|
Node (circuits)
In electrical engineering, a node is any region or joining point on a circuit between two circuit elements. In circuit diagrams, connections are ideal wires with zero resistance. Whether "node" refers to a single point of junction or an entire equipotential region varies by the source. "Node" is often used, especially in mesh analysis, to mean a principal node, which is distinct from the usage defined above. A principal node is a point in a circuit diagram where three or more connections meet. Principal nodes are important points of consideration in applying Kirchhoff's circuit laws, because conservation of current means current can split or combine at these points. When clarification is needed, a region connecting only two circuit elements is referred to as a simple node, where there is no branching of current, while a point connecting three or more elements is a ''principal node''. The full definition uses in this article encompasses both principal and simple nodes. Deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodes2
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex). Node may refer to: In mathematics *Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph *Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet. *Node (autonomous system), behaviour for an ordinary differential equation near a critical point *Singular point of an algebraic variety, a type of singular point of a curve In science and engineering Spherical geometry * node, the points where a great circle crosses a plane of reference, or the equator of a sphere Astronomy *Orbital node, the points where an orbit crosses a plane of reference ** Lunar node, where the orbits of the Sun and Moon intersect ** Longitude of the ascending node, how orbital nodes are parameterized Biology *Lymph node, an immune system organ used to store white blood cells *Node of Ranvier, periodic gaps in the insulating myelin sheaths of myelinated axons *Sinoatrial node and atrioventricular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential
Electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as electric potential energy per unit of electric charge. More precisely, electric potential is the amount of work (physics), work needed to move a test charge from a reference point to a specific point in a static electric field. The test charge used is small enough that disturbance to the field is unnoticeable, and its motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is Earth (electricity), earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar (physics), scalar quantity denoted by or occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltier Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect (temperature differences cause electromotive forces), the Peltier effect (thermocouples create temperature differences), and the Thomson effect (the Seebeck coefficient varies with temperature). The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AC Power Plugs And Sockets
AC power plugs and sockets connect devices to mains electricity to supply them with electrical power. A plug is the connector attached to an electrically operated device, often via a cable. A socket (also known as a receptacle or outlet) is fixed in place, often on the internal walls of buildings, and is connected to an Alternating current, AC electrical circuit. Inserting ("plugging in") the plug into the socket allows the device to draw power from this circuit. Plugs and wall-mounted sockets for portable appliances became available in the 1880s, to replace connections to light sockets. A proliferation of types were subsequently developed for both convenience and protection from electrical injury. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and electric current, current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world, and many obsolete socket types are still found in older buildings. Coordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth. Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons. Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground to protect users from electrical shock hazards. If internal insulation fails, dangerous voltages may appear on the exposed conductive parts. Connecting exposed conductive parts to a "ground" wire which provides a low-impedance path for current to flow back to the incoming neutral (which is also connected to ground, close to the point of entry) will allow circuit breakers (or RCDs) to interrupt power supply in the event of a fault. In electric power distribution systems, a protective earth (PE) conductor is an essential part of the safety provided by the earthing system. Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Wire
In electrical engineering, ground (or earth) and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The neutral conductor carries alternating current (in tandem with one or more ''phase '' conductors) during normal operation of the circuit. By contrast, a ground conductor is not intended to carry current for normal operation, but instead connects exposed conductive parts (such as equipment enclosures or conduits enclosing wiring) to Earth (the ground), and only carries significant current in the event of a circuit fault that would otherwise energize exposed conductive parts and present a shock hazard. In such case the intention is for the fault current to be large enough to trigger a circuit protective device that will either de-energize the circuit, or provide a warning. To limit the effects of leakage current from higher-voltage systems, the neutral conductor is often connected to earth ground at the point of supply. Significant voltage unin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
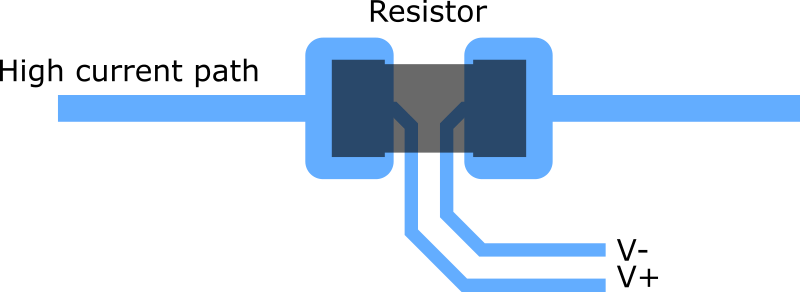
Four-terminal Sensing
In electrical engineering, four-terminal sensing (4T sensing), 4-wire sensing, or 4-point probes method is an electrical impedance measuring technique that uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes to make more accurate measurements than the simpler and more usual two-terminal (2T) sensing. Four-terminal sensing is used in some ohmmeters and impedance analyzers, and in wiring for strain gauges and resistance thermometers. Four-point probes are also used to measure sheet resistance of thin films (particularly semiconductor thin films). Separation of current and voltage electrodes eliminates the lead and contact resistance from the measurement. This is an advantage for precise measurement of low resistance values. For example, an LCR bridge instruction manual recommends the four-terminal technique for accurate measurement of resistance below 100 ohms.Manual for the Racal-Dana Databridge 9343M: "If the resistance value is low, less than 100 ohms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Drop
In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirable because some of the energy supplied is dissipated. The voltage drop across the load is proportional to the power available to be converted in that load to some other useful form of energy. For example, an electric space heater may have a resistance of 10 ohms, and the wires that supply it may have a resistance of 0.2 ohms, about 2% of the total circuit resistance. This means that approximately 2% of the supplied voltage is lost in the wire itself. An excessive voltage drop may result in the unsatisfactory performance of the space heater and the overheating of the wires and connections. National and local electrical codes may set guidelines for the maximum voltage drop allowed in electrical wiring to ensure efficiency of dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |