|
Nociceptin Receptor
The nociceptin opioid peptide receptor (NOP), also known as the nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) receptor or kappa-type 3 opioid receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPRL1'' (opioid receptor-like 1) gene. The nociceptin receptor is a member of the opioid subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors whose natural Ligand (biochemistry), ligand is the 17 amino acid neuropeptide known as nociceptin, nociceptin (N/OFQ). This receptor is involved in the regulation of numerous brain activities, particularly instinctive and emotional behaviors. Antagonists targeting NOP are under investigation for their role as treatments for depression and Parkinson's disease, whereas NOP agonists have been shown to act as powerful, non-addictive painkillers in non-human primates. Although NOP shares high sequence identity (~60%) with the ‘classical’ opioid receptors Μ-opioid receptor, μ-OP (MOP), Κ-opioid receptor, κ-OP (KOP), and Δ-opioid receptor, δ-OP (DOP), it possesses litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 (MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 (MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family was termed "mitogen-activated". With the discovery of other members, even from distant organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. Some neurotransmitters are also stored in large dense core vesicles. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds to. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include Glutamate (neurotransmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response to a present threat, whereas anxiety is the anticipation of a future one. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, Somatic anxiety, somatic complaints, and Rumination (psychology), rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight-or-flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of a future t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Motility
Gastrointestinal physiology is the branch of Human body, human physiology that addresses the physical function of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The function of the GI tract is to process ingested food by mechanical and chemical means, extract nutrients and excrete waste products. The GI tract is composed of the alimentary canal, that runs from the mouth to the anus, as well as the associated glands, chemicals, hormones, and enzymes that assist in digestion. The major processes that occur in the GI tract are: motility, secretion, regulation, digestion and circulation. The proper function and coordination of these processes are vital for maintaining good health by providing for the effective digestion and uptake of nutrients. Motility The gastrointestinal tract generates motility using smooth muscle subunits linked by gap junctions. These subunits fire spontaneously in either a tonic or a phasic fashion. Tonic contractions are those contractions tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotor Activity
Locomotor activity is a measure of animal behavior which is employed in scientific research. Hyperlocomotion, also known as locomotor hyperactivity, hyperactivity, or increased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity (locomotion) is increased. It is induced by certain drugs like psychostimulants and NMDA receptor antagonists and is reversed by certain other drugs like antipsychotics and certain antidepressants. Stimulation of locomotor activity is thought to be mediated by increased signaling in the nucleus accumbens, a major brain area involved in behavioral activation and motivated behavior. Hypolocomotion, also known as locomotor hypoactivity, hypoactivity, and decreased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity is decreased. It is a characteristic effect of many sedative agents and general anesthetics. Antipsychotics, which are dopamine receptor antagonists, and many serotonerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nociception
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the Somatosensory system, sensory nervous system's process of encoding Noxious stimulus, noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal to trigger an appropriate defensive response. In nociception, intense chemical (e.g., capsaicin present in chili pepper or cayenne pepper), mechanical (e.g., cutting, crushing), or thermal (heat and cold) stimulation of sensory neurons called nociceptors produces a signal that travels along a chain of nerve fibers to the brain. Nociception triggers a variety of physiological and behavioral responses to protect the organism against an aggression, and usually results in a subjective experience, or perception, of pain in Sentience, sentient beings. Detection of noxious stimuli Potentially damaging mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli are detecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
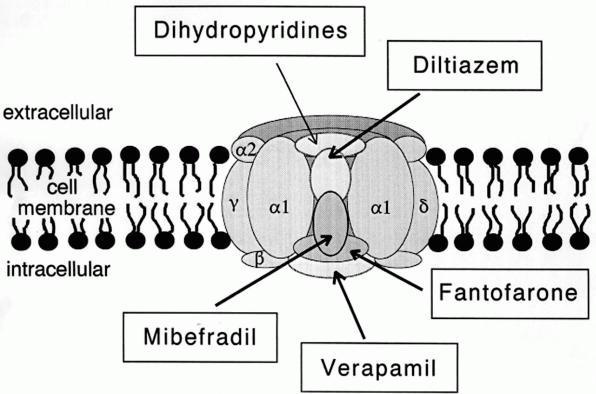
Calcium Channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, which are a type of calcium channel regulated by changes in membrane potential. Some calcium channels are regulated by the binding of a ligand.Striggow F, Ehrlich BE (August 1996). "Ligand-gated calcium channels inside and out". ''Current Opinion in Cell Biology''. 8 (4): 490–495. Doi (identifier), doi:doi:10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80025-1, 10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80025-1. PMID (identifier), PMID]8791458 Other calcium channels can also be regulated by both voltage and ligands to provide precise control over ion flow. Some cation channels allow calcium as well as other cations to pass through the membrane. Calcium channels can participate in the creation of Action potential, action potentials across cell membranes. Calcium channels can also be used to release calcium ions as Second messenger system, second messengers within the cell, affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |