|
Obstetrical
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolytic dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to the world. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In Developed country, developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in Developing country, developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the cervical effacement, shortening and Cervical dilation, opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the Postpartum period, postpartum. The first stage is characterised by abdominal cramping or also back pain in the case of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complications Of Pregnancy
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to or arise during pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. While some complications improve or are fully resolved after pregnancy, some may lead to lasting effects, morbidity, or in the most severe cases, maternal or fetal mortality. Common complications of pregnancy include anemia, gestational diabetes, infections, gestational hypertension, and pre-eclampsia. Presence of these types of complications can have implications on monitoring lab work, imaging, and medical management during pregnancy. Severe complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium are present in 1.6% of mothers in the US, and in 1.5% of mothers in Canada. In the immediate postpartum period (puerperium), 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem. Long-term health problems (pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics And Gynecology
Obstetrics and gynaecology (also spelled as obstetrics and gynecology; abbreviated as Obst and Gynae, O&G, OB-GYN and OB/GYN) is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics (covering pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period) and gynaecology (covering the health of the female reproductive system – vagina, uterus, ovaries, and Breast, breasts). The specialization is an important part of care for women's health. Postgraduate training programs for both fields are usually combined, preparing the practising obstetrician-gynecologist to be adept both at the care of female reproductive organs' health and at the management of pregnancy, although many doctors go on to develop subspecialty interests in one field or the other. Scope United States According to the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG), which is responsible for issuing OB-GYN certifications in the United States, the first step to OB-GYN certification is completing medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialty (medicine)
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care (family medicine). After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other Clinician, clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency (medicine), residency to become a specialist. History of medical specialization To a certain extent, medical practitioners have long been specialized. According to Galen, specialization was common among Roman physicians. The particular system of modern medical specialties evolved gradually during the 19th century. Informal social recognition of medical specialization evolved before the formal legal system. The particular subdivision of the practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rh Blood Group System
The Rh blood group system is a human blood group system. It contains proteins on the surface of red blood cells. After the ABO blood group system, it is most likely to be involved in transfusion reactions. The Rh blood group system consisted of 49 defined blood group antigens in 2005. there are over 50 antigens, of which the five antigens D, C, c, E, and e are among the most prominent. There is no d antigen. Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a ''positive'' (+) or ''negative'' (−) suffix after the ABO type (e.g., someone who is A+ has the A antigen and Rh(D) antigen, whereas someone who is A− has the A antigen but lacks the Rh(D) antigen). The terms ''Rh factor'', ''Rh positive'', and ''Rh negative'' refer to the Rh(D) antigen only. Antibodies to Rh antigens can be involved in hemolytic transfusion reactions and antibodies to the Rh(D) and Rh antigens confer significant risk of hemolytic disease of the newborn. Nomenclature The Rh blood group syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho(D) Immune Globulin
Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is a medication used to prevent RhD isoimmunization in mothers who are RhD negative and to treat idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in people who are Rh positive. RhIG is commonly referred to as 'anti-D'. It is often given both during and following pregnancy. It may also be used when RhD-negative people are given RhD-positive blood. It is given by injection into muscle or a vein. A single dose lasts 12 weeks. It is made from human blood plasma. Common side effects include fever, headache, pain at the site of injection, and red blood cell breakdown. Other side effects include allergic reactions, kidney problems, and a very small risk of viral infections. In those with ITP, the amount of red blood cell breakdown may be significant. Use is safe with breastfeeding. Rho(D) immune globulin is made up of antibodies to the antigen Rho(D) present on some red blood cells. It is believed to work by blocking a person's immune system from rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rh Disease
Rh disease (also known as rhesus isoimmunization, Rh (D) disease, or rhesus incompatibility, and blue baby disease) is a type of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). The term "Rh disease" is commonly used to refer to HDFN due to anti-D antibodies (the D antigen being only one of more than 50 in the Rh complex), and prior to the discovery of anti-Rho(D) immune globulin, it was the most common type of HDFN. The disease ranges from mild to severe, and occurs in the second or subsequent pregnancies of Rh-D negative women when the biological father is Rh-D positive. Due to several advances in modern medicine, HDFN due to anti-D is preventable by treating the mother during pregnancy and soon after delivery with an injection of anti-Rho(D) immune globulin (Rhoclone, Rhogam, AntiD). With successful mitigation of this disease by prevention through the use of anti-Rho(D) immune globulin, other antibodies are more commonly the cause of HDFN today. Mechanism During pregn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coombs Test
The direct and indirect Coombs tests, also known as antiglobulin test (AGT), are blood tests used in immunohematology. The direct Coombs test detects antibodies that are stuck to the surface of the red blood cells. Since these antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells they can cause anemia; this test can help clarify the condition. The indirect Coombs test detects antibodies that are floating freely in the blood. These antibodies could act against certain red blood cells; the test can be carried out to diagnose reactions to a blood transfusion. The direct Coombs test is used to test for autoimmune hemolytic anemia, a condition where the immune system breaks down red blood cells, leading to anemia. The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies or complement system, complement proteins attached to the surface of red blood cells. To perform the test, a blood sample is taken and the red blood cells are washed (removing the patient's plasma and unbound antibodies from the red b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis fetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus at or around birth, when the IgG molecules (one of the five main types of antibodies) produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack antigens on the red blood cells in the fetal circulation, breaking down and destroying the cells. The fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anemia. The intensity of this fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure ( hydrops fetalis) can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts (immature red blood cells) are present in the fetal blood, earning these forms of the disease the name ''erythroblastosis fetalis'' ( HDFN represents a breach of immune privilege for the fetus or some other form of impairment of the immune tolerance in pregnancy. Various types of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
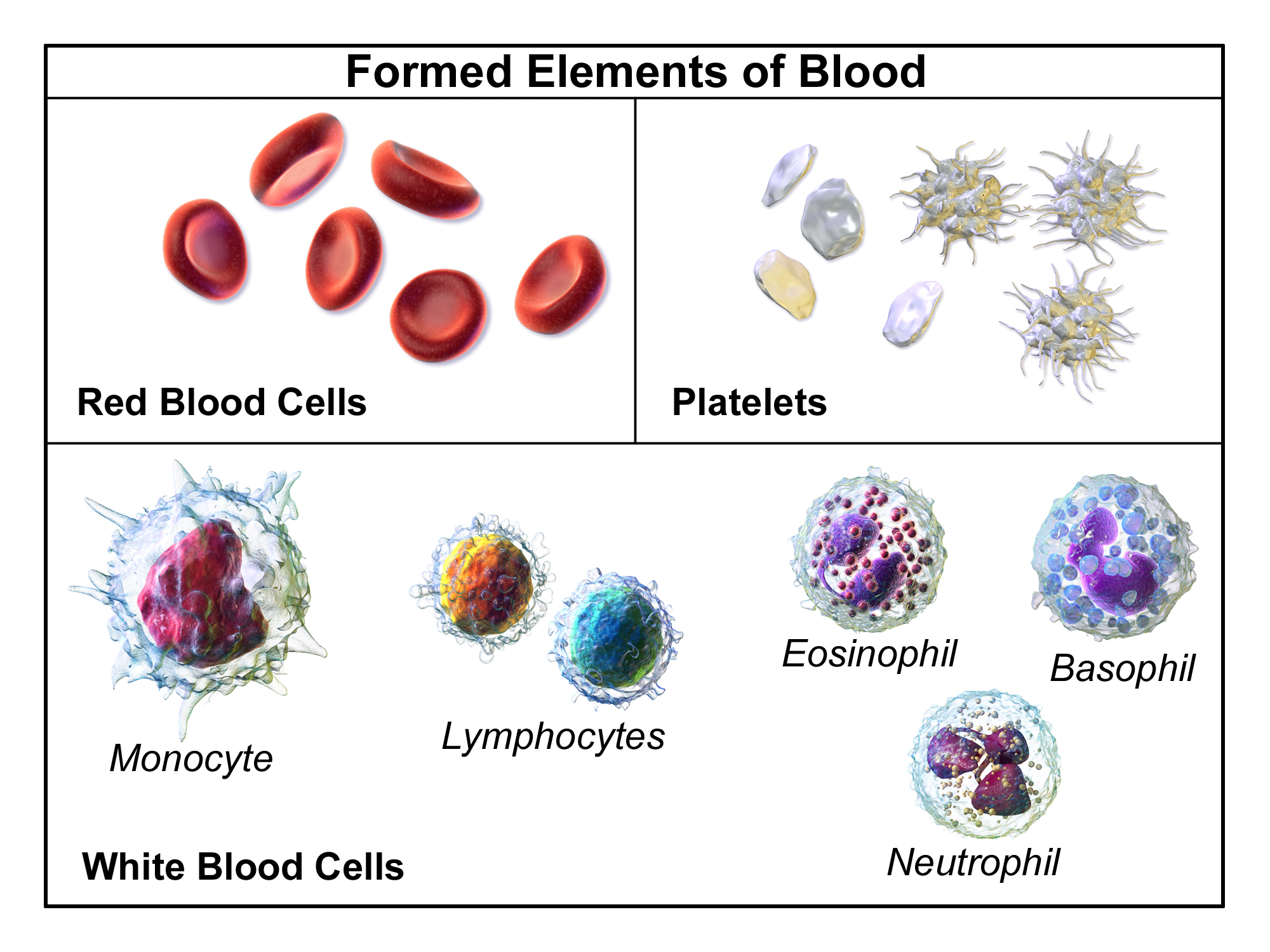
Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells). The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included. The CBC is often carried out as part of a medical assessment and can be used to monitor health or diagnose diseases. The results are interpreted by comparing them to Reference ranges for blood tests, reference ranges, which vary with sex and age. Conditions like anemia and thrombocytopenia are defined by abnormal complete blood count results. The red blood cell indices can provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Plasma Reagin
The rapid plasma reagin test (RPR test or RPR titer) is a type of rapid diagnostic test that looks for non-specific antibodies in the blood of the patient that may indicate an infection by syphilis or related non-venereal treponematoses. It is one of several nontreponemal tests for syphilis (along with the Wassermann test and the VDRL test). The term ''reagin'' means that this test does not look for antibodies against the bacterium itself, ''Treponema pallidum'', but rather for antibodies against substances released by cells when they are damaged by ''T. pallidum'' ( cardiolipin and lecithin). Traditionally, syphilis serologic testing has been performed using a nontreponemal test (NTT) such as the RPR or VDRL test, with positive results then confirmed using a specific treponemal test (TT) such as TPPA or FTA-ABS. This method is endorsed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and is the standard in many parts of the world. After screening for syphilis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy Ulcer_(dermatology), skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter), though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. Latent syphilis has no symptoms and can last years. In tertiary syphilis, there are Gumma (pathology), gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "The Great Imitator, the great imitator", because it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through human sexual activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |