|
Neocognitron
__NOTOC__ The neocognitron is a hierarchical, multilayered artificial neural network proposed by Kunihiko Fukushima in 1979. It has been used for Japanese handwritten character recognition and other pattern recognition tasks, and served as the inspiration for convolutional neural networks. Previously in 1969, he published a similar architecture, but with hand-designed kernels inspired by convolutions in mammalian vision. In 1975 he improved it to the Cognitron, and in 1979 he improved it to the neocognitron, which ''learns'' all convolutional kernels by unsupervised learning (in his terminology, " self-organized by 'learning without a teacher'"). The neocognitron was inspired by the model proposed by Hubel & Wiesel in 1959. They found two types of cells in the visual primary cortex called '' simple cell'' and '' complex cell'', and also proposed a cascading model of these two types of cells for use in pattern recognition tasks. The neocognitron is a natural extension of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feedforward neural network that learns features via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced—in some cases—by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by the regularization that comes from using shared weights over fewer connections. For example, for ''each'' neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded ''convolution'' (or cross-correlation) kernels, only 25 weights for each convolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunihiko Fukushima
Kunihiko Fukushima ( Japanese: 福島 邦彦, born 16 March 1936) is a Japanese computer scientist, most noted for his work on artificial neural networks and deep learning. He is currently working part-time as a senior research scientist at the Fuzzy Logic Systems Institute in Fukuoka, Japan. Notable scientific achievements In 1980, Fukushima published the neocognitron, the original deep convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture. Fukushima proposed several supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms to train the parameters of a deep neocognitron such that it could learn internal representations of incoming data. Today, however, the CNN architecture is usually trained through backpropagation. This approach is now heavily used in computer vision. In 1969 Fukushima introduced the ReLU (Rectifier Linear Unit) activation function in the context of visual feature extraction in hierarchical neural networks, which he called "analog threshold element". (Though the ReLU was fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
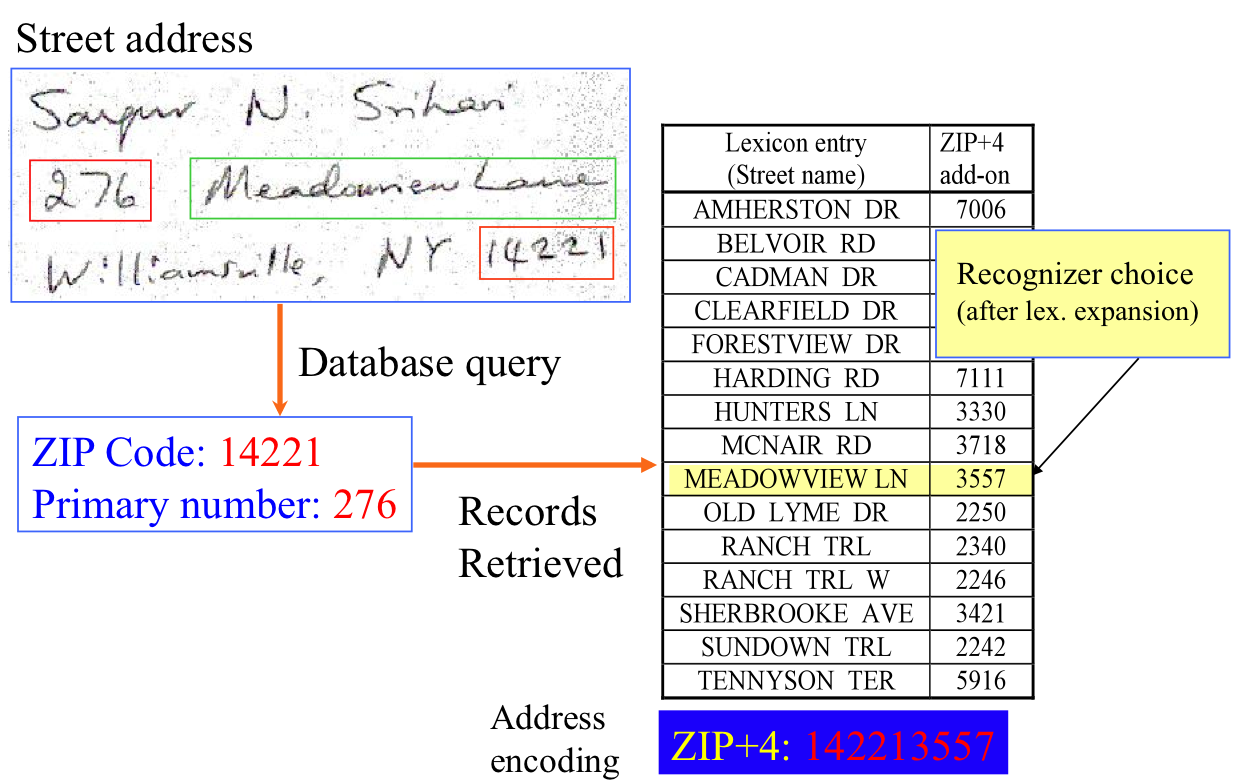
Handwriting Recognition
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwriting, handwritten input from sources such as paper documents, photographs, touch-screens and other devices. The image of the written text may be sensed "off line" from a piece of paper by optical scanning (optical character recognition) or intelligent word recognition. Alternatively, the movements of the pen tip may be sensed "on line", for example by a pen-based computer screen surface, a generally easier task as there are more clues available. A handwriting recognition system handles formatting, performs correct Segment (handwriting), segmentation into characters, and finds the most possible words. Offline recognition Offline handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text in an image into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications. The data obtained by this form is reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsten Wiesel
Torsten Nils Wiesel (born 3 June 1924) is a Swedish Neurophysiology, neurophysiologist. With David H. Hubel, he received the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for their discoveries concerning information processing in the visual system; the prize was shared with Roger W. Sperry for his independent research on the cerebral hemispheres. Career Wiesel was born in Uppsala, Sweden, in 1924, the youngest of five children. In 1947, he began his scientific career in Carl Gustaf Bernhard's laboratory at the Karolinska Institute, where he received his medical degree in 1954. He went on to teach in the institute's department of physiology and worked in the child psychiatry unit of the Karolinska Hospital. In 1955 he moved to the United States to work at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine under Stephen Kuffler. Wiesel began a fellowship in ophthalmology, and in 1958 he became an assistant professor. That same year, he met David Hubel, beginning a collaboration that would last over tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organizing Map
A self-organizing map (SOM) or self-organizing feature map (SOFM) is an unsupervised machine learning technique used to produce a low-dimensional (typically two-dimensional) representation of a higher-dimensional data set while preserving the topological structure of the data. For example, a data set with p variables measured in n observations could be represented as clusters of observations with similar values for the variables. These clusters then could be visualized as a two-dimensional "map" such that observations in proximal clusters have more similar values than observations in distal clusters. This can make high-dimensional data easier to visualize and analyze. An SOM is a type of artificial neural network but is trained using competitive learning rather than the error-correction learning (e.g., backpropagation with gradient descent) used by other artificial neural networks. The SOM was introduced by the Finnish professor Teuvo Kohonen in the 1980s and therefore is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess PR capabilities but their primary function is to distinguish and create emergent patterns. PR has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. Pattern recognition systems are commonly trained from labeled "training" data. When no labeled data are available, other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns. KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
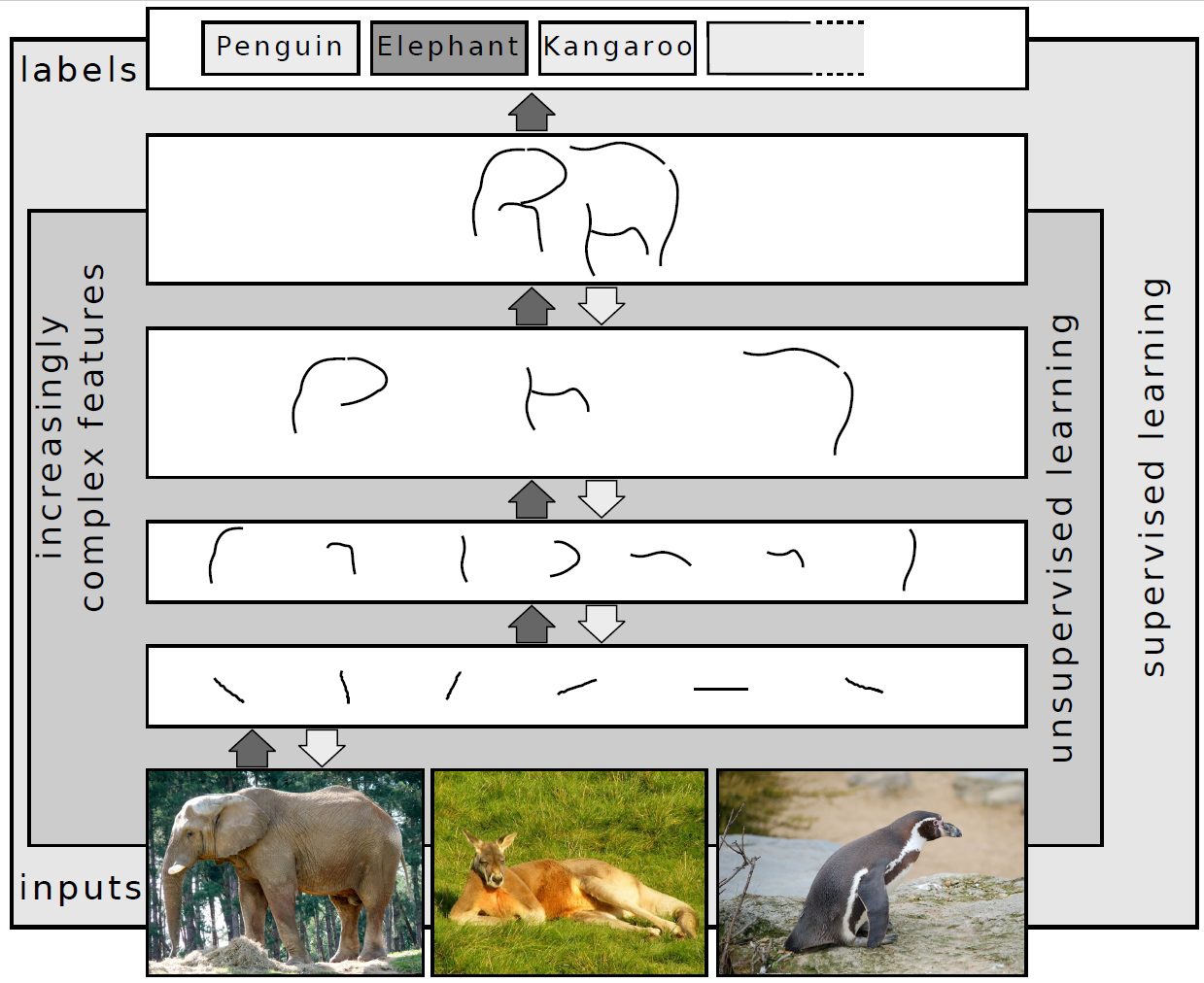
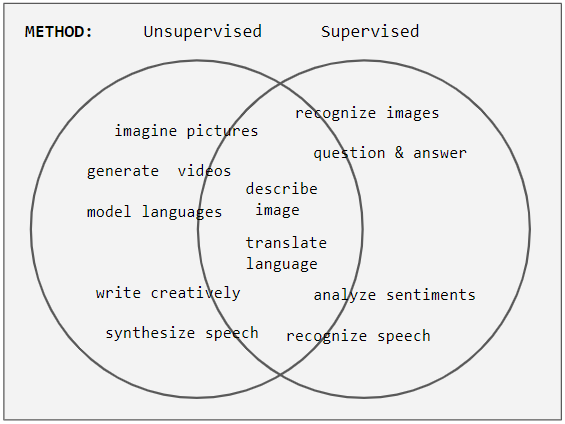
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a framework in machine learning where, in contrast to supervised learning, algorithms learn patterns exclusively from unlabeled data. Other frameworks in the spectrum of supervisions include weak- or semi-supervision, where a small portion of the data is tagged, and self-supervision. Some researchers consider self-supervised learning a form of unsupervised learning. Conceptually, unsupervised learning divides into the aspects of data, training, algorithm, and downstream applications. Typically, the dataset is harvested cheaply "in the wild", such as massive text corpus obtained by web crawling, with only minor filtering (such as Common Crawl). This compares favorably to supervised learning, where the dataset (such as the ImageNet1000) is typically constructed manually, which is much more expensive. There were algorithms designed specifically for unsupervised learning, such as clustering algorithms like k-means, dimensionality reduction techniques l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |