|
Novobiocin
Novobiocin, also known as albamycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete ''Streptomyces niveus'', which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for ''S. spheroides'' a member of the class Actinomycetia. Other aminocoumarin antibiotics include clorobiocin and coumermycin A1. Novobiocin was first reported in the mid-1950s (then called streptonivicin). Clinical use It is active against ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' and may be used to differentiate it from the other coagulase-negative ''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'', which is resistant to novobiocin, in culture. Novobiocin was licensed for clinical use under the tradename Albamycin (Upjohn) in the 1960s. Its efficacy#Pharmacology, efficacy has been demonstrated in Clinical trial#Pre clinical studies, preclinical and Clinical trial, clinical trials. The oral form of the drug has since been withdrawn from the market due to lack of efficacy. A combination product of novobiocin and tetrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
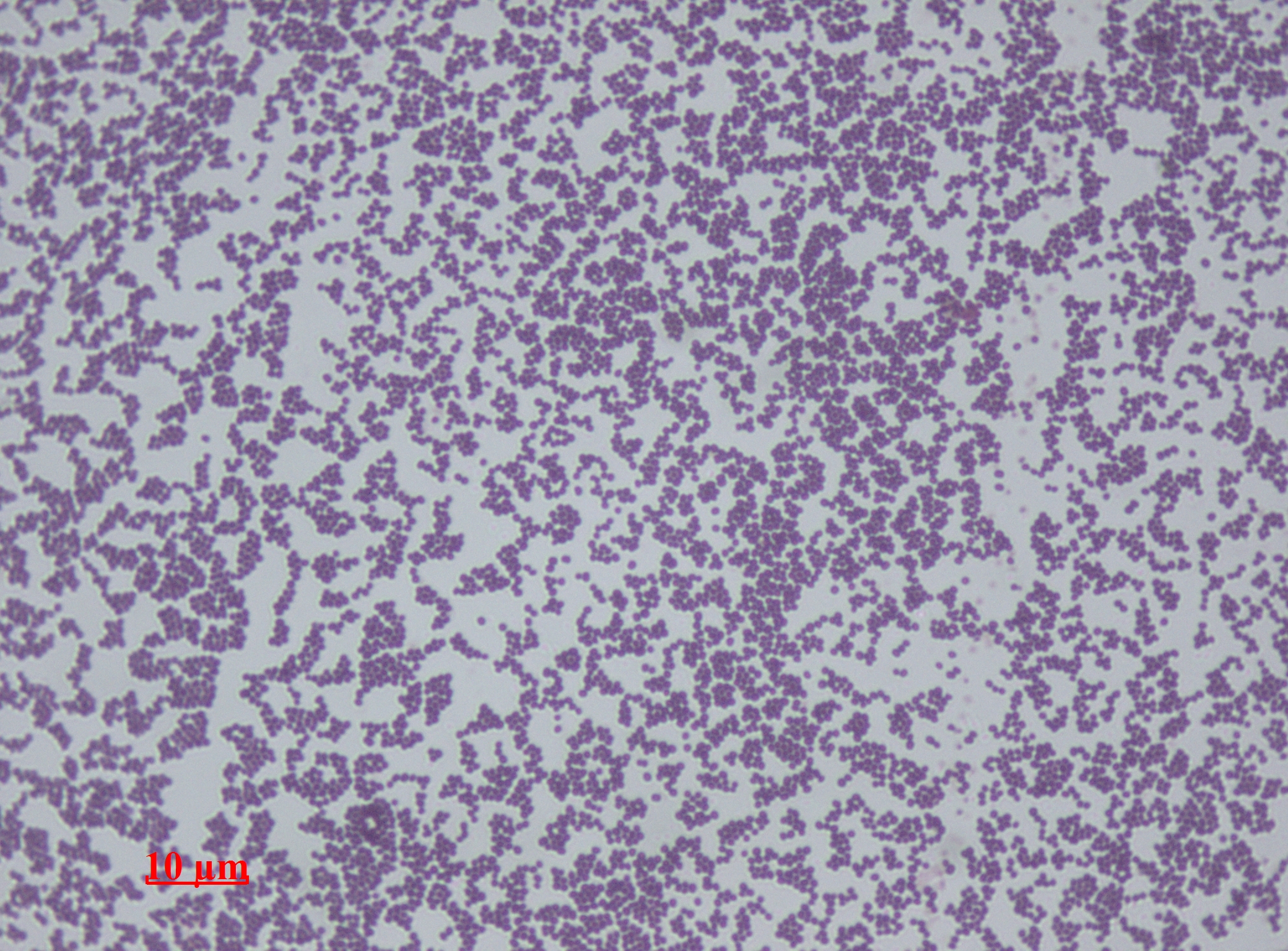
Staphylococcus Saprophyticus
''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' is a Gram-positive coccus belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. ''S. saprophyticus'' is a common cause of community-acquired urinary tract infections. History ''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' was not recognized as a cause of urinary tract infections until the early 1970s, more than 10 years after its original demonstration in urine specimens. Prior to this, the presence of coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) in urine specimens was dismissed as contamination. Epidemiology and pathogenesis In humans, ''S. saprophyticus'' is found in the normal flora of the female genital tract and perineum. It has been isolated from other sources, too, including meat and cheese products, vegetables, the environment, and human and animal gastrointestinal tracts. ''S. saprophyticus'' causes 10–20% of urinary tract infections (UTIs). In females 17–27 years old, it is the second-most common cause of community-acquired UTIs, after ''Escherichia coli''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
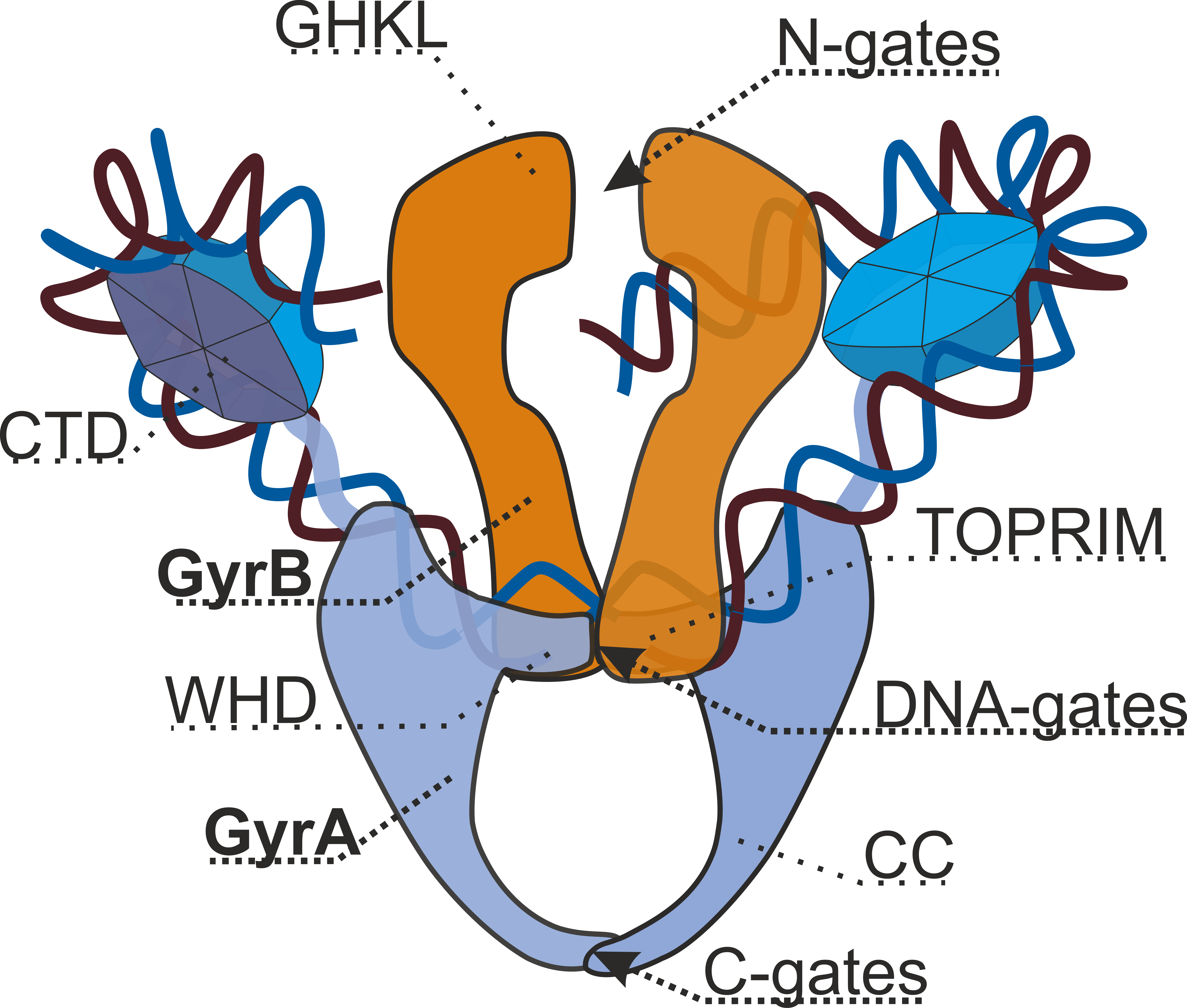
DNA Gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. It is the only known enzyme to actively contribute negative supercoiling to DNA, while it also is capable of relaxing positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in bacteria, whose single circular DNA is cut by DNA gyrase and the two ends are then twisted around each other to form supercoils. Gyrase is also found in eukaryotic plastids: it has been found in the apicoplast of the malarial parasite ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and in chloroplasts of several plants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aminocoumarin
Aminocoumarin is a class of antibiotics that act by an inhibition of the DNA gyrase enzyme involved in the cell division in bacteria. They are derived from ''Streptomyces '' species, whose best-known representative – ''Streptomyces coelicolor'' – was completely sequenced in 2002. The aminocoumarin antibiotics include: * Novobiocin, Albamycin (Pharmacia And Upjohn) * Coumermycin * Clorobiocin Structure The core of aminocoumarin antibiotics is made up of a 3-amino-4,7-dihydroxycumarin ring, which is linked, e.g., with a sugar in 7-Position and a benzoic acid derivative in 3-Position. Clorobiocin is a natural antibiotic isolated from several ''Streptomyces'' strains and differs from novobiocin in that the methyl group at the 8 position in the coumarin ring of novobiocin is replaced by a chlorine atom, and the carbamoyl at the 3' position of the noviose sugar is substituted by a 5-methyl-2-pyrrolylcarbonyl group. Mechanism of action The aminocoumarin antibiotics are known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Staphylococcus Epidermidis
''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. It is part of the human flora, normal human microbiota, typically the skin flora, skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although ''S. epidermidis'' is not usually Pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally Hospital-acquired infection, hospital-acquired. ''S. epidermidis'' is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, ''S. epidermidis'' is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory. Some strains of ''S. epidermidis'' are highly salt tolerant and commonly found in marine environments. S.I. Paul et al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The name was coined in 1880 by Scottish surgeon and bacteriologist Alexander Ogston (1844–1929), following the pattern established five years earlier with the naming of '' Streptococcus''. It combines the prefix "staphylo-" (from ), and suffixed by the (from ). Staphylococcus was one of the leading infections in hospitals and many strains of this bacterium have become antibiotic resistant. Despite strong attempts to get rid of them, staphylococcus bacteria stay present in hospitals, where they can infect people who are most at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Streptomyces Niveus
''Streptomyces niveus'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from soil in the United States. ''Streptomyces niveus'' produces the aminocoumarin antibiotic novobiocin Novobiocin, also known as albamycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete ''Streptomyces niveus'', which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for ''S. spheroides'' a member of the class Actinomycet ... and the compounds nivetetracyclate A and nivetetracyclate B. See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References Further reading * * * * * * * External linksType strain of ''Streptomyces niveus'' at Bac''Dive'' – the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase niveus Bacteria described in 1956 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
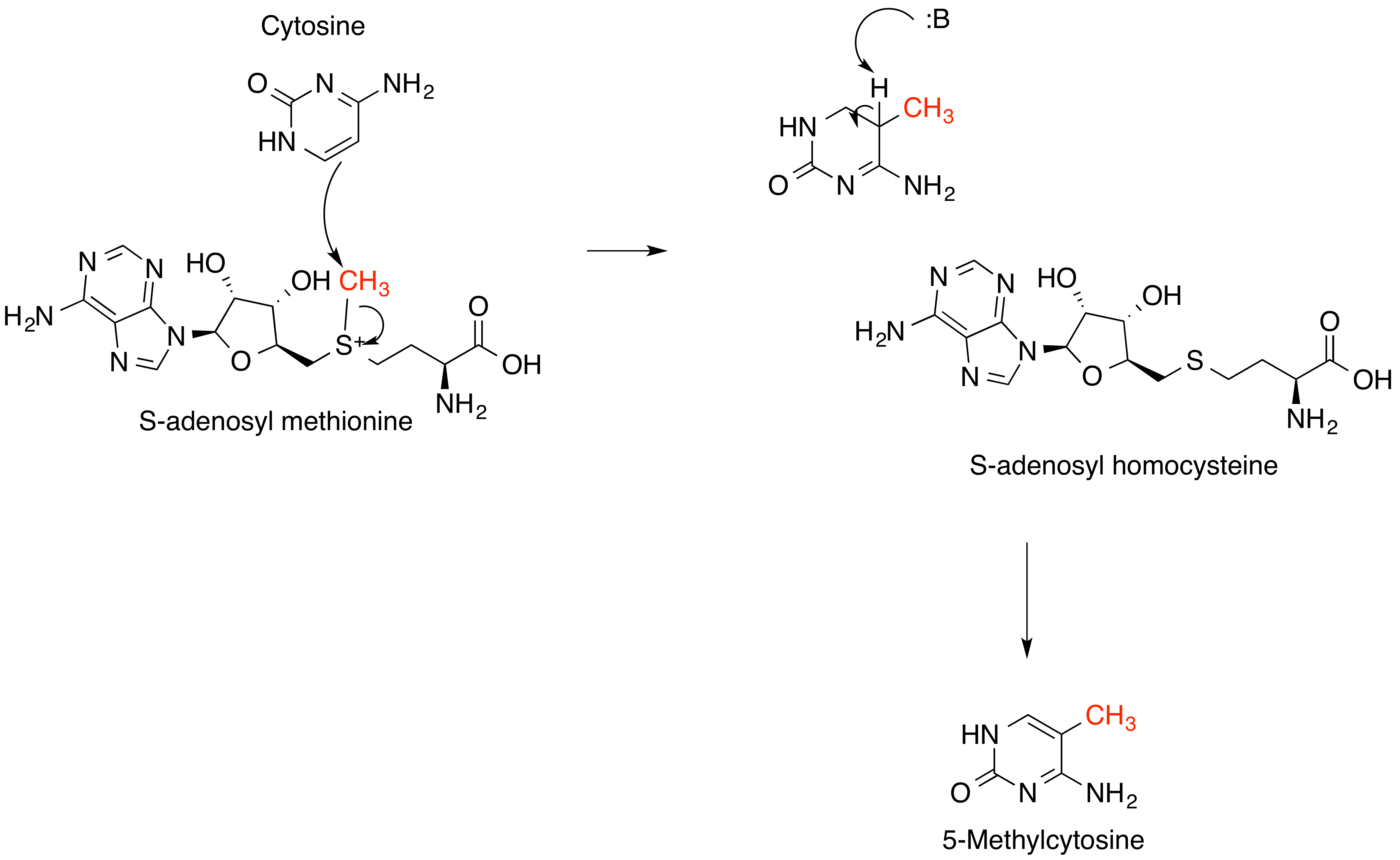
S-adenosyl Methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In cellular metabolism, NAD is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: NAD is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; with H+, this reaction forms NADH, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carbamoyl
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula . It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate . The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.J. B. Bossa, P. Theulé, F. Duvernay, F. Borget and T. Chiavassa (2008): "Carbamic acid and carbamate formation in NH3:CO2 ices – UV irradiation versus thermal processes". ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', volume 492, issue 3, pages 719-724. Carbamic acid could be seen as both an amine and carboxylic acid, and therefore an amino acid;R. K. Khanna and M. H. Moore (1999): "Carbamic acid: molecular structure and IR spectra". ''Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |