|
Nitrogen Balance
In human physiology, nitrogen balance is the net difference between bodily nitrogen intake (ingestion) and loss (excretion). It can be represented as the following: \mbox = - Nitrogen is a fundamental chemical component of amino acids, the molecular building blocks of protein. As such, nitrogen balance may be used as an index of protein metabolism. When more nitrogen is gained than lost by an individual, they are considered to have a positive nitrogen balance and be in a state of overall protein anabolism. In contrast, a negative nitrogen balance, in which more nitrogen is lost than gained, indicates a state of overall protein catabolism. The body obtains nitrogen from dietary protein, sources of which include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, nuts, legumes, cereals, and grains. Nitrogen loss occurs largely through urine in the form of urea, as well as through faeces, sweat, and growth of hair and skin. Blood urea nitrogen and urine urea nitrogen tests can be used to estimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Physiology
The human body is the entire structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organs and then organ systems. The external human body consists of a head, hair, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen), genitals, arms, hands, legs, and feet. The internal human body includes organs, teeth, bones, muscle, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels and blood, lymphatic vessels and lymph. The study of the human body includes anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar, iron, and oxygen in the blood. The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and artists to assist them in their work. Composition The human body is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a tachycardia, fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, goitre, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a hyperthermia, high temperature; this often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score
Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans and their ability to digest it. The PDCAAS rating was recommended by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) the in 1989 (report published in 1991).PDF with searchable text It was adopted by the US FDA in 1993 as "the preferred 'best'" method to determine protein quality. In 2013, FAO proposed changing to Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score. Background The PDCAAS value is different from measuring the quality of protein from the protein efficiency ratio (PER) and the biological value (BV) methods. The PER was based upon the amino acid requirements of growing rats, which differ significantly from those of humans. The PDCAAS allows evaluation of food protein quality based on the needs of humans as it measures the quality of a protein based on the amino acid req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Digestibility
Protein digestibility refers to how well a given protein is digested. Along with the amino acid score, protein digestibility determines the values for PDCAAS and DIAAS. See also * Biological value Biological value (BV) is a measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from a food which becomes incorporated into the proteins of the organism's body. It captures how readily the digested protein can be used in protein synthesis in the cells of ... References Proteins Nutrition {{digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Efficiency Ratio
Protein efficiency ratio (PER) is based on the weight gain of a test subject divided by its intake of a particular food protein during the test period. From 1919 until very recently, the PER had been a widely used method for evaluating the quality of protein in food. The food industry in Canada currently uses the PER as the standard for evaluating the protein quality of foods. The official method for determining the protein efficiency ratio is from Health Canada's Health Protection Branch Method FO-1, October 15, 1981. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ... now uses the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) as the basis for the percent of the U.S. recommended daily allowance (USRDA) for protein shown on food la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Protein Utilization
The net protein utilization (NPU) is the percentage of ingested nitrogen that is retained in the body. Rating It is used to determine the nutritional efficiency of protein in the diet, that is, it is used as a measure of "protein quality" for human nutritional purposes. As a value, NPU can range from 0 to 1 (or 100), with a value of 1 (or 100) indicating 100% utilization of dietary nitrogen as protein and a value of 0 an indication that none of the nitrogen supplied was converted to protein. Certain foodstuffs, such as eggs or milk, rate as 1 on an NPU chart. Experimentally, this value can be determined by determining dietary protein intake and then measuring nitrogen excretion. One formula for apparent NPU is: :NPU = - - / NPU and biological value (BV) both measure nitrogen retention; the difference is that biological value is calculated from nitrogen absorbed, whereas net protein utilization is from nitrogen ingested. Another closely related quantity is the net postpran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Value
Biological value (BV) is a measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from a food which becomes incorporated into the proteins of the organism's body. It captures how readily the digested protein can be used in protein synthesis in the cells of the organism. Proteins are the major source of nitrogen in food. BV assumes protein is the only source of nitrogen and measures the amount of nitrogen ingested in relation to the amount which is subsequently excreted. The remainder must have been incorporated into the proteins of the organisms body. A ratio of nitrogen incorporated into the body over nitrogen absorbed gives a measure of protein "usability" – the BV. Unlike some measures of protein usability, biological value does not take into account how readily the protein can be digested and absorbed (largely by the small intestine). This is reflected in the experimental methods used to determine BV. BV uses two similar scales: #The true percentage utilization (usually shown with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein (nutrient)
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the constituents of Tissue (biology), body tissue and also serve as a Fuel, fuel source. As fuel, proteins have the same energy density as carbohydrates: 17 Joule, kJ (4 Calories, kcal) per gram. The defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition. Proteins are polymer chains made of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. During human digestion, proteins are broken down in the stomach into smaller polypeptide chains via hydrochloric acid and protease actions. This is crucial for the absorption (small intestine), absorption of the essential amino acids that cannot be biosynthesized by the body. There are nine essential amino acids that humans must obtain from their diet to prevent protein–energy malnutrition, protein-energy malnutrition and resulting death. They are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
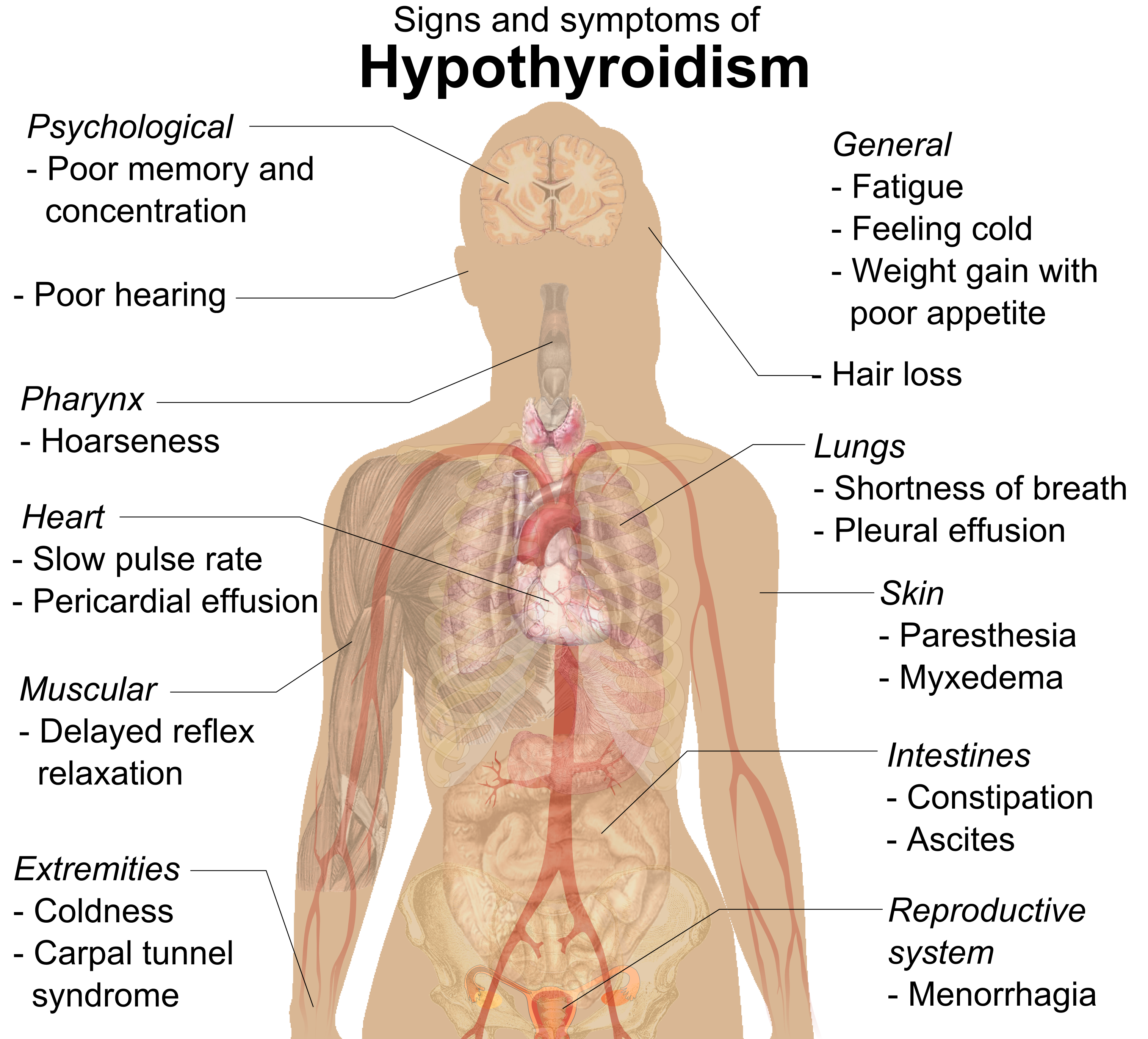
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- (γ-) amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, Chemical polarity, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid ''Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissue (biology), tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Urea Nitrogen
Urine urea nitrogen (UUN) refers to a test that measures the urine urea to assess nitrogen balance. Chemical structure Urea nitrogen is the end product of breakdown of proteins in the body. In individuals with normal kidney and liver functions, urea is excreted via urine. Indication for testing By testing for UUN, clinicians can assess one's nitrogen balance. Calculating nitrogen balance is a useful tool in assessing adequacy of protein provision in clinical setting in: * Patients with questionable protein intake. * Patients with confirmed or suspected protein digestion and absorption problems. * Patients with increased metabolic demand due to catabolic disease status. * Patients on long-term enteral nutrition or parenteral nutrition. Calculation of nitrogen balance UUN is determined from 24-hour urine collection. Along with UUN, values for BUN A bun is a type of bread that is round and small enough that it can generally be eaten hand-held. Whether a bun is considered s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |