () is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm the upper floors as well. The word derives from Ancient Greek ''hupó'' and ''kaustós'' (compare '' caustic''). The earliest reference to such a system suggests that the Temple of Ephesus in 350 BC was heated in this manner, although Vitruvius attributes its invention to Sergius Orata in c. 80 BC. Its invention improved the hygiene and living conditions of citizens, and was a forerunner of modern central heating. Roman operation Hypocausts were used for heating hot baths and other public buildings in ancient Rome. They were also used in private homes. It was considered proper and necessary by the wealthier merchant class for their villas, throughout the Roman Empire. The ruins of Roman hypocausts have been found throughout Europe (for example in It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonry Heater
A masonry heater (also called a masonry stove) is a device for warming an interior space through radiant heating, by capturing the heat from periodic burning of fuel (usually wood), and then radiating the heat at a fairly constant temperature for a long period. Masonry heaters covered in tile are called Kachelofen (also tile stoves or ceramic stoves). The technology has existed in different forms, from back into the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. Archaeological digs have revealed excavations of ancient inhabitants utilizing hot smoke from fires in their subterranean dwellings, to radiate into the living spaces. These early forms eventually evolved into modern systems. Evidence found from 5,000 BC of massive blocks of masonry used to retain heat foreshadowed Underfloor heating#History/, early forms of fire hearths that were used as multifunctional heating sources. Later evolutions came in the Roman ''hypocaust'', Chinese Kang bed-stove, kang, Korean ondol and Spanish Gloria (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kang Bed-stove
The ''kang'' (; Manchu: ''nahan'', ) is a traditional heated platform, 2 metres or more long, used for general living, working, entertaining and sleeping in the northern part of China, where the winter climate is cold. It is made of bricks or other forms of fired clay and more recently of concrete in some locations. The word ''kang'' means "to dry". Its interior cavity, leading to an often-convoluted flue system, channels the hot exhaust from a firewood/coal fireplace, usually the cooking fire from an adjacent room that serves as a kitchen, sometimes from a stove set below floor level. This allows a longer contact time between the exhaust (which still contains much heat from the combustion source) and (indirectly) the inside of the room, hence more heat transfer/recycling back into the room, effectively making it a ducted heating system similar to the Roman hypocaust. A separate stove may be used to control the amount of smoke circulating through the ''kang'', maintaining comfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Architecture
Korean architecture () refers to an architectural style that developed over centuries in Korea. Throughout the history of Korea, various kingdoms and royal dynasties have developed a unique style of architecture with influences from Korean Buddhism, Buddhism and Korean Confucianism. Having been deeply influenced by Chinese architecture, traditional Korean architecture can be mostly recognized by its sloping roofs. Just like in the case of Korean arts, other Korean arts, Korean architecture is distinguished by its naturalistic tendencies, simplicity, economy of shape, and avoidance of extremes. General characteristics In Korean architecture, buildings are structured vertically and horizontally. A construction usually rises from a stone subfoundation to a curved roof covered with tiles, held by a console structure and supported on posts; walls are made of earth (adobe) or are sometimes totally composed of movable wooden doors. Architecture is built according to the Kan (unit), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Korea
The traditional culture of Korea is the shared cultural and historical heritage of Korea before the division of Korea in 1945. Since the mid-20th century, Korea has been split between the North Korean and South Korean sovereign state, states, resulting in a number of cultural differences that can be observed even today. Before the Joseon period, the practice of Korean shamanism was deeply rooted in Korean culture. Clothing The traditional dress known as ''hanbok'' (; alternatively ''joseonot;'' in North Korea) has been worn since ancient times. The ''hanbok'' consists of a shirt (''jeogori'') and a skirt (''chima''). According to social status, Koreans used to dress differently, making clothing an important mark of social rank. Costumes were worn by the ruling class and the royal family. These upper classes also used jewellery, jewelry to distance themselves from the ordinary people. A traditional item of jewellery for women was a pendant in the shape of certain elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeontan
, also known by the names () or ''fēngwōméi'' (, literally "beehive coal"), are coal briquettes used across East Asia for home cooking and residential home heating purposes. They were first invented in Japan, then propagated through the rest of East Asia in the early 20th century, although their usage is now uncommon in contemporary Japan and South Korea. Made from a mixture of lignite coal dust and a gluing agent that keeps the dust particles together, they became a popular alternative to firewood and natural coal because they come in a consistent size and stack easily. There are 5 standard sizes for the briquettes, and the 2nd standard is widely used in households. The 2nd standard briquette is cylindrical in shape, weighs , and is about in height and in diameter. The standard briquette has 22 holes drilled into its top to facilitate steady, efficient burning, and a household typically uses one to three briquettes per day in the winter. A new briquette can be placed on one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as " flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large exposures can result in loss of consciousness, arrhythmias, seizures, or death. The classically described "cherry red skin" rarely occurs. Long-term complications may include chronic fatigue, trouble with memory, and movement problems. CO is a colorless and odorless gas which is initially non-irritating. It is produced during incomplete burning of organic matter. This can occur from motor vehicles, heaters, or cooking equipment that run on carbon-based fuels. Carbon monoxide primarily causes adverse effects by combining with hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin (symbol COHb or HbCO) preventing the blood from carrying oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide as carbaminohemoglobin. Additionally, many other hemoproteins such as myoglob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Mass Heater
A rocket mass heater (RMH), also known as rocket stove mass heater, is a form of slow-release Thermal radiation, radiant heating system, designed to primarily heat people and secondarily to warm areas in Sightline, line of sight around it. Variations of RMH can also be extended for the functions of cooking, Water heating, heating water, and producing warm air for distribution. Rocket mass heaters are developed from rocket stoves, a type of wood-burning stoves, wood-burning stove, and masonry heaters. A primary design of a rocket mass heater consists of an Thermal insulation, insulated combustion chamber where fuel is burned with high efficiency at high temperature, and a large thermal mass in contact with the exhaust gases, which absorbs most of the generated heat before the gases are released to the atmosphere. According to anecdotes a rocket mass heater might reduce fuel consumption by 80–90% compared to "conventional" stoves. In contrast to conventional wood-burning stoves a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Stove
The Russian stove () is a type of masonry stove that first appeared in the 15th century or earlier. These stoves combine the functions of a traditional stove, oven, and fireplace into a single unit, and serve a broad range of purposes, including cooking (boiling, baking, and smoking), drying plants and mushrooms, providing interior heating and ventilation, bathing, and providing a warm place to sleep (many units include a sleeping berth atop the stove). They can be found in traditional Russian, Ukrainian, Romanian, and Belarusian households. Such stoves burn only firewood. Design A Russian stove is designed to retain heat for long periods of time. This is achieved by channeling the smoke and hot air produced by combustion through a complex labyrinth of passages, warming the bricks from which the stove is constructed. A brick flue () in the attic, sometimes with a chamber for smoking food, is required to slow down the cooling of the stove. The Russian stove is usually in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |