|
Northern Celestial Hemisphere
The northern celestial hemisphere, also called the Northern Sky, is the Northern Hemisphere, northern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies north of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere diurnal motion, appears to rotate westward around a celestial pole, polar axis due to Earth's rotation. At any given time, the entire Northern Sky is visible from the geographic North Pole, while less of the hemisphere is visible the latitude, further south the observer is located. The southern counterpart is the southern celestial hemisphere. Astronomy In the context of astronomical discussions or writing about celestial cartography, the northern celestial hemisphere may be referred to as the Northern Hemisphere. For star chart, celestial mapping, astronomers may conceive the sky like the inside of a sphere divided into two halves by the celestial equator. The Northern Sky or Northern Hemisphere is therefore the half of the celestial sphere that is north of the celestial equato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar System as Earth's North Pole. Due to Earth's axial tilt of 23.439281°, there is a seasonal variation in the lengths of the day and night. There is also a seasonal variation in temperatures, which lags the variation in day and night. Conventionally, winter in the Northern Hemisphere is taken as the period from the December solstice (typically December 21 UTC) to the March equinox (typically March 20 UTC), while summer is taken as the period from the June solstice through to the September equinox (typically on 23 September UTC). The dates vary each year due to the difference between the calendar year and the astronomical year. Within the Northern Hemisphere, oceanic currents can change the weather patterns that affect many factors within the north coast. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canes Venatici
Canes Venatici ( ) is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation. Cor Caroli is the constellation's brightest star, with an apparent magnitude of 2.9. La Superba (Y CVn) is one of the reddest naked-eye stars and one of the brightest carbon stars. The Whirlpool Galaxy is a spiral galaxy tilted face-on to observers on Earth, and was the first galaxy whose spiral nature was discerned. In addition, quasar TON 618 is one of the most massive black holes with the mass of 66 billion solar masses. History The stars of Canes Venatici are not bright. In classical times, they were listed by Ptolemy as unfigured stars below the constellation Ursa Major in his star catalogu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer (constellation)
Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as one. Cancer is a medium-size constellation with an area of 506 square degrees and its stars are rather faint, its brightest star Beta Cancri having an apparent magnitude of 3.5. It contains ten stars with known exoplanet, planets, including 55 Cancri, which has five: one Super-Earth, super-Earth and four gas giants, one of which is in the habitable zone and as such has expected temperatures similar to Earth. At the (angular) heart of this sector of our celestial sphere is Beehive Cluster, Praesepe (Messier 44), one of the closest open clusters to Earth and a popular target for amateur astronomers. Characteristics Cancer is a medium-sized constellation that is bordered by Gemini (constellation), Gemini to the west, Lynx (constellation), Lynx to the north, Leo Minor to the northeast, Leo (constellation), Leo to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camelopardalis
Camelopardalis is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius. Some older astronomy books give Camelopardalus or Camelopardus as alternative forms of the name, but the version recognized by the International Astronomical Union matches the genitive form, seen suffixed to most of its brighter stars. Etymology First attested in English in 1785, the word ''camelopardalis'' comes from Latin, and it is the romanization of the Greek "καμηλοπάρδαλις" meaning "giraffe", from "κάμηλος" (''kamēlos''), "camel" + "πάρδαλις" (''pardalis''), "spotted", because it has a long neck like a camel and spots like a leopard. Features Stars Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. In fact, it only contains four stars brighter than magnitude 5.0. * α Cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from , which comes from 'herder, herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, 'ox-driver'; from ''boûs'' 'cow'). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the List of brightest stars, fourth-brightest star in the night sky, the orange giant Arcturus. Epsilon Boötis, or Izar, is a colourful multiple star popular with amateur astronomers. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye. History and mythology In ancient Babylon, the stars of Boötes were known as SHU.PA. They were apparently depicted as the god Enlil, who was the leader of the Babylonian religion, Babyloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
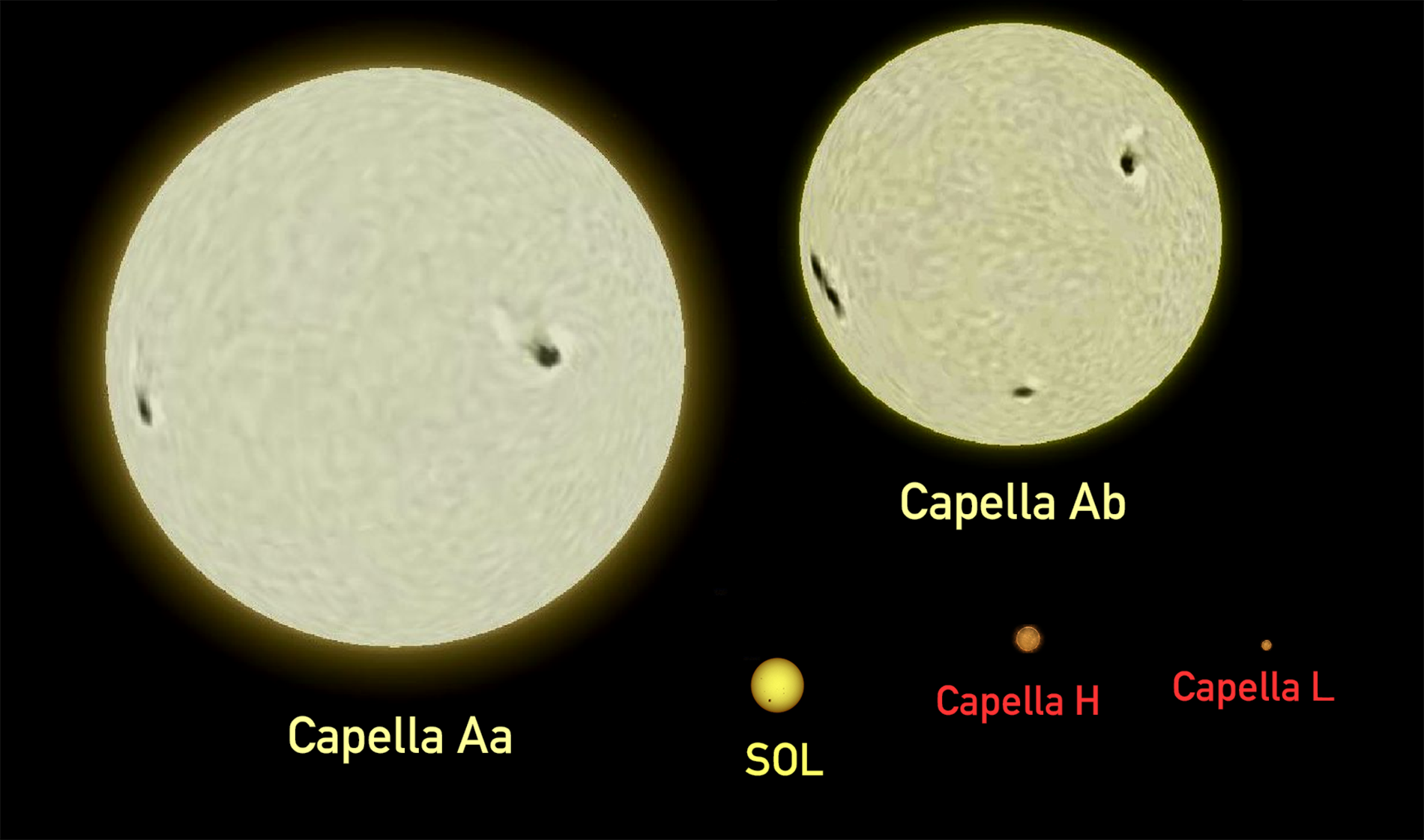
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the List of constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius of Athens, Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as −34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra (constellation), Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella (star), Capella, is an unusual Star system, multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces (constellation), Pisces to the west and Taurus (constellation), Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for sheep, ram. Its traditional astrological symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation ranking 39th in overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere). Aries has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquila (constellation)
Aquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greco-Roman mythology, Greek-Roman mythology. Its brightest star, Altair, is one vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism (astronomy), asterism. The constellation is best seen in the northern summer, as it is located along the Milky Way. Because of this location, many clusters and planetary nebula, nebulae are found within its borders, but they are dim and galaxies are few. History Aquila was one of the 48 constellations described by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It had been earlier mentioned by Eudoxus of Cnidus, Eudoxus in the fourth century BC and Aratus in the third century BC. It is now one of the 88 constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. The constellation was also known as ''Vultur volans'' (the flying vulture) to the Ancient Rome, Romans, not to be confused with ''Vultur cadens'' which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is an celestial equator, equatorial constellation of the zodiac, between Capricornus and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-carrier" or "cup-carrier", and its old astronomical symbol is (♒︎), a representation of water. Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the Sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea (astronomy), Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus (constellation), Eridanus the river. At apparent magnitude 2.9, Beta Aquarii is the brightest star in the constellation. History and mythology Aquarius is identified as "The Great One" in the Babylonian star catalogues and represents the god Ea (god), Ea himself, who is commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae), is a binary star that has also been counted as a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellations
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traverse). The origins of the zodiac re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |