|
Occupational Hazards Of Solar Panel Installation
The introduction and rapid expansion of solar technology has brought with it a number of occupational hazards for workers responsible for panel installation. Guidelines for safe solar panel installation exist,Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA): Solar Construction Safety. (Dec. 2006). Retrieved from http://www.coshnetwork.org/sites/default/files/OSEIA_Solar_Safety_12-06.pdf however the injuries related to panel installation are poorly quantified. There is concern for long term health effects acquired from prolonged ultraviolet radiation and from lifting heavy panels. The lack of data regarding these concerns makes increasing awareness for worker safety more challenging. Exposures and health effects With regard to PV occupational safety, there are differing exposures depending on the stage of involvement in Solar energy production. This can be broken down into four stages. Exposures and their impacts on worker health intricately depend on the PV life-cycle stage, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silicosis (particularly the acute form) is characterized by shortness of breath, cough, fever, and cyanosis (bluish skin). It may often be misdiagnosed as pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs), pneumonia, or tuberculosis. Using workplace controls, silicosis is almost always a preventable disease. Silicosis resulted in at least 43,000 deaths globally in 2013, down from at least 50,000 deaths in 1990. The name ''silicosis'' (from the Latin ''silex'', or flint) was originally used in 1870 by Achille Visconti (1836–1911), prosector in the Ospedale Maggiore of Milan. The recognition of respiratory problems from breathing in dust dates to ancient Greeks and Romans. Agricola, in the mid-16th century, wrote about lung problems from dust inhalation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Compounds
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate. Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. Cadmium was used for a long time as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel, and cadmium compounds are used as red, orang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SiH4
Silane is an inorganic compound with chemical formula, . It is a colourless, pyrophoric, toxic gas with a sharp, repulsive smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental silicon. Silane with alkyl groups are effective water repellents for mineral surfaces such as concrete and masonry. Silanes with both organic and inorganic attachments are used as coupling agents. Production Commercial-scale routes Silane can be produced by several routes. Typically, it arises from the reaction of hydrogen chloride with magnesium silicide: : Mg2Si + 4 HCl -> 2 MgCl2 + SiH4 It is also prepared from metallurgical-grade silicon in a two-step process. First, silicon is treated with hydrogen chloride at about 300 °C to produce trichlorosilane, HSiCl3, along with hydrogen gas, according to the chemical equation : Si + 3 HCl -> HSiCl3 + H2 The trichlorosilane is then converted to a mixture of silane and silicon tetrachloride: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deposition (geology)
Deposition is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or landmass. Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material, which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up layers of sediment. Deposition occurs when the forces responsible for sediment transportation are no longer sufficient to overcome the forces of gravity and friction, creating a resistance to motion; this is known as the null-point hypothesis. Deposition can also refer to the buildup of sediment from organically derived matter or chemical processes. For example, chalk is made up partly of the microscopic calcium carbonate skeletons of marine plankton, the deposition of which has induced chemical processes (diagenesis) to deposit further calcium carbonate. Similarly, the formation of coal begins with the deposition of organic material, mainly from plants, in anaerobic conditions. Null-point hypothesis The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
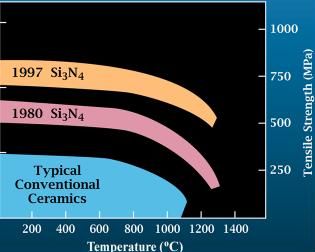
Silicon Nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot . It is very hard (8.5 on the mohs scale). It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications. Production Silicon nitride is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere: :3 Si + 2 → The silicon sample weight increases progressively due to the chemical combination of silicon and nitrogen. Without an iron catalyst, the reaction is complete after several hours (~7), when no further weight increase due to nitrogen absorption (per gram of silicon) is detected. In addition to , several other silicon nitride phases (with chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofluoric Acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers. Uses Production of organofluorine compounds The principal use of hydrofluoric acid is in organofluorine chemistry. Many organofluorine compounds are prepared using HF as the fluorine source, including Teflon, fluoropolymers, fluorocarbons, and refrigerants such as freon. Many pharmaceuticals contain fluorine. Production of inorganic fluorides Most high-volume inorganic fluoride compounds are prepared from hydrofluoric acid. Foremost are Na3AlF6, cryolite, and AlF3, aluminium trifluoride. A molten mixture of these solids serves as a high-temperature solvent for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other polar solvents). Upon contact, and HCl combine to form hydronium cations a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorosilane
Chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride ().. Synthesis Hydrochlorosilanes They are prepared by the Müller-Rochow process, which involves treating silicon with hydrogen chloride at elevated temperatures in the presence of a copper catalyst. The idealized equation is :2 Si + 6 HCl → 2 HSiCl3 + 2 H2, Trichlorosilane (HSiCl3) is the main product; dichlorosilane (H2SiCl2) and silicon tetrachloride (SiCl4) are obtained as byproducts. The process was independently discovered by Eugene G. Rochow and Richard Müller in 1940. Methylchlorosilanes Methyltrichlorosilane (CH3SiCl3), dimethyldichlorosilane ((CH3)2SiCl2), and trimethylsilyl chloride ((CH3)3SiCl) are produced by the direct process. They are key reagents in organosilicon chemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




_0468.jpg)

