|
Nitronium Tetrafluoroborate
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with formula NO2BF4. It is a salt of nitronium cation and tetrafluoroborate anion. It is a colorless crystalline solid, which reacts with water to form the corrosive acids HF and HNO3. As such, it must be handled under water-free conditions. It is sparsely soluble in many organic solvents. Preparation Nitronium tetrafluoroborate can be prepared by adding a mixture of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and boron trifluoride to a nitromethane solution of nitric acid or dinitrogen pentoxide. Applications Nitronium tetrafluoroborate is used in organic synthesis as an electrophilic nitrating agent and a mild oxidant An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "Electron acceptor, accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electr .... References Tetrafluoroborates Nitronium compounds {{ino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosonium Tetrafluoroborate
Nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate, also called nitrosyl tetrafluoroborate, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NOBF4. This colourless solid is used in organic synthesis as a nitrosating agent, diazotizing agent and a mild oxidant. NOBF4 is the nitrosonium salt of fluoroboric acid, and is composed of a nitrosonium cation, Osup>+, and a tetrafluoroborate anion, F4sup>−. Reactions The dominant property of NOBF4 is the oxidizing power and electrophilic character of the nitrosonium cation. It forms colored charge transfer complexes with hexamethylbenzene and with 18-crown-6. The latter, a deep yellow species, provides a means to dissolve NOBF4 in dichloromethane. Nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate may be used to prepare metal salts of the type II(CH3CN)''x''F4sub>2 (M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu). The nitrosonium cation acts as the oxidizer, itself being reduced to nitric oxide gas: : With ferrocene the ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate is formed. In its infrared spectrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitronium Ion
The nitronium ion, , is a cation. It is an onium ion because its nitrogen atom has +1 charge, similar to ammonium ion . It is created by the removal of an electron from the paramagnetic nitrogen dioxide molecule , or the protonation of nitric acid (with removal of ). It is stable enough to exist in normal conditions, but it is generally reactive and used extensively as an electrophile in the nitration of other substances. The ion is generated '' in situ'' for this purpose by mixing concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid according to the equilibrium: : Structure The nitronium ion is isoelectronic with carbon dioxide and has the same linear structure and bond angle of 180°. For this reason it has a similar vibrational spectrum to carbon dioxide. Historically, the nitronium ion was detected by Raman spectroscopy, because its symmetric stretch is Raman-active but infrared-inactive. The Raman-active symmetrical stretch was first used to identify the ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrafluoroborate
Tetrafluoroborate is the anion . This tetrahedral species is isoelectronic with tetrafluoroberyllate (), tetrafluoromethane (CF4), and tetrafluoroammonium () and is valence isoelectronic with many stable and important species including the perchlorate anion, , which is used in similar ways in the laboratory. It arises by the reaction of fluoride salts with the Lewis acid BF3, treatment of tetrafluoroboric acid with base, or by treatment of boric acid with hydrofluoric acid. As an anion in inorganic and organic chemistry The popularization of has led to decreased use of in the laboratory as a weakly coordinating anion. With organic compounds, especially amine derivatives, forms potentially explosive derivatives. Disadvantages to include its slight sensitivity to hydrolysis and decomposition via loss of a fluoride ligand, whereas does not suffer from these problems. Safety considerations, however, overshadow this inconvenience. With a formula weight of 86.8, BF is also conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
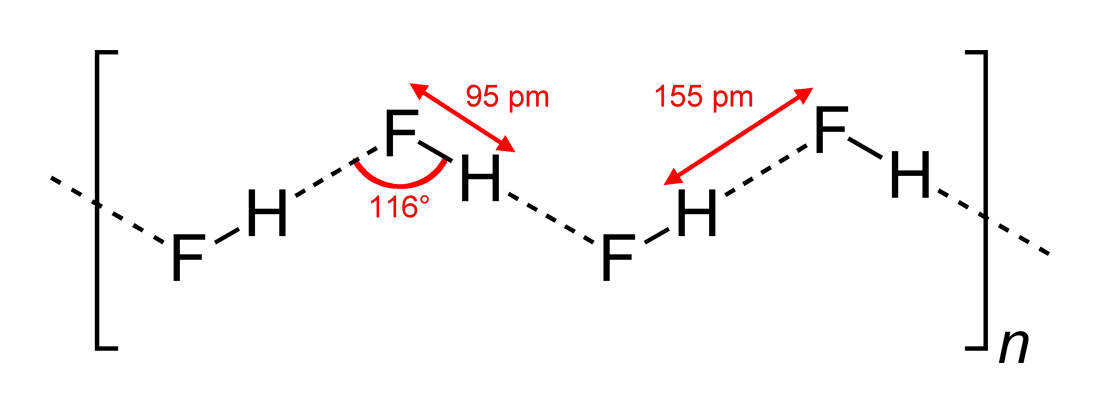
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula . This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds. Structure and bonding The geometry of a molecule of is Trigonal planar molecular geometry, trigonal planar. Its D3h symmetry group, symmetry conforms with the prediction of VSEPR theory. The molecule has no dipole moment by virtue of its high symmetry. The molecule is isoelectronic with the carbonate anion, . is commonly referred to as "electron deficiency, electron deficient," a description that is reinforced by its exothermic reactivity toward Lewis bases. In the boron trihalides, , the length of the B–X bonds (1.30 Å) is shorter than would be expected for single bonds, and this shortness may indicate stronger B–X pi bond, π-bonding in the fluoride. A facile explanation invokes the symmetry-allowed overlap of a p orbital on the boron atom with the in-phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitromethane
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft. Preparation Nitromethane is produced industrially by combining propane and nitric acid in the gas phase at . This exothermic reaction produces the four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane. The reaction involves free radicals, including the alkoxyl radicals of the type , whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide (also known as nitrogen pentoxide or nitric anhydride) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is one of the binary nitrogen oxides, a family of compounds that contain only nitrogen and oxygen. It exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature, yielding a colorless gas.Connell, Peter Steele. (1979) The Photochemistry of Dinitrogen Pentoxide'. Ph. D. thesis, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Dinitrogen pentoxide is an unstable and potentially dangerous oxidizer that once was used as a reagent when dissolved in chloroform for nitrations but has largely been superseded by nitronium tetrafluoroborate (). is a rare example of a compound that adopts two structures depending on the conditions. The solid is a salt, nitronium nitrate, consisting of separate nitronium cations and nitrate anions ; but in the gas phase and under some other conditions it is a covalently-bound molecule. History was first reported by the Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, Enantioselective synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject. Total synthesis A total synthesis refers to the complete chemical synthesis of molecules from simple, Precursor (chemistry), natural precursors. Total synthesis is accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a Linear synthesis, ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed sequentially until the molecule is com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |