|
Oenanthotoxin
Oenanthotoxin is a toxin extracted from hemlock water-dropwort (''Oenanthe crocata'') and other plants of the genus '' Oenanthe''. It is a central nervous system poison, and acts as a noncompetitive antagonist of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid. A case has been made for the presence of this toxin in local '' Oenanthe'' species playing a causative role in euthanasia in ancient Sardinia. It was crystallized in 1949 by Clarke and co-workers. It is structurally closely related to the toxins cicutoxin and carotatoxin. Oenanthotoxin is a C17 polyacetylene isomer of cicutoxin. Occurrence Oenanthotoxin concentration in plants is dependent on seasonal changes and geographical location, the most is present during late winter and early spring. Contrary to most poisonous plants that contain bitter tastes or burning sensations, the water dropwort has a rather sweet and pleasant taste and odor. Water dropwort is characterized by a yellow liquid that changes color due to air expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicutoxin
Cicutoxin is a naturally-occurring poisonous chemical compound produced by several plants from the family Apiaceae including water hemlock ('' Cicuta'' species) and water dropwort (''Oenanthe crocata''). The compound contains polyene, polyyne, and alcohol functional groups and is a structural isomer of oenanthotoxin, also found in water dropwort. Both of these belong to the C17-polyacetylenes chemical class. It causes death by respiratory paralysis resulting from disruption of the central nervous system. It is a potent, noncompetitive antagonist of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor. In humans, cicutoxin rapidly produces symptoms of nausea, emesis and abdominal pain, typically within 60 minutes of ingestion. This can lead to tremors, seizures, and death. LD50(mouse; i.p.) ~9 mg/kg History Johann Jakob Wepfer's book ''Cicutae Aquaticae Historia Et Noxae Commentario Illustrata'' was published in 1679; it contains the earliest published report of toxicity asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyyne
A polyyne is any organic compound with alternating Single bond, single and triple bonds; that is, a series of consecutive alkynes, with ''n'' greater than 1. These compounds are also called polyacetylenes, especially in the natural products and chemical ecology literature, even though this nomenclature more properly refers to acetylene polymers composed of alternating single and double bonds with ''n'' greater than 1. They are also sometimes referred to as oligoynes, or carbinoids after "linear acetylenic carbon, carbyne" , the hypothetical allotrope of carbon that would be the ultimate member of the series. In ''Avancés récentes en chimie des acétylènes – Recent advances in acetylene chemistry'' The synthesis of this substance has been claimed several times since the 1960s, but those reports have been disputed. Indeed, the substances identified as short chains of "carbyne" in many early organic synthesis attempts would be called polyynes today. The simplest polyyne is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oenanthe (plant)
''Oenanthe'', known as water dropworts, oenanthes, water parsleys, and water celeries, are a genus of plants in the family Apiaceae. Most of the species grow in damp ground, such as in marshes or in water. Several of the species are extremely poisonous, the active poison being oenanthotoxin. The most notable of these is ''O. crocata'', which lives in damp, marshy ground, and resembles celery with roots like a bunch of large white carrots. The leaves may be eaten safely by livestock, but the stems, and especially the carbohydrate-rich roots are much more poisonous. Animals familiar with eating the leaves may eat the roots when these are exposed during ditch clearance: one root is sufficient to kill a cow, and human fatalities are also known. It has been referred to as the most poisonous of all British plants, and is considered particularly dangerous because of its similarity to several edible plants. The species '' O. javanica'', commonly known as Chinese celery or Japanese pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oenanthe Crocata
''Oenanthe crocata'', hemlock water-dropwort (sometimes known as dead man's fingers) is a flowering plant in the Apiaceae, carrot family, native to Europe, North Africa and western Asia. It grows in damp grassland and wet woodland, often along river and stream banks. All parts of the plant are extremely toxic and it has been known to cause human and livestock poisoning. Description Hemlock water-dropwort is a robust hairless perennial growing up to 150 cm tall with hollow, cylindrical, grooved stems up to 3.5 cm across. The stems are often branched. The upper part of the roots include five or more obovoid, pale yellow, fleshy tubers up to 6 cm long, which exude a yellowish oily fluid when cut that stains the skin. The lower leaves are 3–4 times pinnate, triangular, with oval toothed leaflets 10–20 mm long, that are basally tapered to the stalk (Glossary_of_leaf_morphology#cuneate, cuneate). The upper leaves are 1–2 pinnate, with narrower lobes and a sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-aminobutyric Acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. GABA is sold as a dietary supplement in many countries. It has been traditionally thought that exogenous GABA (i.e., taken as a supplement) does not cross the blood–brain barrier, but data obtained from more recent research (2010s) in rats describes the notion as being unclear. The carboxylate form of GABA is γ-aminobutyrate. Function Neurotransmitter Two general classes of GABA receptor are known: * GABAA receptor, GABAA in which the receptor is part of a ligand-gated ion channel complex * GABAB receptor, GABAB metabotropic receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors that open or close ion channels via intermediaries (G proteins) Neurons that produce GABA as their output are called GABAergic neurons, and have chiefly inhibito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABAA Receptor
The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous Ligand (biochemistry), ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the Chemical synapse, postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to Chloride, chloride ions () and, to a lesser extent, Bicarbonate, bicarbonate ions (). GABAAR are members of the ligand-gated ion channel receptor superfamily, which is a chloride channel family with a dozen or more heterotetrametric subtypes and 19 distinct subunits. These subtypes have distinct brain regional and subcellular localization, age-dependent expression, and the ability to undergo plastic alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotatoxin
Falcarinol (also known as carotatoxin or panaxynol) is a natural pesticide and fatty alcohol found in carrots (''Daucus carota''), ''Panax ginseng'' and ivy. In carrots, it occurs in a concentration of approximately 2 mg/kg. As a toxin, it protects roots from fungal diseases, such as liquorice rot that causes black spots on the roots during storage. The compound is sensitive to light and heat. Chemistry Falcarinol is a polyyne with two carbon-carbon triple bonds and two double bonds. The double bond at the carbon 9 position has ''cis'' stereochemistry was introduced by the desaturation, which requires oxygen and NADPH (or NADH) cofactors and creates a bend in the molecule. It is structurally related to oenanthotoxin and cicutoxin. Biological effects Falcarinol is an intense irritant that can cause allergic reactions and contact dermatitis. It was shown that falcarinol acts as a covalent cannabinoid receptor type 1 inverse agonist and blocks the effect of anandamide in kerati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from '' toxic''. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. They vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Less strict understandings embrace naturally occurring inorganic toxins, such as arsenic. Other understandings embrace synthetic analogs of naturally occurring organic poisons as toxins, and may or may not embrace naturally oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due to asymptomatic type 1 atrioventricular block. Resting heart rates of less than 50 BPM are often normal during sleep in young and healthy adults and athletes. In large population studies of adults without underlying heart disease, resting heart rates of 45–50 BPM appear to be the lower limits of normal, dependent on age and sex. Bradycardia is most likely to be discovered in the elderly, as age and underlying cardiac disease progression contribute to its development. Bradycardia may be associated with symptoms of fatigue, dyspnea, dizziness, confusion, and syncope due to reduced blood flow to the brain. The types of symptoms often depend on the etiology of the slow heart rate, classified by the anatomical location of a dysfunction withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthotonus
Opisthotonus or opisthotonos (from and ) is a state of severe hyperextension and spasticity in which an individual's head, neck and spinal column enter into a complete "bridging" or "arching" position. This extreme arched pose is an extrapyramidal effect and is caused by spasm of the axial muscles along the spinal column. Among extant animals it naturally occurs in birds, snakes suffering from advanced boid inclusion body disease, and placental mammals; it is also observed in some articulated dinosaur fossils. Causes Opisthotonus is a symptom of some cases of severe cerebral palsy and traumatic brain injury, or as a result of the severe muscular spasms associated with tetanus. It can be a feature of severe acute hydrocephalus, poisoning, and drowning. Infants Opisthotonus is more pronounced in infants. Opisthotonus in the neonate may be a symptom of meningitis, tetanus, severe kernicterus, or the rare maple syrup urine disease. This marked extensor tone can cause infants to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a medical condition with abnormally prolonged seizures. It can have long-term consequences, manifesting as a single seizure lasting more than a defined time (time point 1), or 2 or more seizures over the same period without the person returning to normal between them. The seizures can be of the Generalized tonic–clonic seizure, tonic–clonic type, with a regular pattern of contraction and extension of the arms and legs, also known as convulsive status epilepticus, or of types that do not involve contractions, such as absence seizures or complex partial seizures. Convulsive status epilepticus is a life-threatening medical emergency, particularly if treatment is delayed. For convulsive status epilepticus, the most dangerous type, 5 minutes is the time point at which the seizure or seizures would be considered status epilepticus, so this is defined as a convulsion lasting more than 5 minutes, or two convulsions within 5 minutes without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
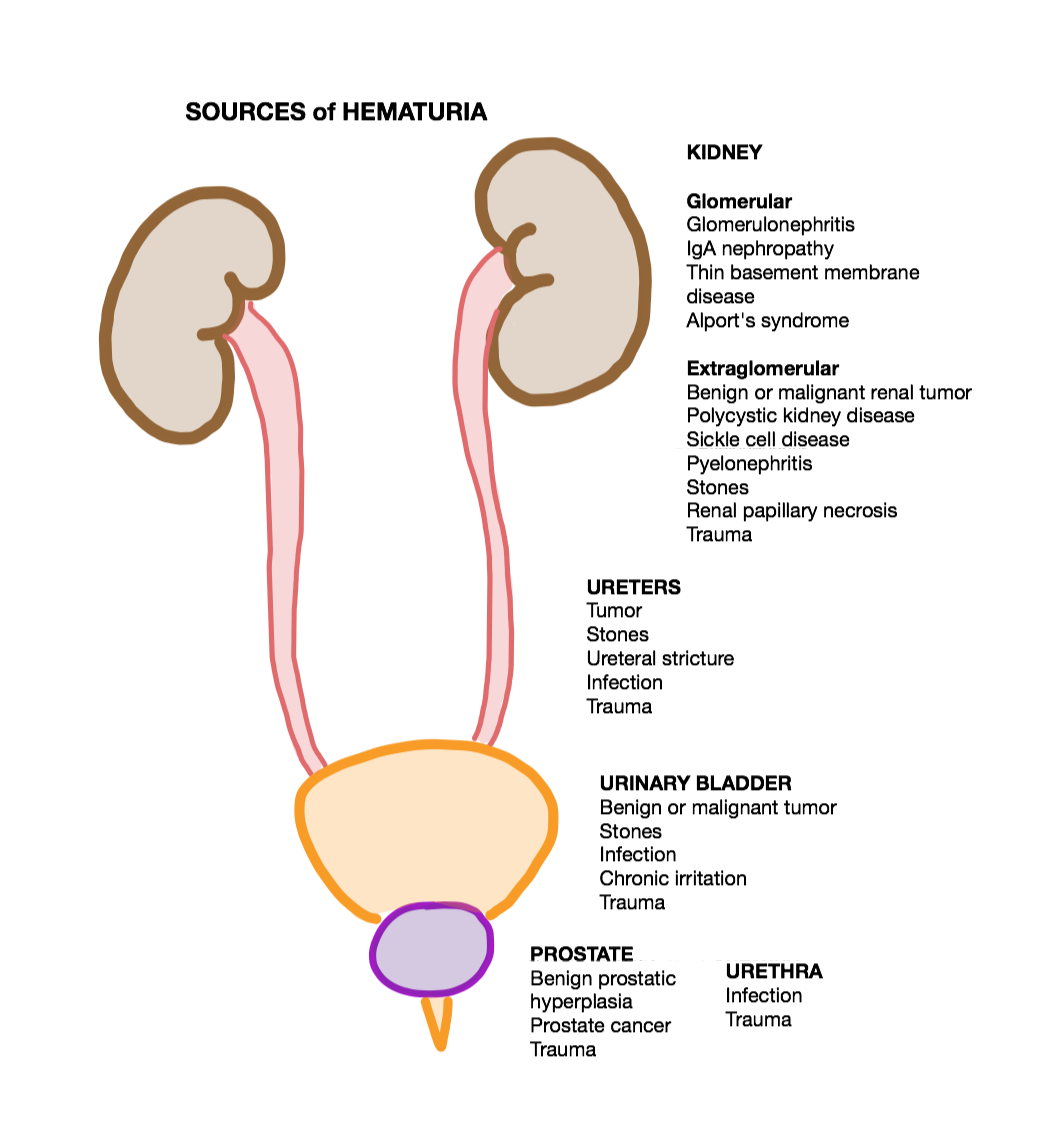
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and some foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |