|
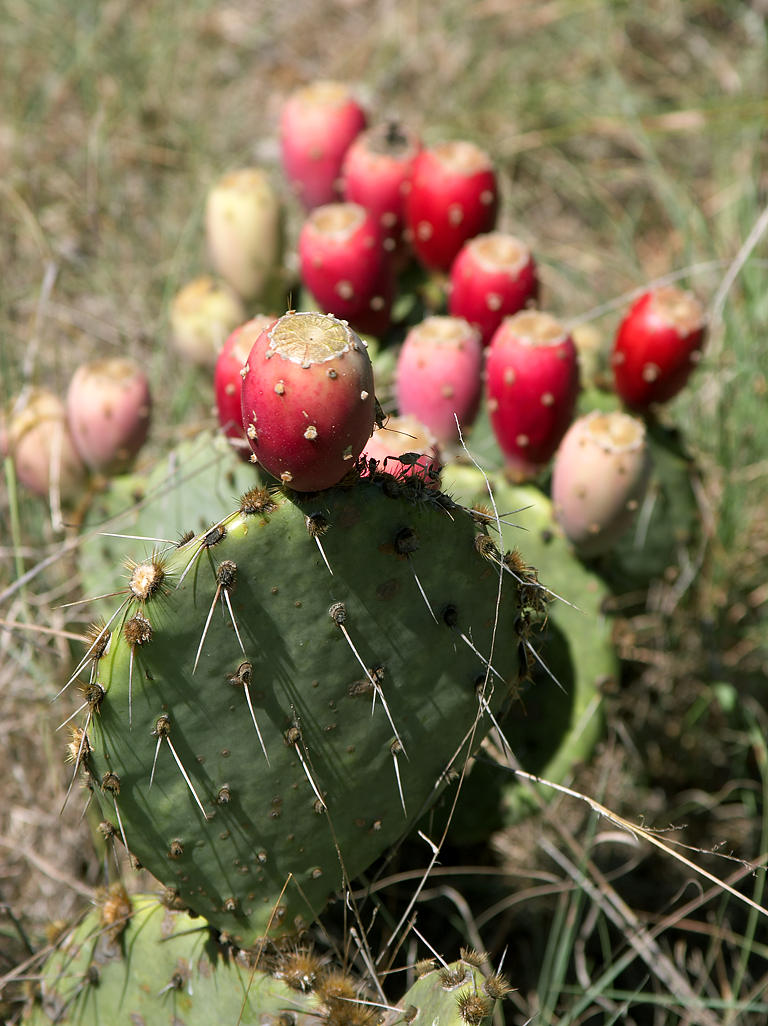
Nopales
''Nopal'' (plural ''nopales'') is a common name in Spanish for ''Opuntia'' cacti (commonly referred to in English as prickly pear or tender cactus), as well as for its pads. The name ''nopal'' derives from the Nahuatl word for the pads of the plant. Description There are about 114 known species in Mexico, where it is a common ingredient in numerous Mexican cuisine dishes. The ''nopal'' pads can be eaten raw or cooked, used in marmalades, soups, stews and salads, as well as being used for traditional medicine or as fodder for animals. Farmed ''nopales'' are most often of the species ''Opuntia ficus-indica'' or '' Opuntia matudae'' although the pads of almost all ''Opuntia'' species are edible. The other edible part of the ''nopal'' cactus is the fruit, called in Spanish and "prickly pear" in English. Culinary use ''Nopales'' are generally sold fresh in Mexico, cleaned of spines, and sliced to the customer's wishes on the spot. They can also be found canned or bottled as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opuntia
''Opuntia'', commonly called the prickly pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae, many known for their flavorful fruit and showy flowers. Cacti are native to the Americas, and are well adapted to arid climates; however, they are still vulnerable to alterations in precipitation and temperature driven by climate change. The plant has been introduced to parts of Australia, southern Europe, the Middle East, and northern Africa. ''Prickly pear'' alone is more commonly used to refer exclusively to the fruit, but may also be used for the plant itself; in addition, other names given to the plant and its specific parts include ''tuna'' (fruit), ''sabra'', ''sabbar'', '' nopal'' (pads, plural ''nopales'') from the Nahuatl word , nostle (fruit) from the Nahuatl word , and paddle cactus. The genus is named for the Ancient Greek city of Opus. The fruit and leaves are edible. The most common culinary species is the "Barbary fig" ('' Opuntia ficus-indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Cuisine
Mexican cuisine consists of the cuisines and associated traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican Cuisine, Mesoamerican cuisine. Mexican cuisine's ingredients and methods arise from the area's first agricultural communities, such as those of the Olmecs, Olmec and Maya civilization, Maya, who domesticated maize, created the standard process of nixtamalization, and established foodways. Successive waves of other Mesoamerican groups brought with them their cooking methods. These included the Teotihuacanos, Toltec, Huastec civilization, Huastec, Zapotec civilization, Zapotec, Mixtec, Otomi people, Otomi, Tarascan state, Purépecha, Totonac, Mazatec, Mazahua people, Mazahua, and Nahuas, Nahua. With the Mexica formation of the multi-ethnic Triple Alliance (Aztec Empire), culinary foodways became infused (Aztec cuisine). Today's food staples native to the land include corn (maize), turkey, beans, squash, amaranth, Chia seed, chia, avocados, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opuntia Ficus-indica
''Opuntia ficus-indica'', the Indian fig opuntia, fig opuntia, or prickly pear, is a species of cactus that has long been a domesticated crop plant grown in agricultural economies throughout Arid climate, arid and Semi-arid climate, semiarid parts of the world. ''O. ficus-indica'' is the most widespread and most commercially important cactus. It is grown primarily as a fruit crop, and also for the vegetable nopales and other uses. Cacti are good crops for dry areas because they efficiently convert water into biomass. ''O. ficus-indica'' is the most widespread of the long-domesticated cactuses. ''Opuntia'' species hybrid (biology), hybridize easily, but the wild origin of ''O. ficus-indica'' is likely to have been in central Mexico, where its closest genetic relatives are found. Names Most culinary references to the "prickly pear" refer to this species. The Spanish name ''tuna'' is also used for the fruit of this cactus and for ''Opuntia'' in general; according to Alexander von H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
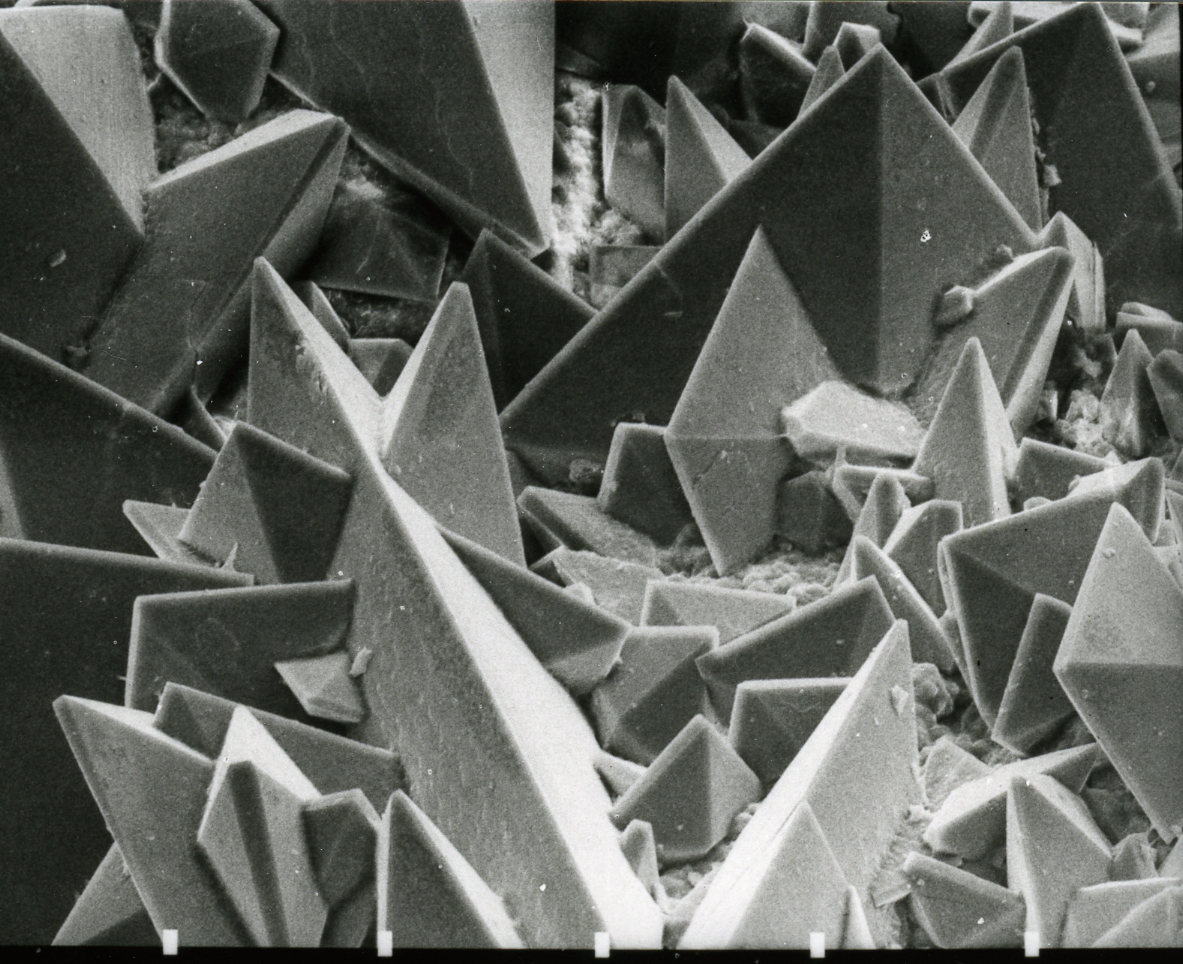
Calcium Oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula or . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate , which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries. Occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queso Panela
Queso panela (panela cheese) is a fresh cheese common in Mexico made from pasteurized cow's milk. It is also known as ''queso canasta'' or ''queso de la canasta''. It is derived from the Greek word for basket cheese. The cheese also has similarities to the Indian cheese ''paneer''. Like related cheeses, panela cheese is often used as a garnish and as a filling in its crumbled form. It may also be fried, since it holds its shape and does not melt very easily. Although it becomes softer when heated, it generally retains its shape instead of melting into a gooey texture like some other types of cheese. It is used in many Mexican foods, such as enchiladas, tacos, '' nopal'' salads or quesadillas. Regional differences as well as different degrees of maturation yield variation within the panela family. One remarkable regional variety is that of the evergreen mountain town Tapalpa.Skinner, Thalassa, and Laurel Miller. "Chapter 8: The Americas." ''Cheese For Dummies''. Toronto: J. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Value
In the U.S. and Canada, the Reference Daily Intake (RDI) is used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products to indicate the daily intake level of a nutrient that is considered to be sufficient to meet the requirements of 97–98% of healthy individuals in every demographic in the United States. While developed for the US population, it has been adopted by Canada. The RDI is used to determine the Daily Value (DV) of foods, which is printed on nutrition facts labels (as %DV) in the United States and Canada, and is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and by Health Canada, respectively. The labels "high", "rich in", or "excellent source of" may be used for a food if it contains 20% or more of the DV. The labels "good source", "contains", or "provides" may be used on a food if it contains between 10% and 20% of the DV, and "low source" applies if the %DV is 5% or lower. The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) were a set of nutrition recommenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietary Mineral
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element. Some "minerals" are essential for life, but most are not. ''Minerals'' are one of the four groups of essential nutrients; the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. The five major minerals in the human body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and magnesium. The remaining minerals are called " trace elements". The generally accepted trace elements are iron, chlorine, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, iodine, selenium, and bromine; there is some evidence that there may be more. The four organogenic elements, namely carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen ( CHON), that comprise roughly 96% of the human body by weight, are usually not considered as minerals (nutrient). In fact, in nutrition, the term "mineral" refers more generally to all the other functional and structural elements found in living organisms. Plants obtain minerals from soil. Animals ingest plants, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |