|
Occipitofrontalis
The occipitofrontalis muscle (epicranius muscle) is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. It consists of two parts or bellies: the occipital belly, near the occipital bone, and the frontal belly, near the frontal bone. It is supplied by the supraorbital artery, the supratrochlear artery, and the occipital artery. It is innervated by the facial nerve. In humans, the occipitofrontalis helps to create facial expressions. Structure The occipitofrontalis muscle consists of two parts or bellies: * the occipital belly, near the occipital bone. It originates on the lateral two-thirds of the highest nuchal line, and on the mastoid process of the temporal bone. It inserts into the epicranial aponeurosis. * the frontal belly, near the frontal bone. It originates from an intermediate tendon that connects to the occipital belly. It inserts in the fascia of the facial muscles and in the skin above the eyes and nose. Some sources consider the occipital and frontal bellies to be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forehead
In human anatomy, the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features, two of the skull and one of the scalp. The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline, the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. The bottom of the forehead is marked by the supraorbital ridge, the bone feature of the skull above the eyes. The two sides of the forehead are marked by the temporal ridge, a bone feature that links the supraorbital ridge to the coronal suture line and beyond. However, the eyebrows do not form part of the forehead. In ''Terminologia Anatomica'', ''sinciput'' is given as the Latin equivalent to "forehead". (Etymology of ''sinciput'': from ''semi-'' "half" + ''caput'' "head".) Structure The bone of the forehead is the squamous part of the frontal bone. The overlying muscles are the occipitofrontalis, procerus, and corrugator supercilii muscles, all of which are controlled by the temporal branch of the facial nerve. The sensory nerves of the forehead conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontalis Muscle
The frontalis muscle () is a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull. Some sources consider the frontalis muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the occipitalis muscle. In humans, the frontalis muscle only serves for facial expressions. The frontalis muscle is supplied by the facial nerve and receives blood from the supraorbital and supratrochlear arteries. Structure The frontalis muscle is thin, of a quadrilateral form, and intimately adherent to the superficial fascia. It is broader than the occipitalis and its fibers are longer and paler in color. It is located on the front of the head. The muscle has no bony attachments. Its medial fibers are continuous with those of the procerus; its intermediate fibers blend with the corrugator and orbicularis oculi muscles, thus attached to the skin of the eyebrows; and its lateral fibers are also blended with the latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporoparietalis Muscle
The temporoparietalis muscle is a distinct muscle of the head. It lies above the auricularis superior muscle. It lies just inferior to the epicranial aponeurosis of the occipitofrontalis muscle. The temporoparietalis muscle may be used in reconstructive Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes cranio ... ear surgery. References Muscles of the head and neck {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipitalis Muscle
The occipitalis muscle (occipital belly) is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. Some sources consider the occipital muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the frontalis muscle. The occipitalis muscle is thin and quadrilateral in form. It arises from tendinous fibers from the lateral two-thirds of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone and from the mastoid process of the temporal and ends in the epicranial aponeurosis. The occipitalis muscle is innervated by the facial nerve and its function is to move the scalp back. The muscles receives blood from the occipital artery. Additional image File:Occipitalis muscle animation small.gif, Position of occipitalis muscle (shown in red). See also * Occipitofrontalis muscle The occipitofrontalis muscle (epicranius muscle) is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. It consists of two parts or bellies: the occipital bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
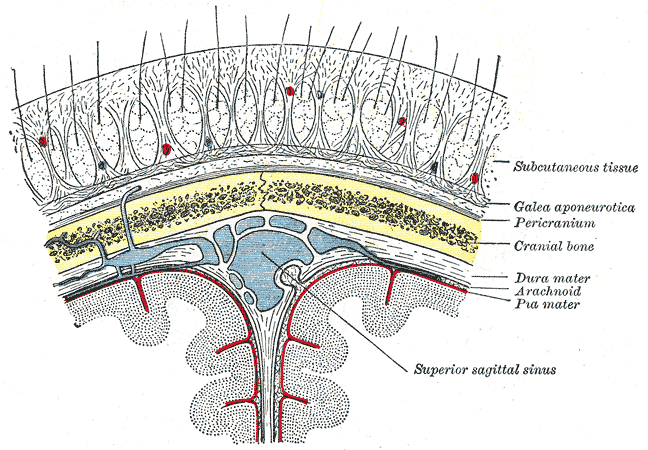
Epicranial Aponeurosis
The epicranial aponeurosis (aponeurosis epicranialis, galea aponeurotica) is an aponeurosis (a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue). It covers the upper part of the skull in humans and many other animals. Structure In humans, the epicranial aponeurosis originates from the external occipital protuberance and highest nuchal lines of the occipital bone. It merges with the occipitofrontalis muscle. In front, it forms a short and narrow prolongation between its union with the frontalis muscle (the frontal part of the occipitofrontalis muscle). On either side, the epicranial aponeurosis attaches to the anterior auricular muscles and the superior auricular muscles. Here it is less aponeurotic, and is continued over the temporal fascia to the zygomatic arch as a layer of laminated areolar tissue. It is closely connected to the integument by the firm, dense, fibro-fatty layer which forms the superficial fascia of the scalp. It is attached to the pericranium by loose cellular t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders (imprint)
Saunders is an American academic publisher based in the United States. It is currently an imprint of Elsevier. Formerly independent, the W. B. Saunders company was acquired by CBS in 1968, who added it to their publishing division Holt, Rinehart & Winston. When CBS left the publishing field in 1986, it sold the academic publishing units to Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier RELX plc (pronounced "Rel-ex") is a British multinational information and analytics company headquartered in London, England. Its businesses provide scientific, technical and medical information and analytics; legal information and analytics; ... in 2001. . Northern Il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atony
This glossary of medical terms is a list of definitions about medicine, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. A * Aarskog–Scott syndrome – (AAS) A rare, inherited (X-linked) disease characterized by short stature, facial abnormalities, skeletal and genital anomalies. *Abdomen – The part of the body between the chest and pelvis, which contains most of the tubelike organs of the digestive tract, as well as several solid organs. *Abdominal external oblique muscle – The largest, and outermost, of the three flat muscles of the lateral anterior abdominal wall. * Abdominal internal oblique muscle – A muscle of the abdominal wall, which lies below the external oblique and just above the transverse abdominal muscles. * Abductor pollicis brevis muscle – A muscle in the hand that abducts (straightens) the thumb. * Abductor pollicis longus muscle – One of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. * Abscess – A collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. Structure The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic: * S: The skin on the head from which head hair grows. It contains numerous sebaceous glands and hair follicles. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: The aponeurosis called epicranial aponeurosis (or galea aponeurotica) is the next layer. It is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis posteriorly. * L: The loose areolar connective tissue layer provides an easy plane of separation between the upper three layers and the pericranium. In scalping the scalp is torn off through this layer. It also provides a plane of access in craniofacial surgery and neurosurgery. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Livingstone
Churchill Livingstone is an academic publisher. It was formed in 1971 from the merger of Longman's medical list, E & S Livingstone (Edinburgh, Scotland) and J & A Churchill (London, England) and was owned by Pearson. Harcourt acquired Churchill Livingstone in 1997. It is now integrated as an imprint in Elsevier's health science division after Elsevier acquired Harcourt in 2001. In the past it published a number of classic medical texts, including Sir William Osler's textbook ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine ''The Principles and Practice of Medicine: Designed for the Use of Practitioners and Students of Medicine'' is a medical textbook by Sir William Osler. It was first published in 1892 by D. Appleton & Company, while Osler was professor of Medicine ..., Gray's Anatomy,'' and '' Myles' Textbook for Midwives.'' In the 1980s, in addition to new texts in all areas of clinical medicine, it published an extensive list of medical and nursing textbooks in low-cost edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and ''visceral'' or ''parietal'' fascia, or by its function and anatomical location. Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia. Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambdoid Suture
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture. Structure The lambdoid suture is between the paired parietal bones and the occipital bone of the skull. It runs from the asterion on each side. Nerve supply The lambdoid suture may be supplied by a branch of the supraorbital nerve, a branch of the frontal branch of the trigeminal nerve. Clinical significance At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called "plagiocephaly". Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis. The lambdoid s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |