|
Omnia Sunt Communia
is a Latin phrase and slogan translated as "all things are to be held in common" or simply "all things in common". Originating in the Latin translation of the Acts of the Apostles, altered forms of the slogan were applied as a legal maxim in canon law and later in secular law. The phrase was also a central inspiration for Christian communism. Origin derives from Acts 2:44 and 4:32 in the Christian Bible. The standard Koine Greek texts of the New Testament describe the Early Christians of the Apostolic Age as "having all things in common" ( grc-gre, εἶχον ἅπαντα κοινά, eîchon hápanta koiná). after the miracles of Pentecost while the apostles celebrated Shavuot in Jerusalem shortly after Jesus's crucifixion, resurrection, and ascension. This event is celebrated by Christians as the beginning of the church and usually dated to somewhere between AD30 and 36. After Peter's first trial before the Sanhedrin at some later date, the Christians are described as "o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Latin Phrases
__NOTOC__ This is a list of Wikipedia articles of Latin phrases and their translation into English. ''To view all phrases on a single, lengthy document, see: List of Latin phrases (full)'' The list also is divided alphabetically into twenty pages: * List of Latin phrases (A) * List of Latin phrases (B) * List of Latin phrases (C) * List of Latin phrases (D) * List of Latin phrases (E) * List of Latin phrases (F) * List of Latin phrases (G) * List of Latin phrases (H) * List of Latin phrases (I) * List of Latin phrases (L) * List of Latin phrases (M) * List of Latin phrases (N) * List of Latin phrases (O) * List of Latin phrases (P) * List of Latin phrases (Q) * List of Latin phrases (R) * List of Latin phrases (S) * List of Latin phrases (T) * List of Latin phrases (U) * List of Latin phrases (V) See also * Latin influence in English * Latinism Lists * List of abbreviations used in medical prescriptions * List of ecclesiastical abbreviations *List of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow Jews on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summa Theologica
The ''Summa Theologiae'' or ''Summa Theologica'' (), often referred to simply as the ''Summa'', is the best-known work of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), a scholastic theologian and Doctor of the Church. It is a compendium of all of the main theological teachings of the Catholic Church, intended to be an instructional guide for theology students, including seminarians and the literate laity. Presenting the reasoning for almost all points of Christian theology in the West, topics of the ''Summa'' follow the following cycle: God; Creation, Man; Man's purpose; Christ; the Sacraments; and back to God. Although unfinished, it is "one of the classics of the history of philosophy and one of the most influential works of Western literature." Moreover, the ''Summa'' remains Aquinas' "most perfect work, the fruit of his mature years, in which the thought of his whole life is condensed." Among non-scholars, the ''Summa'' is perhaps most famous for its five arguments for the existence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardus Papiensis
Bernardus Papiensis (pre-1150 – 18 September 1213) was an Italian canonist and bishop of the Christian Church. Born at Pavia, he studied law and theology at Bologna under Gandulphus and Faventinus. Later, he was provost of the cathedral of Pavia until 1191, Bishop of Faenza until 1198, and then Bishop of Pavia until his death there in 1213. Background Papiensis' very extensive works on the canon law helped elevate canon law to a legal system in its own right, taught at universities, that was recognised to change over time. In particular, Papiensis is renowned for his "Breviarium extravagantium" (later called "Compilatio prima antiqua"), a collection of canonical texts comprising ancient canons not inserted in the "Decretum" of Gratian and also later documents. The work was compiled between 1187 and 1191, and was edited by Friedberg (''Quinque compilationes antiquæ'', 1882). Papiensis is the author of a "Summa Summa and its diminutive summula (plural ''summae'' and ''su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Fuldensis
The Codex Fuldensis, also known as the Victor Codex (Hessian State Library, ''Codex Bonifatianus I''), designated by F, is a New Testament manuscript based on the Latin Vulgate made between 541 and 546. The codex is considered the second most important witness to the Vulgate text; and is also the oldest complete manuscript witness to the order of the Diatessaron. It is an important witness in any discussion about the authenticity of 1 Corinthians 14:34-35Philip B. Payne''Fuldensis, Sigla for Variants in Vaticanus and 1 Cor 14.34-5'' NTS 41 (1995) 251-262. and the Comma Johanneum. It is one of the earliest dated manuscripts of the New Testament. It was corrected until 2 May, 546 AD. Description It contains the Diatessaron and 23 canonical books of the New Testament; plus the Epistle to the Laodiceans, and a copy of Jerome's ''Prologue to the Canonical Gospels''. It represents the Italian type of text. The four gospels are harmonised into a single continuous narrative, according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome. Jerome was born at Stridon, a village near Emona on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia. He is best known for his translation of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate) and his commentaries on the whole Bible. Jerome attempted to create a translation of the Old Testament based on a Hebrew version, rather than the Septuagint, as Latin Bible translations used to be performed before him. His list of writings is extensive, and beside his biblical works, he wrote polemical and historical essays, always from a theologian's perspective. Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially to those living in cosmopolitan centers such as Rome. In many cases, he fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Bible translations into Latin, Latin translation of the Bible. The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels used by the Diocese of Rome, Roman Church. Later, on his own initiative, Jerome extended this work of revision and translation to include most of the books of the Bible. The Vulgate became progressively adopted as the Bible text within the Western Church. Over succeeding centuries, it eventually eclipsed the . By the 13th century it had taken over from the former version the designation (the "version commonly used") or for short. The Vulgate also contains some ''Vetus Latina'' translations which Jerome did not work on. The Vulgate was to become the Catholic Church's officially Promulgation (Catholic canon law), promulgated Latin version of the Bible as the Sixtine Vulgate (1590), then as the Clementine Vul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
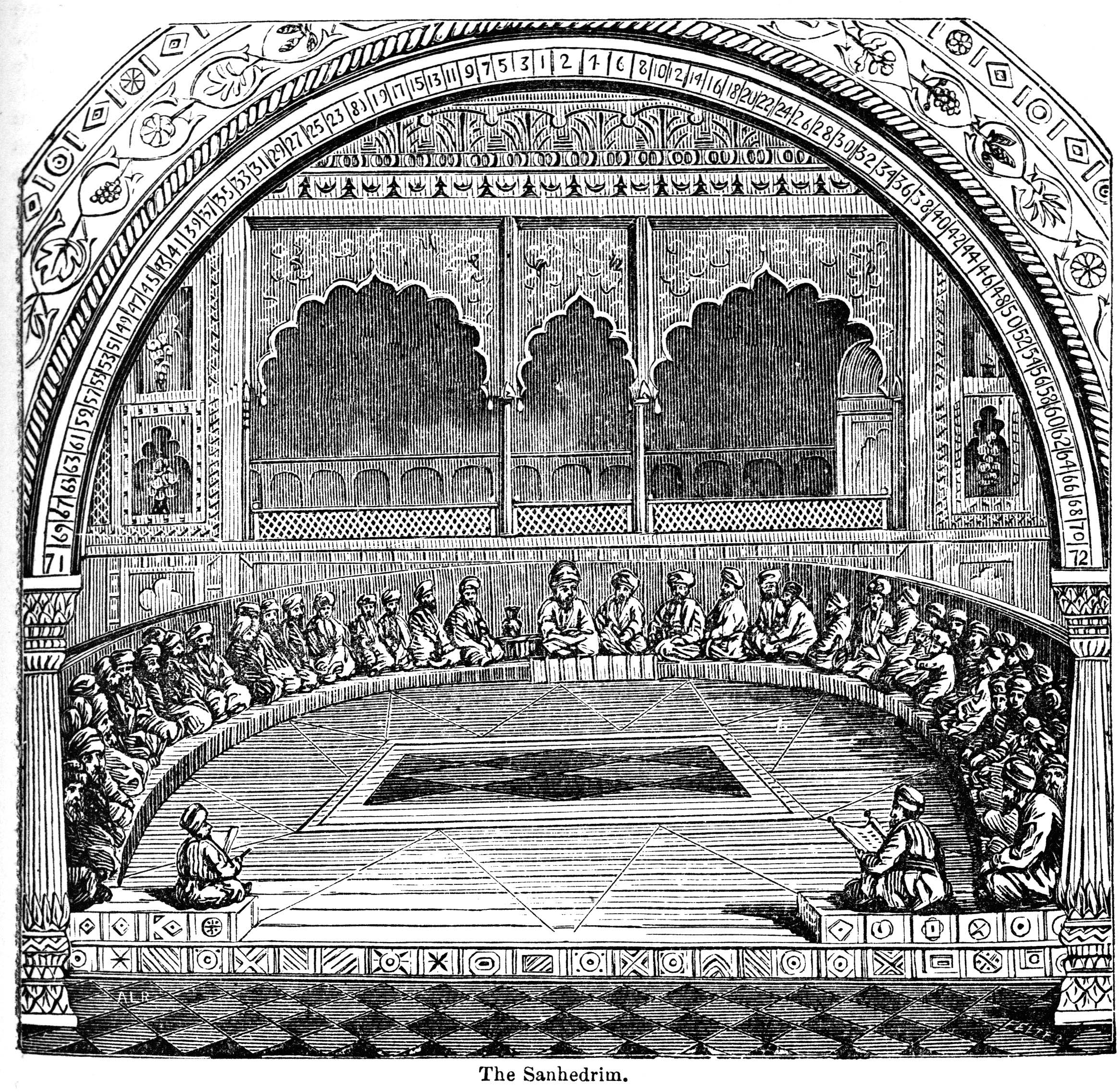
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the '' Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the '' Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon) , birth_date = , birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire , death_date = Between AD 64–68 , death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire , parents = John (or Jonah; Jona) , occupation = Fisherman, clergyman , feast_day = , venerated = All Christian denominations that venerate saints and in Islam , canonized_date = Pre- Congregation , attributes = Keys of Heaven, Red Martyr, pallium, papal vestments, rooster, man crucified upside down, vested as an Apostle, holding a book or scroll, Cross of Saint Peter , patronage = Patronage list , shrine = St. Peter's Basilica Saint Peter; he, שמעון בר יונה, Šimʿōn bar Yōnāh; ar, سِمعَان بُطرُس, translit=Simʿa̅n Buṭrus; grc-gre, Πέτρος, Petros; cop, Ⲡⲉⲧⲣⲟⲥ, Petros; lat, Petrus; ar, شمعون الصفـا, Sham'un al-Safa, Simon the Pure.; tr, Aziz Petrus (died between AD 64 and 68), also known as Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology Of Jesus
A chronology of Jesus aims to establish a timeline for the events of the life of Jesus. Scholars have correlated Jewish and Greco-Roman documents and astronomical calendars with the New Testament accounts to estimate dates for the major events in Jesus's life. Two main approaches have been used to estimate the year of the birth of Jesus: one based on the accounts in the Gospels of his birth with reference to King Herod's reign, and the other by subtracting his stated age of "about 30 years" when he began preaching. Most scholars, on this basis, assume a date of birth between 6 and 4 BC. John P. Meier (1991). ''A Marginal Jew: Rethinking the Historical Jesus'', v. 1; ''The Roots of the Problem and the Person'', ch. 11, ... "A Chronology of Jesus Life," pp. 373–433. Anchor Bible Reference Library.D. A. Carson, Douglas J. Moo & Leon Morris. (1992). ''An Introduction to the New Testament'', 54, 56. Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan Publishing House. Three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the " one true church", to the exclusion of the others. For many Protestant Christians, the Christian Church has two components: the church visible, institutions in which "the Word of God purely preached and listened to, and the sacraments administered according to Christ's institution", as well as the church invisible—all "who are truly saved" (with these beings members of the visible church). In this understanding of the invisible church, "Christian Church" (or catholic Church) does not refer to a particular Christian denomination, but includes all individuals who have been saved. The branch the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)