|
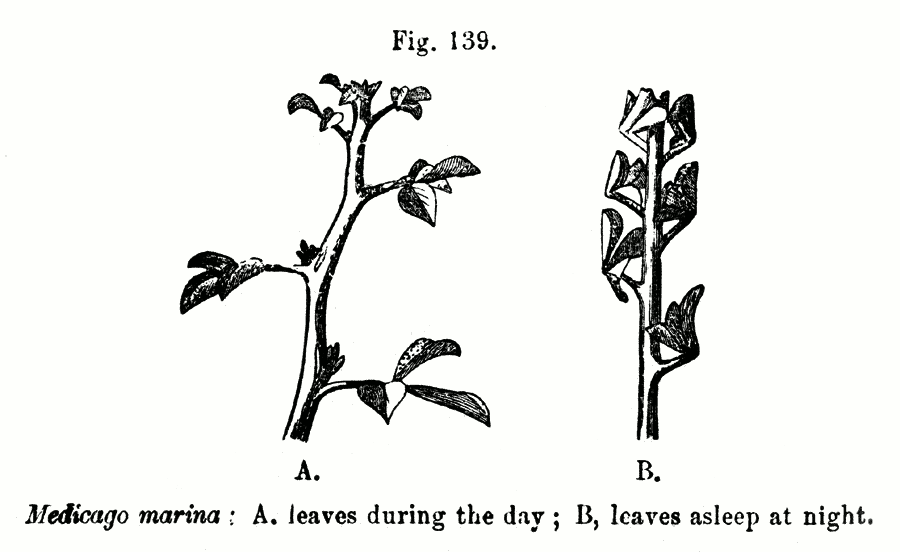
Nyctinastic
In plant biology, nyctinasty is the circadian rhythm-based nastic movement of higher plants in response to the onset of darkness, or a plant "sleeping". Nyctinastic movements are associated with diurnal light and temperature changes and controlled by the circadian clock. It has been argued that for plants that display foliar nyctinasty, it is a crucial mechanism for survival; however, most plants do not exhibit any nyctinastic movements. Nyctinasty is found in a range of plant species and across xeric, mesic, and aquatic environments, suggesting that this singular behavior may serve a variety of evolutionary benefits. Examples are the closing of the petals of a flower at dusk and the sleep movements of the leaves of many legumes. Physiology A tulip with closed petals, thumb Plants use phytochrome to detect red and far red light. Depending on which kind of light is absorbed, the protein can switch between a Pr state that absorbs red light and a Pfr state that absorbs far red l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulvinus
A pulvinus (pl. ''pulvini'') may refer to a joint-like thickening at the base of a plant leaf or leaflet that facilitates growth-independent movement. Pulvinus is also a botanical term for the persistent peg-like bases of the leaves in the coniferous genera ''Spruce, Picea'' and ''Tsuga''. Pulvinar movement is common, for example, in members of the bean family Fabaceae (Leguminosae) and the prayer plant family Marantaceae. Pulvini may be present at the base of the Petiole (botany), leaf stalk or on its other end (Apex (leaf), apex), where the leaf is attached, or in a compound leaf at the place where the leaflets are joined to its Rachis#In botany, middle stem. They consist of a core of vascular tissue within a flexible, bulky cylinder of thin-walled Ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma cells. A pulvinus is also sometimes called a geniculum (meaning a knee-like structure in Latin). Pulvinar movement is caused by changes in turgor pressure leading to a contraction or expansion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollinating animals travel from plant to plant carrying pollen on their bodies in a vital interaction that allows the transfer of genetic material critical to the reproductive system of most flowering plants. Self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work. In angiosperms, after the pollen grain (gametophyte) has landed on the stigma (botany), stigma, it germinates and develops a pollen tube which grows down the style (botany), style until it reaches an ovary (botany), ovary. Its two gametes travel down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male Conifer cone, cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it Germination, germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and Forensic science, forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid male genetic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a Common descent, common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental scientific concept. In a joint presentation with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this Phylogenetics, branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding.. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by Burials and memorials in Westminster Abbey, burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh Medical Schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th-century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by changes in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albizia Lebbeck
''Albizia lebbeck'' is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent and Myanmar. It is widely cultivated and naturalised in other tropical and subtropical regions, including Australia. Common names in English include siris, Indian siris, East Indian walnut, Broome raintree, lebbeck, lebbek tree, frywood, koko and woman's tongue tree. The latter name is a play on the sound the seeds make as they rattle inside the pods. Siris is also a common name of the genus ''Albizia''. Description It is a tree growing to a height of tall with a trunk in diameter. The leaves are bipinnate, long, with one to four pairs of pinnae, each pinna with 6–18 leaflets. The flowers are white, with numerous long stamens, and very fragrant. The fruit is a pod long and broad, containing six to twelve seeds. Habitat ''Albizia lebbeck'' is found in a wide range of climates. The variety can be semi-desert, to humid regions. It can last in long cold winters, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albizia Saman
''Albizia'' is a genus of more than 160 species of mostly fast-growing Subtropics, subtropical and Tropics, tropical trees and shrubs in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the family (biology), family Fabaceae. The genus is pantropical, occurring in Asia, Africa, Madagascar, America and Australia, but mostly in the Old World tropics. In some locations, some species are considered weeds. They are commonly called silk plants, silk trees, or sirises. The obsolete spelling of the generic name – with double 'z' – is still common, so the plants may be called albizzias. The generic name honors the Italian nobleman Albizzi, Filippo degli Albizzi, who introduced ''Albizia julibrissin'' to Europe in the mid-18th century. Some species are commonly called mimosa, which more accurately refers to plants of genus ''Mimosa''. Species from southeast Asia used for timber are sometime termed East Indian walnut. Description They are usually small trees or shrubs with a short lifespan, though the fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamaecrista Mimosoides
''Chamaecrista'' is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family, Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae. Members of the genus are commonly known as sensitive pea. Several species are capable of rapid plant movement. Unlike the related genera '' Cassia'' and '' Senna'', members of ''Chamaecrista'' form root nodules. ''Chamaecrista'' has 367 species, with a wide distribution – the Americas from Minnesota to northern Argentina, sub-Saharan Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Iran, the Indian Subcontinent, Indochina, China, Korea, Japan, Malesia, New Guinea, and Australia. Species ''Chamaecrista'' comprises the following species, organized into sections, subsections, and series: Section ''Apoucouita'' Benth. Series Apoucouita * ''Chamaecrista aiarana'' (H.S.Irwin) H.S.Irwin & Barneby * ''Chamaecrista apoucouita'' (Aubl.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby * ''Chamaecrista aspidiifolia'' H.S.Irwin & Barneby * ''Chamaecrista bahiae'' (H.S.Irwin) H.S.Irwin & Barneby * ''Chamaecrista boyanii'' (H.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllanthus Urinaria
''Phyllanthus'' is the largest genus in the plant family Phyllanthaceae. Estimates of the number of species in this genus vary widely, from 750David J. Mabberley. 2008. ''Mabberley's Plant-Book.'' third edition (2008). Cambridge University Press. to 1200. ''Phyllanthus'' has a remarkable diversity of growth forms including annual and perennial herbs, shrubs, climbers, floating aquatics, and pachycaulous succulents. Some have flattened leaflike stems called cladodes. It has a wide variety of floral morphologies and chromosome numbers and has one of the widest range of pollen types of any seed plant genus. Despite their variety, almost all ''Phyllanthus'' species express a specific type of growth called "phyllanthoid branching" in which the vertical stems bear deciduous, floriferous (flower-bearing), plagiotropic (horizontal or oblique) stems. The leaves on the main (vertical) axes are reduced to scales called "cataphylls", while leaves on the other axes develop normally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic Acid
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4-HPPA) is an intermediate in the metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. The aromatic side chain of phenylalanine is hydroxylated by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase to form tyrosine. The conversion from tyrosine to 4-HPPA is in turn catalyzed by tyrosine aminotransferase. Additionally, 4-HPPA can be converted to homogentisic acid Homogentisic acid (2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid) is a phenolic acid usually found in ''Arbutus unedo'' (strawberry-tree) honey. It is also present in the bacterial plant pathogen ''Xanthomonas campestris'' pv. ''phaseoli'' as well as in the ye ... which is one of the precursors to ochronotic pigment. It is an intermediary compound in the biosynthesis of scytonemin. See also * 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase References {{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid Natural phenols Alpha-keto acids Propionic acids Hydroxy acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lespedeza Cuneata
''Lespedeza cuneata'' is a species of flowering plant in the Fabaceae, legume family known by the common names Chinese bushclover and sericea lespedeza, or just sericea.Gucker, Corey. (2010) (Revised from Munger, Gregory T., 2004)''Lespedeza cuneata'' In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. Retrieved 11-26-2011. It is native to Asia and is present elsewhere as an introduced species and sometimes an invasive species, invasive plant. Australian populations of ''Lespedeza juncea'' have sometimes been considered to belong to this species but are now considered to be distinct. Description This plant is a perennial herb with branching stems reaching a maximum height around two meters. It grows from a woody taproot which may exceed one meter in length and which is topped with a woody caudex. The stems are covered densely in leaves, which are each divided into leaflets up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |