|
Node-to-node Data Transfer
In telecommunications, node-to-node data transfer is the movement of data from one node (networking), node of a Telecommunications network, network to the next. In the OSI model it is handled by the lowest two layers, the data link layer and the physical layer. In most communication systems, the transmitting point applies source coding, followed by channel coding, and lastly, line coding. This produces the baseband signal. The presence of filters may perform pulse shaping. Some systems then use modulation to multiplex many baseband signals into a broadband signal. The receiver un-does these transformations in reverse order: demodulation, trellis decoding, error detection and correction, decompression. Some communication systems omit one or more of these steps, or use techniques that combine several of these steps together. For example, a Morse code transmitter combines source coding, channel coding, and line coding into one step, typically followed by an amplitude modulation step. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
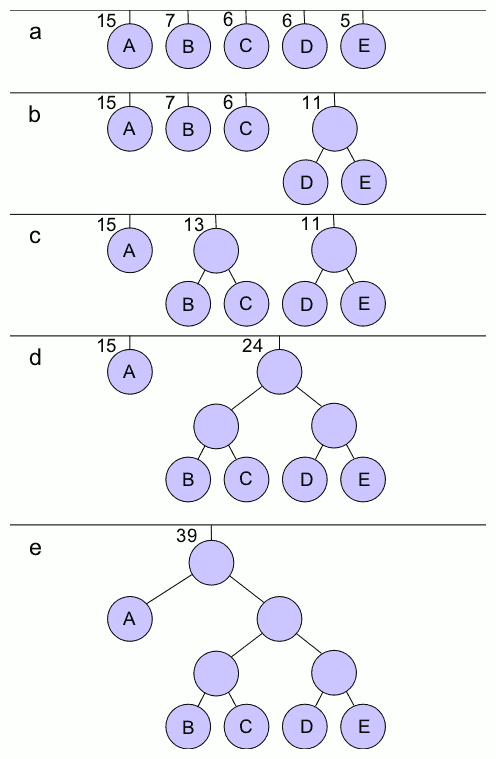
Huffman Coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Doctor of Science, Sc.D. student at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear time, linear to the number of input weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal (electronics)
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete space, discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuity (mathematics), continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
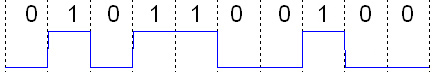
Line Code
In telecommunications, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmission (telecommunications), transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are Unipolar encoding, unipolar, Polar encoding, polar, Bipolar encoding, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamming Code
In computer science and telecommunications, Hamming codes are a family of linear error-correcting codes. Hamming codes can detect one-bit and two-bit errors, or correct one-bit errors without detection of uncorrected errors. By contrast, the simple parity code cannot correct errors, and can detect only an odd number of bits in error. Hamming codes are perfect codes, that is, they achieve the highest possible rate for codes with their block length and minimum distance of three. Richard W. Hamming invented Hamming codes in 1950 as a way of automatically correcting errors introduced by punched card readers. In his original paper, Hamming elaborated his general idea, but specifically focused on the Hamming(7,4) code which adds three parity bits to four bits of data. In mathematical terms, Hamming codes are a class of binary linear code. For each integer there is a code-word with block length and message length . Hence the rate of Hamming codes is , which is the highest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity Check
A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code. Parity bits are a simple form of error detecting code. Parity bits are generally applied to the smallest units of a communication protocol, typically 8-bit octets (bytes), although they can also be applied separately to an entire message string of bits. The parity bit ensures that the total number of 1-bits in the string is even or odd. Accordingly, there are two variants of parity bits: even parity bit and odd parity bit. In the case of even parity, for a given set of bits, the bits whose value is 1 are counted. If that count is odd, the parity bit value is set to 1, making the total count of occurrences of 1s in the whole set (including the parity bit) an even number. If the count of 1s in a given set of bits is already even, the parity bit's value is 0. In the case of odd parity, the coding is reversed. For a given set of bits, if the count of bits with a value of 1 is even, the parity bit value is se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Digit
A numerical digit (often shortened to just digit) or numeral is a single symbol used alone (such as "1"), or in combinations (such as "15"), to represent numbers in positional notation, such as the common base 10. The name "digit" originates from the Latin ''digiti'' meaning fingers. For any numeral system with an integer base, the number of different digits required is the absolute value of the base. For example, decimal (base 10) requires ten digits (0 to 9), and binary (base 2) requires only two digits (0 and 1). Bases greater than 10 require more than 10 digits, for instance hexadecimal (base 16) requires 16 digits (usually 0 to 9 and A to F). Overview In a basic digital system, a numeral is a sequence of digits, which may be of arbitrary length. Each position in the sequence has a place value, and each digit has a value. The value of the numeral is computed by multiplying each digit in the sequence by its place value, and summing the results. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error-detecting Code
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Many communication channels are subject to channel noise, and thus errors may be introduced during transmission from the source to a receiver. Error detection techniques allow detecting such errors, while error correction enables reconstruction of the original data in many cases. Definitions ''Error detection'' is the detection of errors caused by noise or other impairments during transmission from the transmitter to the receiver. ''Error correction'' is the detection of errors and reconstruction of the original, error-free data. History In classical antiquity, copyists of the Hebrew Bible were paid for their work according to the number of stichs (lines of verse). As the prose books of the Bible were hardly ever w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal (signal Processing)
In the context of digital signal processing (DSP), a digital signal is a discrete time, quantized amplitude signal. In other words, it is a sampled signal consisting of samples that take on values from a discrete set (a countable set that can be mapped one-to-one to a subset of integers). If that discrete set is finite, the discrete values can be represented with digital words of a finite width. Most commonly, these discrete values are represented as fixed-point words (either proportional to the waveform values or companded) or floating-point words. The process of analog-to-digital conversion produces a digital signal. The conversion process can be thought of as occurring in two steps: # sampling, which produces a continuous-valued discrete-time signal, and # quantization, which replaces each sample value with an approximation selected from a given discrete set (for example, by truncating or rounding). An analog signal can be reconstructed after conversion to digital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |