|
Ombrotrophic
Ombrotrophic ("cloud-fed"), from Ancient Greek ὄμβρος (''ómvros'') meaning "rain" and τροφή (''trofí'') meaning "food"), refers to Soil, soils or vegetation which receive all of their water and nutrients from precipitation, rather than from streams or springs. Such environments are hydrology, hydrologically isolated from the surrounding landscape, and since rain is acidic and very low in Plant nutrition, nutrients, they are home to organisms tolerant of acidic, low-nutrient environments. The vegetation of ombrotrophic peatlands is often bog, dominated by ''Sphagnum'' mosses. The hydrology of these environments are directly related to their climate, as precipitation is the water and nutrient source, and temperatures dictate how quickly water evaporates from these systems. Ombrotrophic circumstances may occur even in landscapes composed of limestone or other nutrient-rich substrates – for example, in high-rainfall areas, limestone boulders may be capped by acidic o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poor Fen
A fen is a type of peat-accumulating wetland fed by mineral-rich Groundwater, ground or surface water. It is one of the main types of wetland along with marshes, swamps, and bogs. Bogs and fens, both peat-forming ecosystems, are also known as mires. The unique water chemistry of fens is a result of the ground or surface water input. Typically, this input results in higher mineral concentrations and a more Base (chemistry), basic pH than found in bogs. As peat accumulates in a fen, groundwater input can be reduced or cut off, making the fen ombrotrophic rather than minerotrophic. In this way, fens can become more acidic and transition to bogs over time. Fens can be found around the world, but the vast majority are located at the mid to high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. They are Dominance (ecology), dominated by Cyperaceae, sedges and mosses, particularly graminoids that may be rarely found elsewhere, such as the sedge species ''Carex exilis''. Fens are highly biodiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minerotrophic
Minerotrophic refers to environments that receive nutrients primarily through groundwater that flows through mineral-rich soils or rock,Environment Canada (2014). Ontario wetland evaluation system: Northern Manual, 1st edition, version 3.2. Queen’s printer for Ontario. or surface water flowing over land. Minerotrophic, “minerogenous”, and “geogenous” are now often used interchangeably, although the latter two terms refer primarily to hydrological systems, while the former refers to nutrient dynamics. The hydrologic process behind minerotrophic wetlands results in water that has acquired dissolved chemicals which raise the nutrient levels and reduce the acidity. This in turn affects vegetation assemblages and diversity in the wetland in question.Brinson, M. M. (1993). A Hydrogeomorphic Classification for Wetlands. ''Environmental Laboratory (U.S.) & Engineer Research and Development Center (U.S.).'' Retrieved from https://erdc-library.erdc.dren.mil/jspui/bitstream/11681/6483 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peatlands
A peatland is a type of wetland whose soils consist of Soil organic matter, organic matter from decaying plants, forming layers of peat. Peatlands arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to Waterlogging (agriculture), water-logging and subsequent anoxic waters, anoxia. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning. The formation of peatlands is primarily controlled by climatic conditions such as precipitation and temperature, although terrain relief is a major factor as waterlogging occurs more easily on flatter ground and in basins. Peat formation typically initiates as a paludification of a mineral soil forests, terrestrialisation of lakes, or primary peat formation on bare soils on previously glaciated areas. A peatland that is actively forming peat is called a ''mire''. All types of mires share the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koitjärve Raba 05-2015
Koitjärve is a village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County in northern Estonia. The western part of the village's territory is occupied by Soodla training area and a small portion on the southeastern part is occupied by Keskpolügoon, both training areas of the Estonian Defence Forces The Estonian Defence Forces () is the unified military force of the Republic of Estonia. The Estonian Defence Forces consists of the Estonian Land Forces, the Estonian Navy, the Estonian Air Force, and the paramilitary Estonian Defence Leagu .... References Villages in Harju County Kreis Harrien {{Harju-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at Abundance of the chemical elements, seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element chemical bond, bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
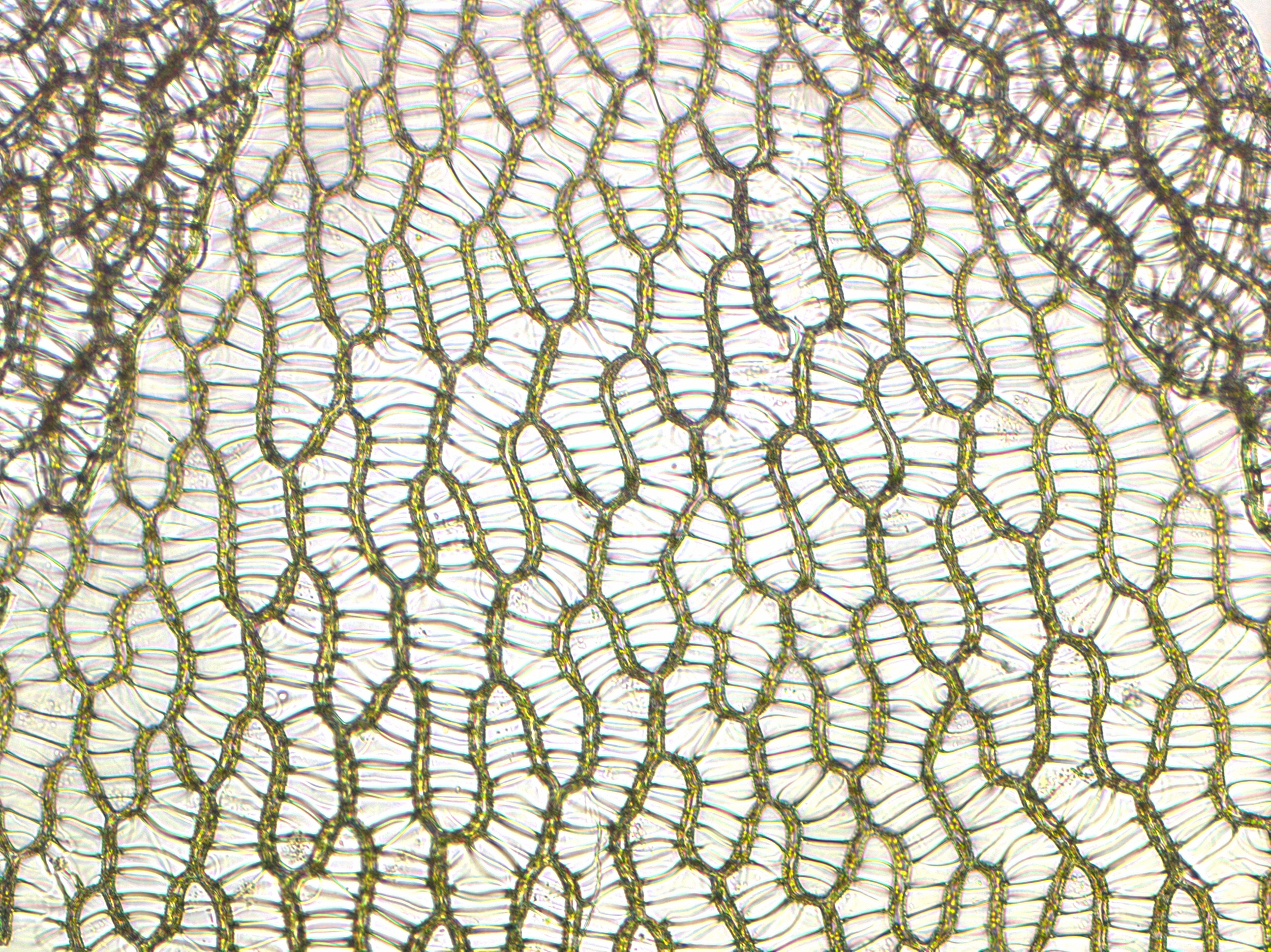
Sphagnum Mosses
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Cycle
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle, sulfur cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle, phosphorus cycle, oxygen cycle, among others that continually recycle along with other mineral nutrients into productive ecological nutrition. Overview The nutrient cycle is nature's recycling system. All forms of recycling have feedback loops that use energy in the process of putting material resources back into use. Recycling in ecology is regulated to a large extent during the process of decomposition. Ecosystems employ biodiversity in the food webs that recycle natural materials, such as mineral nutrients, which includes water. Recycling in natural systems is one of the many ecosystem services that sustain and contribute to the well-being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration (storage) to and release from carbon sinks. To describe the dynamics of the carbon cycle, a distinction can be made between the ''fast'' and ''slow'' carbon cycle. The fast cycle is also referred to as the ''biological carbon cycle''. Fast cycles can complete within years, moving substances from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. Slow or geological cycles (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |