|
Neovascular
Neovascularization is the natural formation of new blood vessels ('' neo-'' + ''vascular'' + '' -ization''), usually in the form of functional microvascular networks, capable of perfusion by red blood cells, that form to serve as collateral circulation in response to local poor perfusion or ischemia. Growth factors that inhibit neovascularization include those that affect endothelial cell division and differentiation. These growth factors often act in a paracrine or autocrine fashion; they include fibroblast growth factor, placental growth factor, insulin-like growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and platelet-derived endothelial growth factor. There are three different pathways that comprise neovascularization: (1) vasculogenesis, (2) angiogenesis, and (3) arteriogenesis. Three pathways of neovascularization Vasculogenesis Vasculogenesis is the de novo formation of blood vessels. This primarily occurs in the developing embryo with the development of the first primitive v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Neovascularization
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is the in-growth of new blood vessels from the pericorneal plexus into avascular Cornea, corneal tissue as a result of oxygen deprivation. Maintaining avascularity of the corneal stroma is an important aspect of healthy corneal physiology as it is required for corneal transparency and optimal vision. A decrease in corneal transparency causes visual acuity deterioration. Corneal tissue is avascular in nature and the presence of vascularization, which can be deep or superficial, is always pathologically related. Corneal neovascularization is a sight-threatening condition that can be caused by inflammation related to infection, chemical injury, Autoimmune disease, autoimmune conditions, immune hypersensitivity, post-corneal transplantation, and traumatic conditions among other ocular pathologies. Common causes of CNV within the cornea include trachoma, corneal ulcer, corneal ulcers, phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitisrosacea keratitis interstitial kerati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroidal Neovascularization
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is the creation of new blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye. Choroidal neovascularization is a common cause of neovascular degenerative maculopathy (i.e. 'wet' macular degeneration) commonly exacerbated by extreme myopia, malignant myopic degeneration, or age-related developments. Causes CNV can occur rapidly in individuals with defects in Bruch's membrane, the innermost layer of the choroid. It is also associated with excessive amounts of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). As well as in wet macular degeneration, CNV can also occur frequently with the rare genetic disease pseudoxanthoma elasticum and rarely with the more common optic disc drusen. CNV has also been associated with extreme myopia or malignant myopic degeneration, where in choroidal neovascularization occurs primarily in the presence of cracks within the retinal (specifically) macular tissue known as lacquer cracks. Symptoms CNV can create a sudden deterioration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
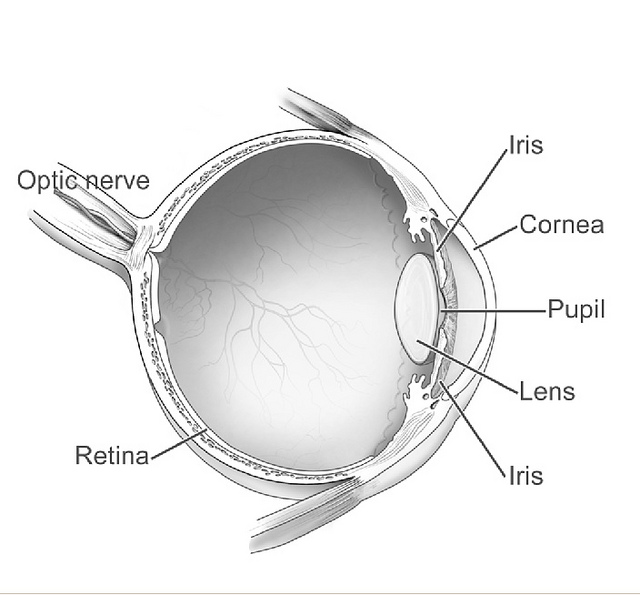
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as Intraocular pressure, intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word ''glaucoma'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'. Of the different types of glaucoma, the most common are called open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma. Inside the eye, a liquid called Aqueous humour, aqueous humor helps to maintain shape and provides nutrients. The aqueous humor normally drains through the trabecular meshwork. In open-angle glaucoma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruch's Membrane
Bruch's membrane or lamina vitrea is the innermost layer of the choroid of the eye. It is also called the ''vitreous lamina'' or ''Membrane vitriae'', because of its glassy microscopic appearance. It is 2–4 μm thick. Anatomy Structure Bruch's membrane consists of five layers (from inside to outside): #the basement membrane of the retinal pigment epithelium #the inner collagenous zone #a central band of elastic fibers #the outer collagenous zone #the basement membrane of the choriocapillaris Development The membrane grows thicker with age. With age, lipid-containing extracellular deposits may accumulate between the membrane and the basal lamina of the retinal pigmental epithelium, impairing exchange of solutes and contributing to age-related pathology. Embryology Bruch's membrane is present by midterm in fetal development as an elastic sheet. Function The membrane is involved in the regulation of fluid and solute passage from the choroid to the retina. Pathology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placental Growth Factor
Placental growth factor (PlGF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PGF'' gene. Placental growth factor is a member of the VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) sub-family - a key molecule in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis, in particular during embryogenesis. The main source of PlGF during pregnancy is the placental trophoblast. ''PGF'' is also expressed in many other tissues, including the villous trophoblast. The placental growth factor gene (''PGF'') is a protein-coding gene and a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family. ''PGF'' is expressed only in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and the placenta. PGF is ultimately associated with angiogenesis. Specifically, PGF plays a role in trophoblast growth and differentiation. Trophoblast cells, specifically extravillous trophoblast cells, are responsible for invading the uterine wall and the maternal spiral arteries. The extravillous trophoblast cells produce a blood vessel of lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculogenesis
Vasculogenesis is the process of blood vessel formation, occurring by a ''De novo synthesis, de novo'' production of endothelial cells. It is the first stage of the formation of the vascular network, closely followed by angiogenesis. Process In the word sense, sense distinguished from angiogenesis, vasculogenesis is different in one aspect: whereas angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, vasculogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels, in blood islands, when there are no pre-existing ones. For example, if a monolayer of endothelial cells begins sprouting to form capillary, capillaries, angiogenesis is occurring. Vasculogenesis, in contrast, is when endothelial precursor cells (angioblasts) migrate and differentiate in response to local cues (such as growth factors and extracellular matrices) to form new blood vessels. These vascular trees are then pruned and extended through angiogenesis. Occurrences Vasculogenesis occurs during embryon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collateral Circulation
Collateral circulation is the alternate Circulatory system, circulation around a blocked blood vessel, artery or vein via another path, such as nearby minor vessels. It may occur via preexisting vascular redundancy (analogous to redundancy (engineering), engineered redundancy), as in the circle of Willis in the brain, or it may occur via new branches formed between adjacent blood vessels (neovascularization), as in the eye after a retinal embolism or in the brain when an instance of arterial constriction occurs due to Moyamoya disease. Its formation may be related by pathological conditions such as high vascular resistance or ischaemia. It is occasionally also known as accessory circulation, auxiliary circulation, or secondary circulation. It has surgery, surgically created analogues in which shunt (medical), shunts or circulatory anastomosis, anastomoses are constructed to bypass circulatory problems. An example of the usefulness of collateral circulation is a systemic thromboem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of Cystine knot, cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the ''De novo synthesis, de novo'' formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). It is part of the system that restores the oxygen supply to tissues when blood circulation is inadequate such as in hypoxic conditions. Serum concentration of VEGF is high in bronchial asthma and diabetes mellitus. VEGF's normal function is to create new blood vessels during embryonic development, new blood vessels after injury, muscle following exercise, and new vessels (collateral circulation) to bypass blocked vessels. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by the macrophages. They are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function will lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as a systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans, and released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |