|
Oldman Saltbush
''Atriplex nummularia'' is a species of saltbush from the family ''Amaranthaceae'' and is a large woody shrub known commonly as oldman saltbush. ''A. nummularia'' is native to Australia and occurs in each of the mainland states, thriving in arid and semi-arid inland regions. Description ''Atriplex nummularia'' is a Perennial plant, perennial halophyte species that is extremely hardy, thriving in particularly harsh environments such as saline and alkaline lowlands. ''A. nummularia'' is the largest species of Australian saltbush, typically growing 2–4m wide and up to 3m tall in either a sprawling or erect arrangement. It develops a lattice of woody stems which branch from or close to ground level and utilises a taproot with a subsequent root system that is moderate to deep. It is an evergreen plant, with simple alternate leaves that often have dull teeth and are irregular in shape, varying between circular and triangular. The leaves range between 1–5 cm long and have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Lindley
John Lindley Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (5 February 1799 – 1 November 1865) was an English botanist, gardener and orchidology, orchidologist. Early years Born in Old Catton, Catton, near Norwich, England, John Lindley was one of four children of George and Mary Lindley. George Lindley was a nurseryman and pomologist and ran a commercial nursery garden. Although he had great horticultural knowledge, the undertaking was not profitable and George lived in a state of indebtedness. As a boy he would assist in the garden and also collected wild flowers he found growing in the Norfolk countryside. Lindley was educated at Norwich School. He would have liked to go to university or to buy a commission in the army but the family could not afford either. He became Belgium, Belgian agent for a London seed merchant in 1815. At this time Lindley became acquainted with the botanist William Jackson Hooker who allowed him to use his botanical library and who introduced him to Sir Joseph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
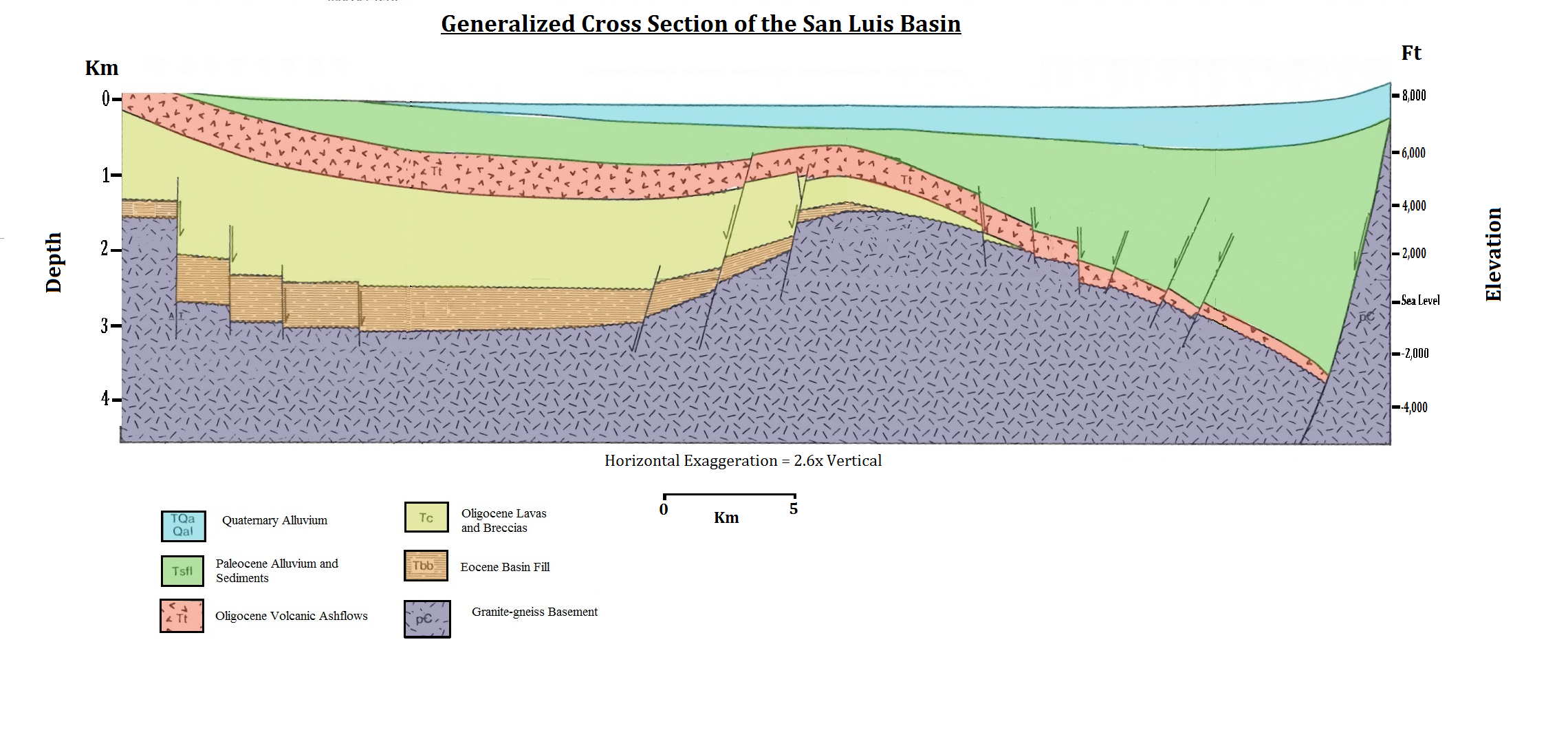
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which includes some of the most arid parts of the continent, and with 1.8 million people. It is the fifth-largest of the states and territories by population. This population is the second-most highly centralised in the nation after Western Australia, with more than 77% of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 26,878. South Australia shares borders with all the other mainland states. It is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria (state), Victoria, and to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) or lepidopterans is an order (biology), order of winged insects which includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera have been described, representing 10% of the total described species of living organisms, making it the second largest insect order (behind Coleoptera) with 126 family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic rank, superfamilies, and one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scale (anatomy), scales that cover the torso, bodies, large triangular Insect wing, wings, and a proboscis for siphoning nectars. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give butterflies and moths their wide variety of colors and patterns. Almost all species have some form of membranous wings, except for a few that have reduced wings or are wingless. Mating and the laying of eggs is normally performe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sminthurus Viridis
''Sminthurus viridis'' is a member of the Collembola, the springtails, an order in the subphylum Hexapoda. The species is known by common names such as clover springtail, lucerne flea, or lucerne earth flea. Common names such as lucerne flea are misleading because, being a member of the Collembola, this species is not even remotely related to the fleas. Calling it a "flea" simply is a reference to its jumping ability and its small size. The species originated in Eurasia, but in particular in Europe. However, it has been Introduced species, spread unintentionally by human agency. It now is present in southern regions of Australia and Tasmania, where it is considered a Pest (organism), pest. It also is present in South Africa, New Zealand, and the Americas. Its pest status varies from negligible to severe, depending on local circumstances. The human-facilitated dispersal methods that have allowed this species to become so widespread are most commonly the movement of eggs and liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not Consolidation (geology), consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present Scientific consensus, consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the French term for al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
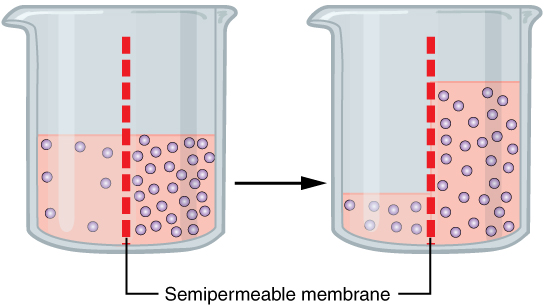
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do Work (physics), work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative properties, colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biology, bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, at the centre of the land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second-least populated after Antarctica. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones immediately to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° to 40° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical (Köppen climate classification: Cfa/Cwa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler months, such as the Mediterranean Basin or Southern California. Subtropical climates can also occur at high elevations within the tropics, such as in the southern end of the Mexican Plateau an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Temperate Climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small; they usually differ only in the amount of precipitation. In temperate climates, not only do latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but various sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistence of frost. However, some adaptations of Köppen set the minimum at . Continental climates are classified as D and considered to be varieties of temperate climates, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |