|
Obwarzanek Krakowski
An ' (, plural: ' ; also spelled ') is a braided ring-shaped bread that is boiled and sprinkled with salt and sesame or poppy seeds before being baked. It has a white, sweetish, moist and chewy crumb underneath a crunchy golden-brown crust. Traditionally sold from street carts, it is a popular snack in the Polish city of Kraków, where it has the status of a regional food with protected geographical indication. It is closely related to, but distinct from, bagels, bubliks and pretzels. Etymology The term ' is Polish. The Polish noun ', or ', derives from the verb ', "to parboil", which refers to the distinctive technique of boiling the dough before baking. The adjective ' denotes anything coming from or related to the city of Kraków. Description An ' is a ring-shaped baked product with a hole in the middle. It takes the form of an oval or, seldom, a circle. Its surface is formed by strands of dough, round or oval in cross-section, twisted into a spiral. The colour rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 (2023), with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596, and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Kraków Old Town, Old Town was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the world's first sites granted the status. The city began as a Hamlet (place), hamlet on Wawel Hill and was a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. In 1038, it became the seat of King of Poland, Polish monarchs from the Piast dynasty, and subsequently served as the centre of administration under Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings and of the Polish–Lithuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagel
A bagel (; ; also spelled beigel) is a bread roll originating in the Jewish communities of Poland. Bagels are traditionally made from yeasted wheat dough that is shaped by hand into a torus or ring, briefly boiled in water, and then baked. The result is a dense, chewy, doughy interior with a browned and sometimes crisp exterior. Bagels are often topped with seeds baked on the outer crust—traditional choices include poppy and sesame seeds—or with salt grains. Different dough types include whole-grain and rye. The basic roll-with-a-hole design, hundreds of years old, allows even cooking and baking of the dough; it also allows groups of bagels to be gathered on a string or dowel for handling, transportation, and retail display. The earliest known mention of a boiled-then-baked ring-shaped bread can be found in a 13th-century Syrian cookbook, where they are referred to as . Bagel-like bread known as obwarzanek was common earlier in Poland as seen in royal family account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I Albert
John I Albert (; 27 December 1459 – 17 June 1501) was King of Poland Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ... from 1492 to his death and Duke of Głogów from 1491 to 1498. He was the fourth Polish sovereign from the Jagiellonian dynasty and the son of Casimir IV Jagiellon, Casimir IV and Elizabeth of Austria (1436–1505), Elizabeth of Austria. Related to the House of Habsburg, John Albert was groomed to become emperor in the Holy Roman Empire, a plan that ultimately failed. He was well-educated and tutored by scholars such as Johannes Longinus and Filippo Buonaccorsi, Callimachus, whom he had subsequently befriended. Heavily influenced by the Italian Renaissance, John sought to strengthen royal authority at the expense of the Catholic Church and the clergy. In 1487 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków Grosz
The Kraków grosz ( (sing.), ' (pl.), , ) were medieval silver coins minted in 14th century Kraków. Following the Bohemian Prague groschen in use since 1300, and other large silver groschen-type coins issued in the Holy Roman Empire, the coin was introduced in 1367 during the reign of King Casimir III of Poland. Its obverse and reverse The obverse and reverse are the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags, seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, ''obverse'' mean ... sides had the following text: *''KAZIMIRVS PRIMUS DEI GRATIA REX POLONIE'' *''GROSI CRACOVIENSESS'' (sic!) References Medieval currencies Currencies of Poland History of Kraków Groschen {{Poland-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidia (Roman province), Numidia and Africa (Roman province), Africa Proconsularis under the Vandals, the Exarchate of Africa, Byzantines and the Kingdom of Altava, Romano-Berber Kingdoms, until it declined after the Arab conquest of North Africa, Arab Conquest. Medieval Latin in Southern and Central Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Hispania, conquered by the Arabs immediately after North Africa, experienced a similar fate, only recovering its importance after the Reconquista by the Northern Christian Kingdoms. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned as the main medium of scholarly exchange, as the liturgical language of the Roman Catholic Church, Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
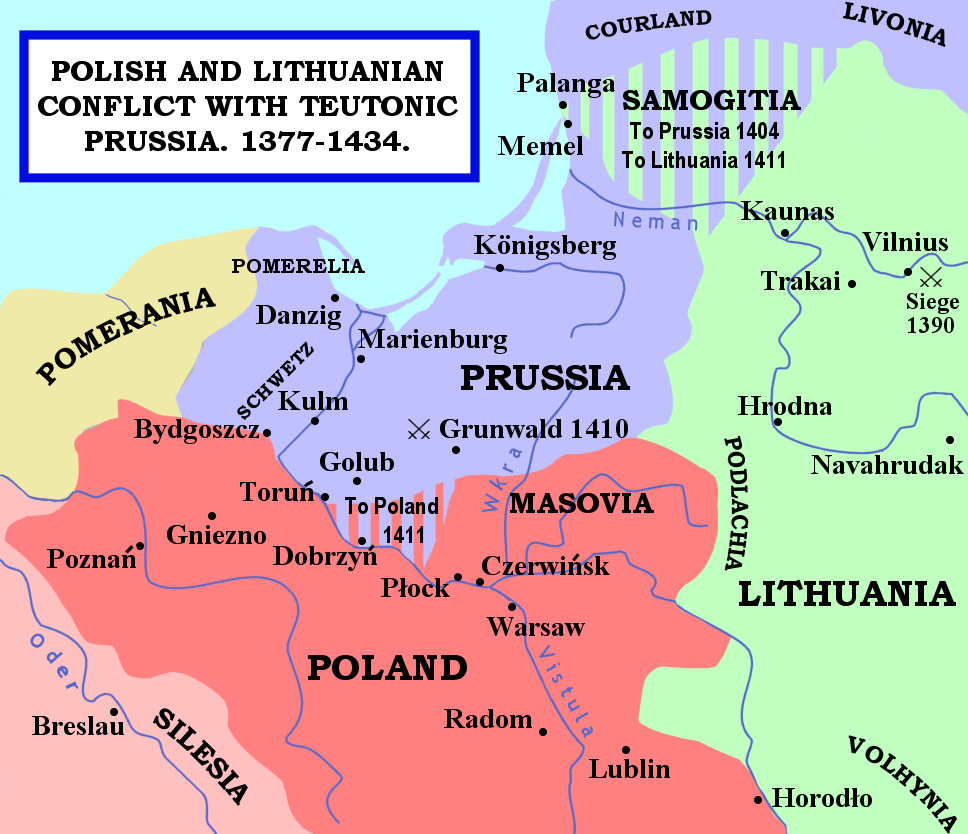
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło (),Other names include (; ) (see also Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło) was Grand Duke of Lithuania beginning in 1377 and starting in 1386, becoming King of Poland as well. As Grand Duke, he ruled Lithuania from 1377 to 1381 and from 1382 to 1401, at which time he became the Supreme Duke of Lithuania in exchange for naming his cousin Vytautas as the new Grand Duke. Władysław II initially served as King of Poland alongside his wife Jadwiga of Poland, Jadwiga until her death in 1399, and then the sole ruler until his own death in 1434. Raised a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and baptized as Ladislaus () in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he Christianization of Lithuania, converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obwarzanki Salesman In Krakow
An ' (, plural: ' ; also spelled ') is a braided ring-shaped bread that is boiled and sprinkled with salt and sesame or poppy seeds before being baked. It has a white, sweetish, moist and chewy crumb underneath a crunchy golden-brown crust. Traditionally sold from street carts, it is a popular snack in the Polish city of Kraków, where it has the status of a regional food with protected geographical indication. It is closely related to, but distinct from, bagels, bubliks and pretzels. Etymology The term ' is Polish. The Polish noun ', or ', derives from the verb ', "to parboil", which refers to the distinctive technique of boiling the dough before baking. The adjective ' denotes anything coming from or related to the city of Kraków. Description An ' is a ring-shaped baked product with a hole in the middle. It takes the form of an oval or, seldom, a circle. Its surface is formed by strands of dough, round or oval in cross-section, twisted into a spiral. The colour ranges fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' , from Latin ), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classified as a separate species until 2011. The onion's close relatives include garlic, scallion, leek, and chives. The genus contains several other species variously called onions and cultivated for food, such as the Japanese bunching onion '' Allium fistulosum'', the tree onion ''Allium'' × ''proliferum'', and the Canada onion '' Allium canadense''. The name '' wild onion'' is applied to a number of ''Allium'' species, but ''A. cepa'' is exclusively known from cultivation. Its ancestral wild original form is not known, although escapes from cultivation have become established in some regions. The onion is most frequently a biennial or a perennial plant, but is usually treated as an annual and harvested in its first growing season. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheese
Cheese is a type of dairy product produced in a range of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk (usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats or sheep). During production, milk is usually acidified and either the enzymes of rennet or bacterial enzymes with similar activity are added to cause the casein to coagulate. The solid curds are then separated from the liquid whey and pressed into finished cheese. Some cheeses have aromatic molds on the rind, the outer layer, or throughout. Over a thousand types of cheese exist, produced in various countries. Their styles, textures and flavors depend on the origin of the milk (including the animal's diet), whether they have been pasteurised, the butterfat content, the bacteria and mold, the processing, and how long they have been aged. Herbs, spices, or wood smoke may be used as flavoring agents. Other added ingredients may include black pepper, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Pepper
Black pepper (''Piper nigrum'') is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit (the peppercorn), which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. The fruit is a drupe (stonefruit) which is about in diameter (fresh and fully mature), dark red, and contains a stone which encloses a single pepper seed. Peppercorns and the ground pepper derived from them may be described simply as ''pepper'', or more precisely as ''black pepper'' (cooked and dried unripe fruit), ''green pepper'' (dried unripe fruit), or ''white pepper'' (ripe fruit seeds). Black pepper is native to the Malabar Coast of India, and the Malabar pepper is extensively cultivated there and in other tropical regions. Ground, dried, and cooked peppercorns have been used since antiquity, both for flavour and as a traditional medicine. Black pepper is the world's most traded spice, and is one of the most common spices added to cuisines around the world. Its spiciness is due to the che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caraway
Caraway, also known as meridian fennel and Persian cumin (''Carum carvi''), is a biennial plant in the family Apiaceae, native to western Asia, Europe, and North Africa. Etymology The etymology of "caraway" is unclear. Caraway has been called by many names in different regions, with names deriving from the Latin ( cumin), the Greek ''karon'' (again, cumin), which was adapted into Latin as (now meaning caraway), and the Sanskrit ''karavi'', sometimes translated as "caraway", but other times understood to mean "fennel".Katzer's Spice PagesCaraway Caraway (''Carum carvi'' L.)/ref> English use of the term caraway dates to at least 1440, possibly having Arabic origin.Walter William Skeat, Principles of English Etymology, Volume 2, page 319. 189Words of Arabic Origin/ref> Description The plant is similar in appearance to other members of the carrot family, with finely divided, feathery leaves with thread-like divisions, growing on stems. The main flower stem is tall, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paprika
Paprika is a spice made from dried and ground red peppers, traditionally ''capsicum annuum''. It can have varying levels of Pungency, heat, but the peppers used for hot paprika tend to be milder and have thinner flesh than those used to produce chili powder. The milder, sweet paprika is mostly composed of the fruit of the pepper with most of the seeds removed; whereas some seeds and stalks are retained in the peppers used for hotter paprika. Paprika, like all capsicum varieties and their derivatives, is descended from wild ancestors from the Amazon River, cultivated in ancient times in South, Central and North America, in particular Mexican Plateau, central Mexico. The peppers were introduced to Europe, via Spanish Empire, Spain and Portuguese Empire, Portugal, in the sixteenth century. The trade in paprika expanded from the Iberian Peninsula to Africa and Asia and ultimately reached central Europe through the Balkans. European cuisines in which paprika is a frequent and major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |