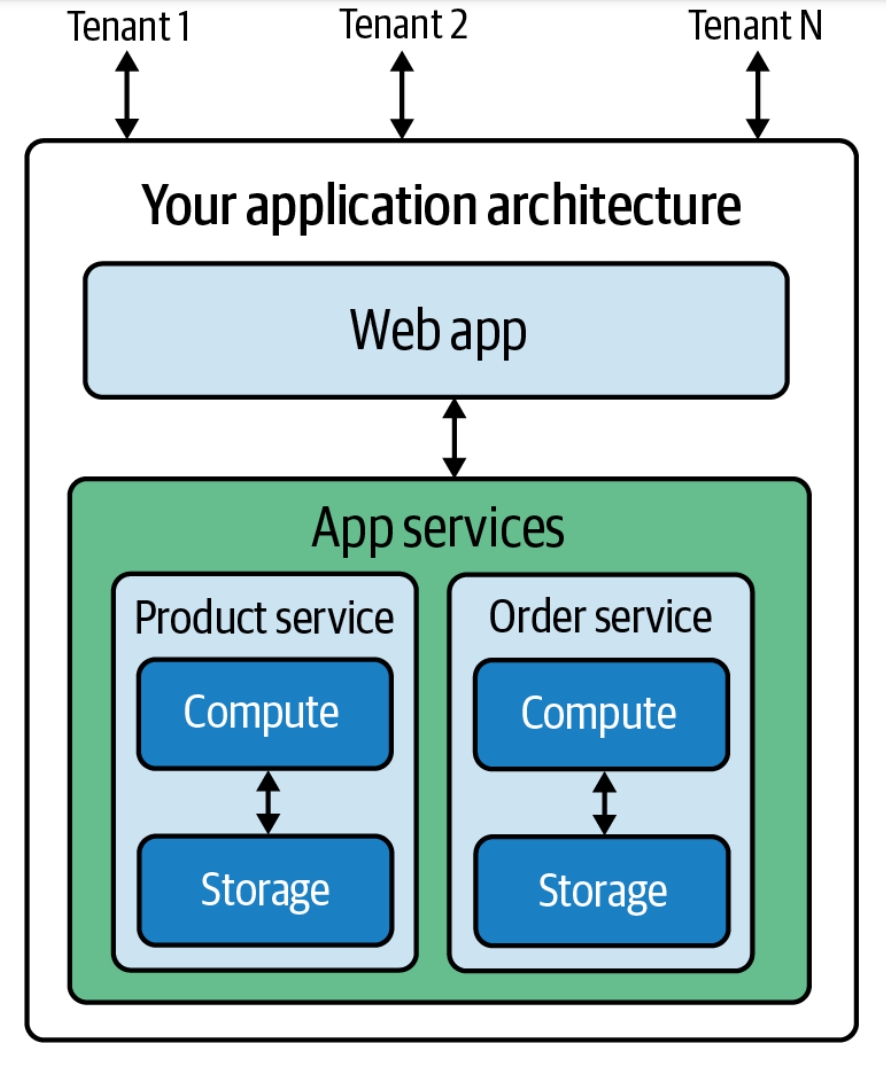
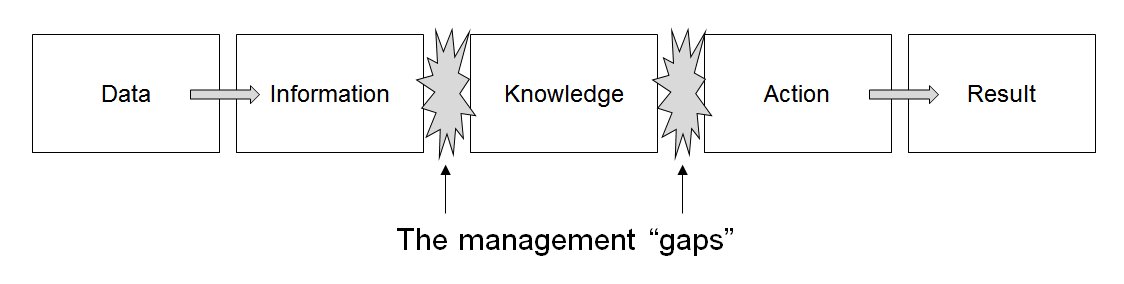
|
On-premise
On-premises software (abbreviated to on-prem, and often written as "on-premise") is installed and runs on computers on the premises of the person or organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility such as a server farm or cloud. On-premises software is sometimes referred to as " shrinkwrap" software, and off-premises software is commonly called "software as a service" ("SaaS") or "cloud computing". The software consists of database and modules that are combined to particularly serve the unique needs of the large organizations regarding the automation of corporate-wide business system and its functions. Comparison between on-premises and cloud (SaaS) Location On-premises software is established within the organisation's internal system along with the hardware and other infrastructure necessary for the software to function. Cloud-based software is usually served via internet and it can be accessed by users online regardless of the time and their location. Unli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud-based
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for Standardization, ISO. Essential characteristics In 2011, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) identified five "essential characteristics" for cloud systems. Below are the exact definitions according to NIST: * On-demand self-service: "A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider." * Broad network access: "Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations)." * Pooling (resource management), Resource pooling: " The provider' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software As A Service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a cloud computing service model where the provider offers use of application software to a client and manages all needed physical and software resources. SaaS is usually accessed via a web application. Unlike other software delivery models, it separates "the possession and ownership of software from its use". SaaS use began around 2000, and by 2023 was the main form of software application deployment. Unlike most self-hosted software products, only one version of the software exists and only one operating system and configuration is supported. SaaS products typically run on rented infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or platform as a service (PaaS) systems including hardware and sometimes operating systems and middleware, to accommodate rapid increases in usage while providing instant and continuous availability to customers. SaaS customers have the abstraction of limitless computing resources, while economy of scale drives down the cost. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software—typically a suite of integrated applications—that an organization can use to collect, store, manage and interpret data from many business activities. ERP systems can be local-based or cloud-based. Cloud-based applications have grown in recent years due to the increased efficiencies arising from information being readily available from any location with Internet access. ERP differs from integrated business management systems by including planning all resources that are required in the future to meet business objectives. This includes plans for getting suitable staff and manufacturing capabilities for future needs. ERP provides an integrated and continuously updated view of the core business processes using common databases maintained by a database manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Delivery Methods
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th century. Early programs were written in the machine language specific to the hardware. The introduction of high-level programming languages in 1958 allowed for more human-readable instructions, making software development easier and more portable across different computer architectures. Software in a programming language is run through a compiler or interpreter to execute on the architecture's hardware. Over time, software has become complex, owing to developments in networking, operating systems, and databases. Software can generally be categorized into two main types: # operating systems, which manage hardware resources and provide services for applications # application software, which performs specific tasks for users The rise of clou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadband
In telecommunications, broadband or high speed is the wide-bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth data transmission that exploits signals at a wide spread of frequencies or several different simultaneous frequencies, and is used in fast Internet access. The transmission medium can be coaxial cable, optical fiber, wireless Internet (radio), twisted pair cable, or satellite broadband, satellite. Originally used to mean 'using a wide-spread frequency' and for services that were analog at the lowest level, nowadays in the context of Internet access, 'broadband' is often used to mean any high-speed Internet access that is seemingly always 'on' and is faster than Dial-up Internet access, dial-up access over traditional plain old telephone service, analog or ISDN public switched telephone network, PSTN services. The ideal telecommunication network has the following characteristics: ''broadband'', ''multi-media'', ''multi-point'', ''multi-rate'' and economical implementation for a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-hosting (web Services)
Self-hosting is the practice of running and maintaining a website or service using a private web server, instead of using a service outside of the administrator's own control. Self-hosting allows users to have more control over their data, privacy, and computing infrastructure, as well as potentially saving costs and improving skills. History The practice of self-hosting web services became more feasible with the development of cloud computing and virtualization technologies, which enabled users to run their own servers on remote hardware or virtual machines. The first public cloud service, Amazon Web Services (AWS), was launched in 2006, offering Simple Storage Service (S3) and Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) as its initial products. Self-hosting web services became more popular with the rise of free software projects, open source software projects and free and open-source software projects that provide alternatives to various web-based services and applications, such as file storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client (computing)
is a computer that gets information from another computer called server in the context of client–server model of computer networks. The server is often (but not always) on another computer system, in which case the client accesses the service by way of a network. A client is a program that, as part of its operation, relies on sending a request to another program or a computer hardware or software that accesses a service made available by a server (which may or may not be located on another computer). For example, web browsers are clients that connect to web servers and retrieve web pages for display. Email clients retrieve email from mail servers. Online chat uses a variety of clients, which vary on the chat protocol being used. Multiplayer video games or online video games may run as a client on each computer. The term "client" may also be applied to computers or devices that run the client software or users that use the client software. A client is part of a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business-to-business
Business-to-business (B2B or, in some countries, BtoB) refers to trade and commercial activity where a business sees other businesses as its customer base. This typically occurs when: * A business sources materials for its production process for output (e.g., a food manufacturer purchasing salt), i.e. providing raw material to the other company that will produce output. * A business needs the services of another for operational reasons (e.g., a food manufacturer employing an accountancy firm to audit their finances). * A business re-sells goods and services produced by others (e.g., a retailer buying the end product from the food manufacturer). Business-to-business activity is thought to allow business segmentation. B2B is often contrasted with business-to-consumer (B2C) trade. Organization Successful B2B operations depend upon sales personnel understanding the purchasing behaviour and outlook of the types of business they wish to work with. B2B involves specific challenges a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Management
Information management (IM) is the appropriate and optimized capture, storage, retrieval, and use of information. It may be personal information management or organizational. Information management for organizations concerns a cycle of organizational activity: the acquisition of information from one or more sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to those who need it, and its ultimate disposal through archiving or deletion and extraction. This cycle of information organisation involves a variety of stakeholder (corporate), stakeholders, including those who are responsible for assuring the quality (business), quality, accessibility and utility of acquired information; those who are responsible for its safe Data storage device, storage and :wikt:disposal, disposal; and those who need it for decision making. Stakeholders might have rights to originate, change, distribute or delete information according to organisational information management policies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a strategic process that organizations use to manage, analyze, and improve their interactions with customers. By leveraging data-driven insights, CRM helps businesses optimize communication, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth. CRM systems compile data from a range of different communication channels, including a company's website, telephone (which many services come with a softphone), email, live chat, marketing materials and more recently, social media. They allow businesses to learn more about their target audiences and how to better cater to their needs, thus retaining customers and driving sales growth. CRM may be used with past, present or potential customers. The concepts, procedures, and rules that a corporation follows when communicating with its consumers are referred to as CRM. This complete connection covers direct contact with customers, such as sales and service-related operations, forecasting, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salesforce
Salesforce, Inc. is an American cloud-based software company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It provides applications focused on sales, customer service, marketing automation, e-commerce, analytics, artificial intelligence, and application development. Founded by former Oracle executive Marc Benioff in March 1999, Salesforce grew quickly, making its initial public offering in 2004. As of September 2022, Salesforce is the 61st largest company in the world by market cap with a value of nearly US$153 billion. It became the world's largest enterprise applications firm in 2022. Salesforce ranked 491st on the 2023 edition of the ''Fortune'' 500, making $31.352 billion in revenue. Since 2020, Salesforce has also been a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. History Salesforce was founded on March 8, 1999 by former Oracle executive Marc Benioff, together with Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez as a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |