|
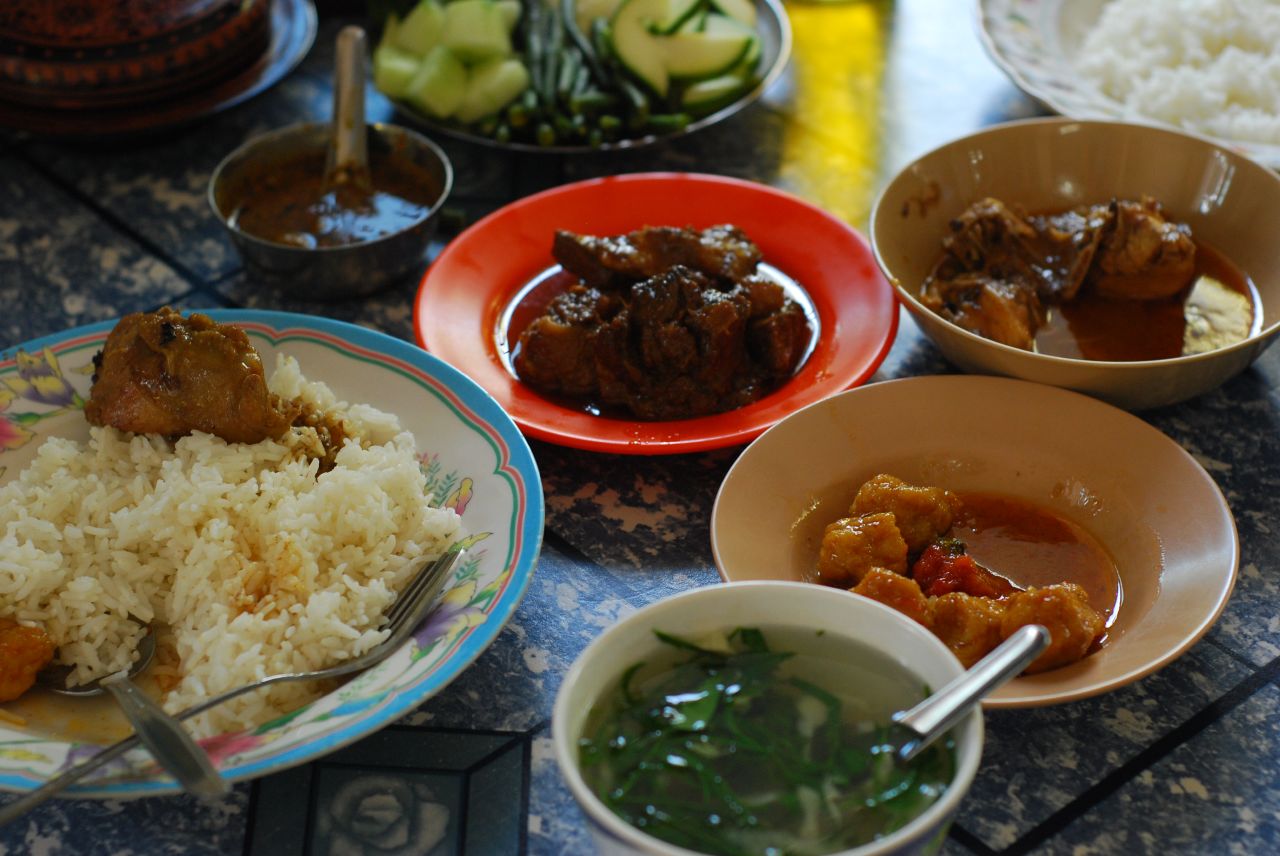
Ngapi
''Ngapi'' ( , ) is a pungent paste made of either fish or shrimp used in Burmese cuisine. ''Ngapi'' is typically made by fermenting fish or shrimp that is salted and ground then sundried. Like cheese, it can be distinguished based on main ingredient and regional origin. ''Ngapi'' can be distinguished by the type of fish used to make it. ''Ngapi'' can come from whole fish (such as ''ngapi kaung''), from small fish (''hmyin ngapi'') or from prawns (''seinza ngapi''). ''Ngapi'' is a main ingredient of Lower Burmese cooking and is used as a condiment or additive in most dishes. Raw ''ngapi'', with some exceptions, is not intended for direct consumption. Similar fermented seafood pastes are common across the Southeast Asian cuisines, notably Malay ''belacan'' and Thai ''kapi'' and ''pla ra'', Lao '' padaek'', and Khmer '' prahok''. Etymology ''Ngapi'' is a compound word in the Burmese language, literally meaning "pressed fish". The Burmese term was borrowed into the Thai, Lao, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Cuisine
Burmese cuisine encompasses the diverse regional culinary traditions of Myanmar, which have developed through longstanding agricultural practices, centuries of sociopolitical and economic change, and cross-cultural contact and trade with neighboring countries at the confluence of Southeast Asia, East Asia, and South Asia, such as modern-day nations of Thailand, China, and India, respectively. Burmese cuisine is typified by a wide-ranging array of dishes, including traditional Burmese curry, Burmese curries and stews, Burmese salads, accompanied by soups and a medley of vegetables that are traditionally eaten with white rice. Burmese curries are generally distinguished from other Southeast Asian curries in the former's prominent use of an aromatic trio of garlic, shallots, and ginger (in common with South Asian curries), and the general lack of coconut milk. Burmese cuisine also features Indian breads as well as noodles, which are fried or prepared in salads and noodle soups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrimp Paste
Shrimp paste or prawn sauce is a Fermentation, fermented condiment commonly used in Southeast Asian cuisine, Southeast Asian and Coastal Chinese cuisines. It is primarily made from finely crushed Shrimp and prawn as food, shrimp or krill mixed with salt, and then fermented for several weeks. It is sold either in its wet form or sun-dried and either cut into blocks or sold in bulk. It is an essential ingredient in many curry, curries, sauces and sambal. Shrimp paste can be found in many meals in Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. It is often an ingredient in Dip (food), dip for fish or vegetables. History Shrimp paste originated in continental Southeast Asia, probably among the Cham people, Cham and Mon people, from where it spread southwards to insular Southeast Asia. In Java, fermented shrimp paste (''trasi'' or ''terasi''), as mentioned in two ancient Sundanese language, Sundanese scriptures, ''Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prahok
''Prahok'' (; , ) is a salted and fermented fish paste (usually of mudfish) used in Cambodian cuisine as a seasoning or a condiment. It originated as a way of preserving fish during the time of the year when fresh fish was not available in abundant supply. Because of its saltiness and strong flavor, it was used as an addition to many meals in Cambodian cuisine, including soups and sauces. A Cambodian saying goes, "No ''prahok'', no salt," referring to a dish lacking in flavour, highlighting its essentiality in Cambodian cuisine. ''Prahok'' has a strong and distinct odor reminiscent of Limburger or ripe Camembert, which has earned it the nickname "Cambodian cheese". ''Prahok'' is usually eaten as a main course with white rice and vegetables such as yardlong beans, cucumbers, winged beans and a variety of eggplants. ''Prahok'' is sometimes distributed as a donation to victims of flood or drought by charities and other organizations. Varieties and production ''Prahok'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngachin
''Ngachin'' (; ), also called pickled fish, is a traditional fermented fish product used in Burmese cuisine. ''Ngachin'' consists of raw freshwater fish, which is pressed with a mixture of cooked rice gruel and salt as it ferments, and is traditionally packed in ''taungzun'' leaves. Bronze featherback is typically used for ''ngachin'', although other freshwater varieties like rohu can be substituted. The version using shrimp is called ''bazunchin'' (ပုစွန်ချဉ်, ). ''Ngachin'' is popularly served in a Burmese salad, mixed with garlic, shallots, fresh chillies, coriander and served with rice. In Madauk, ''ngachin'' is commonly served in mohinga, a rice noodle soup. In popular culture ''Ngachin'' is the subject of a popular Burmese proverb, "homemade ''ngachin'' tastes better" (ကိုယ့်ငါးချဉ် ကိုယ်ချဉ်), reflecting the shortcomings of personal biases. See also * Burmese cuisine * Shrimp paste * Fermented fish Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padaek
''Padaek'' or ''padek'' ( Lao: ປາແດກ) is a traditional Lao condiment made from pickled or fermented fish that has been cured. It often contains chunks of fish and is thicker, as well as more seasoned than fish sauce. Unlike other versions of fish sauce in Southeast Asia, ''padaek'' is made from freshwater fish, owing to the landlocked nature of the former kingdom of Lan Xang. ''Padaek'' is used in many Lao dishes, most notably '' tam maak hoong''. See also * * * * * *, Burmese fish paste *PatisFish sauce Fish sauce is a liquid condiment made from fish or krill that have been coated in salt and fermented for up to two years. It is used as a staple seasoning in East Asian cuisine and Southeast Asian cuisine, particularly Myanmar, Cambodia, L ... - Philippine-fish sauce References External linksWhat is Padaek? Fish sauces Umami enhancers Lao cuisine {{condiment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konbaung Dynasty
The Konbaung dynasty (), also known as the Third Burmese Empire (တတိယမြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်), was the last dynasty that ruled Burma from 1752 to 1885. It created the second-largest empire in history of Myanmar, Burmese history and continued the administrative reforms begun by the Toungoo dynasty, laying the foundations of the modern state of Burma. The reforms, however, proved insufficient to stem the advance of the British Empire, who defeated the Burmese in all three Anglo-Burmese Wars over a six-decade span (1824–1885) and ended the millennium-old Burmese monarchy in 1885. Pretenders to the dynasty claim descent from Myat Phaya Lat, one of Thibaw's daughters. An expansionist dynasty, the Konbaung kings waged campaigns against the Mizo Chieftainship, Lushai Hills, Möng Mao, Manipur, Assam, Kingdom of Mrauk U, Arakan, the Mon people, Mon kingdom of Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Pegu, Siam, and the Qing dynasty of China—thus establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pho Hlaing
Pho Hlaing (, also spelt Hpo Hlaing) was a Burmese noble and civil servant, best known for his treatise, ' (), which proposed sweeping reforms to transform Burma's monarchy into a constitutional monarchy and an early advocate of indigenous democracy. Pho Hlaing was an accomplished writer and wrote a number of important treatises throughout his lifetime, on politics, mathematics and Buddhist philosophy. Names and titles Pho Hlaing was known by a number of titles and names, including the Yaw Atwinwun (), Shwepyi Atwinwun (), Wetmasut Myoza (), Magwe Myoza () and posthumously called the Yaw Mingyi () and Shwepyi Mingyi (). ''Atwinwun'' is roughly analogous to 'Minister of the Interior', ''Myoza'' is roughly 'Duke', and ''Mingyi'' is a title reserved for the monarch or high-ranking ministers. Early life Pho Hlaing was born in 1830 in Ywapale, a small village in Myingyan District in Upper Burma to Thado Minhlakyawhtin (father) and Me Nyein (mother). His father, a royal official (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon Kingdoms
Mon kingdoms were polities established by the Mon language, Mon-speaking people in parts of present-day Myanmar and Thailand. The polities ranged from Dvaravati and Haripuñjaya in present-day northern Thailand to Thaton Kingdom, Thaton, Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Hanthawaddy (1287–1539), and the Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Restored Hanthawaddy (1740–1757) in southern Myanmar. Early states The first recorded kingdom attributed to the Mon people is Dvaravati,Coedès 1968: 63, 76–77 which prospered until around 1000 Common era, CE when their capital was ruled by the Khmer Empire and a significant portion of the inhabitants fled west to present-day Lower Burma and eventually founded new polities. Another Mon-speaking state Haripuñjaya also existed in northern Thailand down to the late 13th century.Coedès 1968: 208 Thaton (9th century?–1057?) According to British rule in Burma, colonial period scholarship, the Mon established small polities (or large city-states) in Lower B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizo Language
Mizo is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken mainly in the Indian state of Mizoram, where it is the official language and lingua franca. It is the mother tongue of the Mizo people and some members of the Mizo diaspora. Other than Mizoram, it is also spoken in Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, and Assam states of India, Sagaing Region and Chin State in Myanmar, and Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. It is mainly based on the Lusei dialect but it has also derived many words from its surrounding Mizo clans such as Hmar, Pawi, etc. The language is also known as Duhlian and Lushai, a colonial term, as the Duhlian people were the first among the Mizo people to be encountered by the British in the course of their colonial expansion. Classification Mizo is related to the other languages of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The Zohnahtlak languages (which native Mizo speakers call ''Zohnahthlâk ṭawngho''/''Mizo ṭawngho'') have a substantial number of words in common. Phonology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoin (resin)
Benzoin or benjamin (corrupted pronunciation) is a balsamic resin obtained from the bark of several species of trees in the genus '' Styrax''. It is used in perfumes and some kinds of incense and as a flavoring and medicine (see tincture of benzoin). It is distinct from the chemical compound benzoin, which is ultimately derived chemically from benzoin resin; the primary active ingredient of benzoin resin is actually benzoic acid, not benzoin. Benzoin is sometimes called gum benzoin or gum benjamin, and in India ''Sambrani or'' loban, though loban is, via Arabic ''lubān'', a generic term for frankincense-type incense, e.g., fragrant tree resin. The syllable "benz" ultimately derives from the Arabic lubān jāwī (لبان جاوي, "frankincense from Java"). (mid 16th century: from French ''benjoin'', based on Arabic ''lubānjāwī'' ‘incense of Java’.) Benzoin is also called storax, not to be confused with the balsam of the same name obtained from the Hamamelidaceae fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
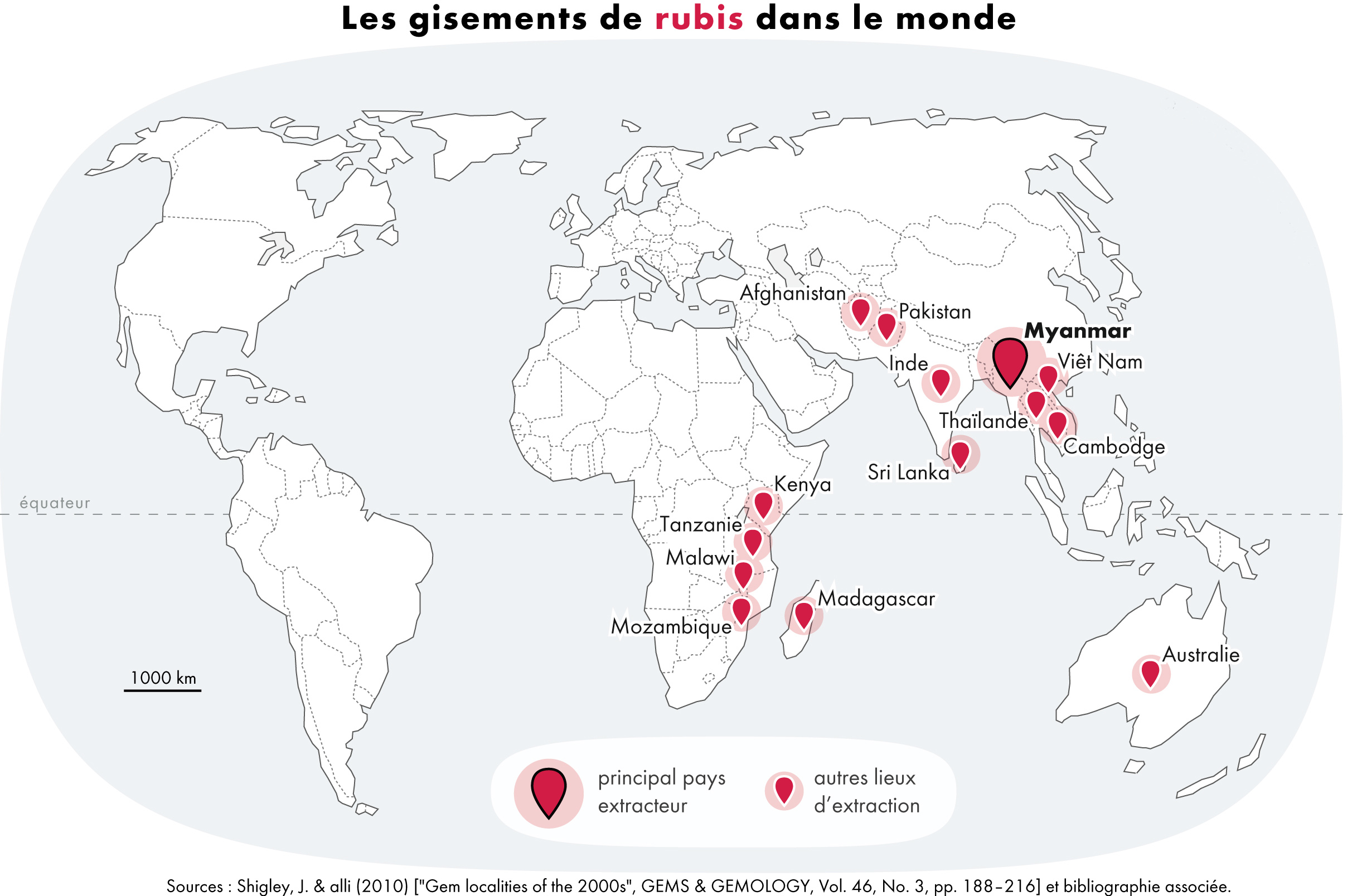
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
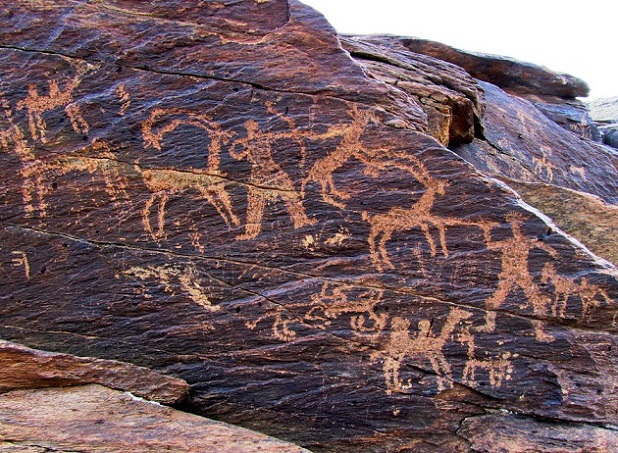
Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix , from meaning " stone", and meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as . In scholarly texts, a ''petroglyph'' is a rock engraving, whereas a '' petrograph'' (or ''pictograph'') is a rock painting. In common usage, the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |