|
Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Pleistocene. Neanderthal extinction occurred roughly 40,000 years ago with the immigration of modern humans (Cro-Magnons), but Neanderthals in Gibraltar may have persisted for thousands of years longer. The first recognised Neanderthal fossil, Neanderthal 1, was discovered in 1856 in the Neander Valley, Germany. At first, Neanderthal 1 was considered to be one of the racial hierarchy, lower races in accord with historical race concepts. As more fossils were discovered through the early 20th century, Neanderthals became characterised most especially by Marcellin Boule as a unique species of underdeveloped human. By the mid-20th century, human evolution was described as progressing from an apelike ancestor, through a "Neanderthal phase", ending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal Behaviour
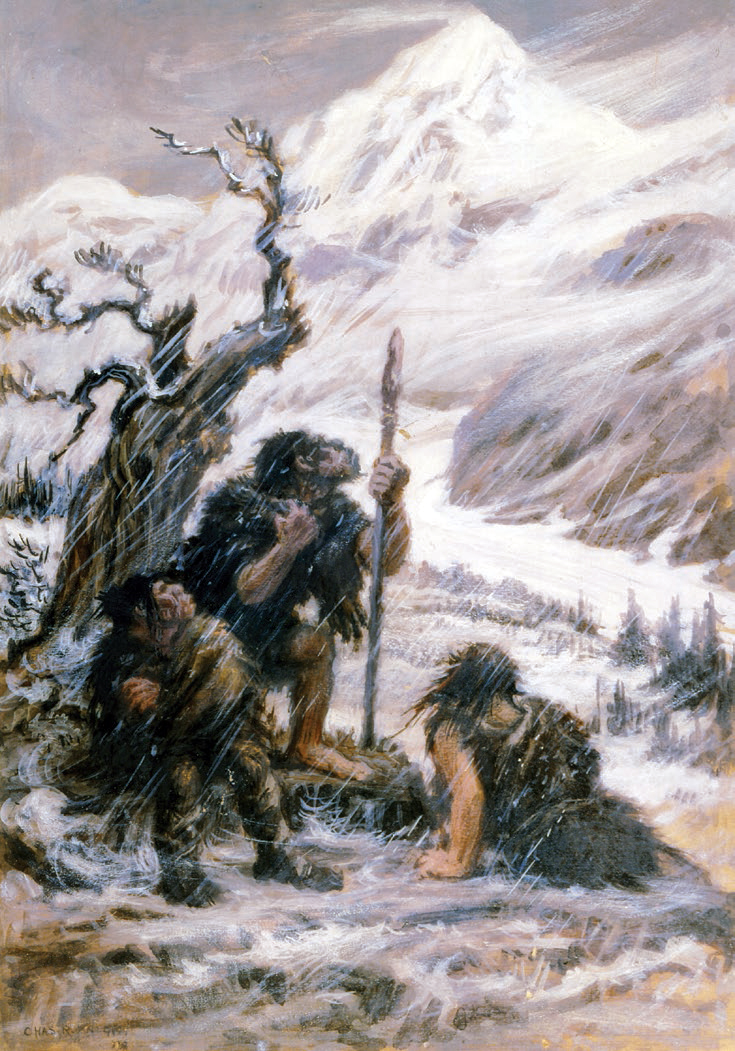
For much of the early 20th century, Neanderthal behaviour was depicted as primitive, unintelligent, and brutish; unevolved compared to their modern human contemporaries, the Cro-Magnons. Although knowledge and perception of Neanderthals has markedly changed since then in the scientific community, the image of the underdeveloped Caveman, caveman archetype remains prevalent in popular culture. Neanderthal technology achieved a degree of sophistication. It includes the Mousterian stone tool industry (archaeology), industry as well as the abilities to maintain and possibly to Control of fire by early humans, create fire, build cave hearths, craft at least simple clothes similar to blankets and ponchos, make use of medicinal plants#Prehistoric times, medicinal plants, treat severe injuries, store food, and use various cooking techniques such as roasting, boiling, and smoking (cooking), smoking. Overall, Neanderthals maintained a low population and population density, and also mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interbreeding Between Archaic And Modern Humans
Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans occurred during the Middle Paleolithic and early Upper Paleolithic. The interbreeding happened in several independent events that included Neanderthals and Denisovans, as well as several unidentified hominins. In Europe, Asia and North Africa, interbreeding between archaic humans and Early modern human, modern humans took place several times. The introgression events into modern humans are estimated to have happened about 47,000–65,000 years ago with Neanderthals and about 44,000–54,000 years ago with Denisovans. Neanderthal-derived DNA has been found in the genomes of most contemporary populations, varying noticeably by region. It accounts for 1–4% of modern genomes for people outside Sub-Saharan Africa, although estimates vary, and either none or up to 0.3% for those in Sub-Saharan Africa. Cushitic-speaking peoples, Cushitic and Semitic languages, Semitic speaking populations from the Horn of Africa (such as Ethiopians), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
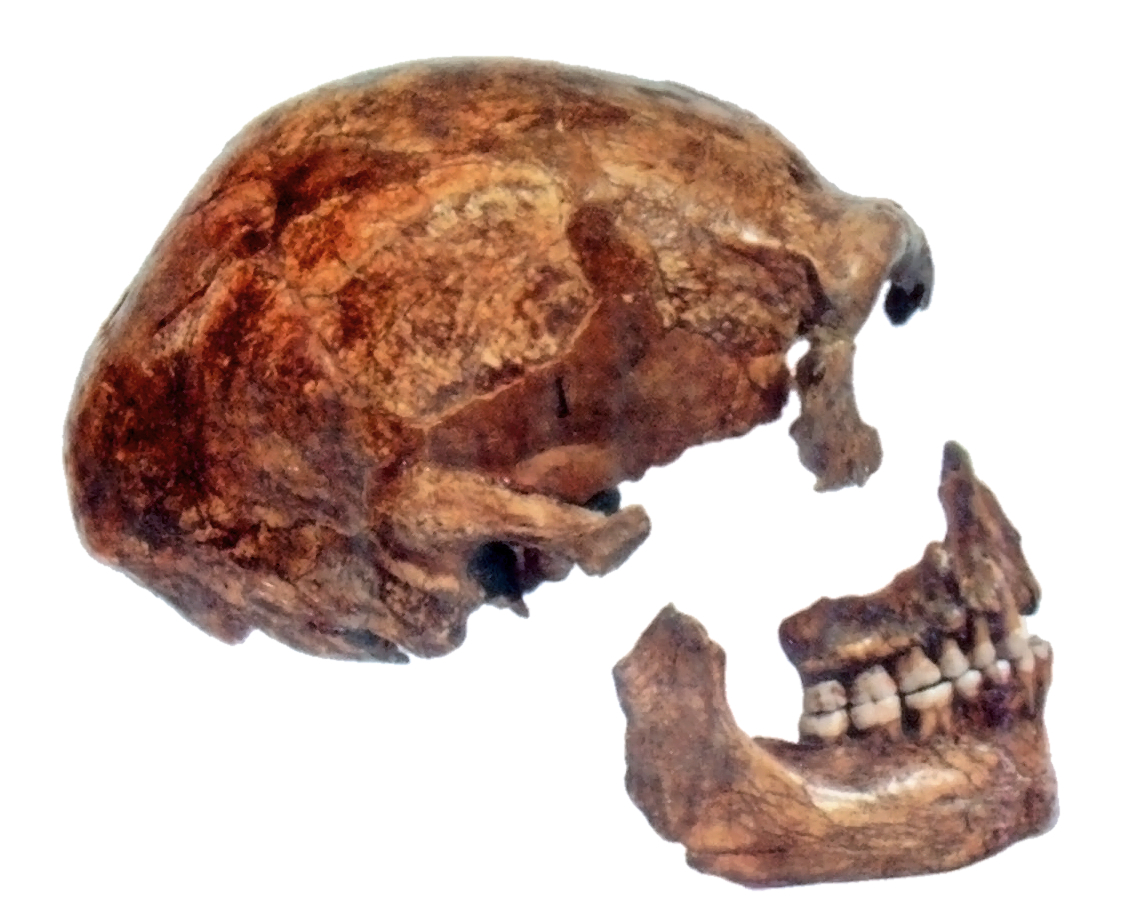
Neanderthal Anatomy
Neanderthal anatomy is characterised by a long, flat skull and a stocky body plan. When first discovered, Neanderthals were thought to be anatomically comparable to Aboriginal Australians, in accord with historical race concepts. As more fossils were discovered in the early 20th century, French palaeontologist Marcellin Boule defined them as a slouching, apelike species; a popular image until the middle of the century. Neanderthal features gradually accreted in European populations over the Chibanian, Middle Pleistocene, driven by natural selection in a cold climate, as well as genetic drift when populations crashed during glacial periods. This culminated in the "classical Neanderthal" anatomy by the Last Interglacial. The Neanderthal skull is distinctive by namely a rounded supraorbital torus (brow ridge), large orbit (anatomy), orbits (eye sockets) and nose, and an occipital bun at the back of the skull. The jaws and teeth are strong, which may have been a response to habitual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal Genetics
Neanderthal genetics testing became possible in the 1990s with advances in ancient DNA analysis. In 2008, the Neanderthal genome project published the full sequence Neanderthal mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), and in 2010 the full Neanderthal genome. Genetic data is useful in testing hypotheses about Neanderthal evolution and their divergence from early modern humans, as well as understanding Neanderthal demography, and interbreeding between archaic and modern humans. Modern humans and Neanderthals had multiple different interbreeding episodes, but Neanderthal-derived genes in the present-day human genome descends from an episode 250,000 years ago probably in Eurasia, and 47,000 to 65,000 years ago in the Near East. While 20% of the Neanderthal genome survives today, most people only carry about a few percentage points of Neanderthal DNA, and most Neanderthal-derived genes is non-coding DNA. Neanderthals maintained a low genetic diversity and suffered from inbreeding depression; consequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal Extinction
Neanderthals became extinct around 40,000 years ago. Hypotheses on the causes of the extinction include violence, transmission of diseases from modern humans which Neanderthals had no immunity to, competitive replacement, extinction by interbreeding with early modern human populations, natural catastrophes, climate change and inbreeding depression. It is likely that multiple factors caused the demise of an already low population. Upper Palaeolithic Transition The extinction of Neanderthals was part of the broader Late Pleistocene megafaunal extinction event. Whatever the cause of their extinction, Neanderthals were replaced by modern humans, indicated by near full replacement of Middle Palaeolithic Mousterian stone technology with modern human Upper Palaeolithic Aurignacian stone technology across Europe (the Middle-to-Upper Palaeolithic Transition) from 41,000 to 39,000 years ago. By between 44,200 and 40,600 BP, Neanderthals vanished from northwestern Europe. However, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Evolution
''Homo sapiens'' is a distinct species of the hominid family of primates, which also includes all the great apes. Over their evolutionary history, humans gradually developed traits such as Human skeletal changes due to bipedalism, bipedalism, dexterity, and complex language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins (a tribe of the Homininae, African hominid subfamily), indicating that human evolution was not linear but weblike. The study of the origins of humans involves Interdisciplinary, several scientific disciplines, including Biological anthropology, physical and evolutionary anthropology, paleontology, and genetics; the field is also known by the terms anthropogeny, anthropogenesis, and anthropogony—with the latter two sometimes used to refer to the related subject of hominization. Primate evolution, Primates diverged from other mammals about (Myr, mya), in the Late Cretaceous period, with their earliest fossils appearing over 55 mya, during the Paleocene. Prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthals In Gibraltar
The Neanderthals in Gibraltar were among the first to be discovered by modern scientists and have been among the most well studied of their species according to a number of extinction studies which emphasize regional differences, usually claiming the Iberian Peninsula partially acted as a “refuge” for the shrinking Neanderthal populations and the Gibraltar population of Neanderthals as having been one of many dwindling populations of archaic human populations, existing just until around 42,000 years ago. Many other Neanderthal populations went extinct around the same time. The skull of a Neanderthal woman, discovered in a quarry in 1848, was only the second Neanderthal skull ever found and the first adult Neanderthal skull to be discovered, eight years before the discovery of the skull for which the species was named in Neandertal, Germany; had it been recognised as a separate species, it might have been called Calpican (or Gibraltarian) rather than Neanderthal Man. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal 1
Feldhofer 1 or Neanderthal 1 is the scientific name of the 40,000-year-old Type (biology), type specimen fossil of the species Neanderthal, ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The fossil was discovered in August 1856 in the Kleine Feldhofer Grotte cave in the Neander Valley (''Neandertal''), located east of Düsseldorf, Germany. In 1864, the fossil's description was first published in a scientific journal, where it was officially named.William King (geologist), William King: ''The Reputed Fossil Man of the Neanderthal''. In: ''Quarterly Journal of Science''. Vol. 1, 1864, pp. 88–97Full text (PDF; 356 kB)/ref> Neanderthal 1 was not the first Neanderthal fossil ever discovered. Other Neanderthal fossils had been found earlier but were not recognized as belonging to a distinct species. Discovery Limestone has been mined in the Neander Valley since the early 16th century. By the mid-19th century, mining operations had expanded to an industrial scale. In August 1856, two Italian wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cro-Magnon
Cro-Magnons or European early modern humans (EEMH) were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They interacted and interbred with the indigenous Neanderthals (''H. neanderthalensis'') of Europe and Western Asia, who went extinct 35,000 to 40,000 years ago. The first wave of modern humans in Europe ( Initial Upper Paleolithic) left no genetic legacy to modern Europeans; however, from 37,000 years ago a second wave succeeded in forming a single founder population, from which all subsequent Cro-Magnons descended and which contributes ancestry to present-day Europeans. Cro-Magnons produced Upper Palaeolithic cultures, the first major one being the Aurignacian, which was succeeded by the Gravettian by 30,000 years ago. The Gravettian split into the Epi-Gravettian in the east and Solutrean in the west, due to major climatic degradation during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recent African Origin Of Modern Humans
The recent African origin of modern humans or the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA) is the most widely accepted paleoanthropology, paleo-anthropological model of the geographic origin and Early human migrations, early migration of early modern human, anatomically modern humans (''Human, Homo sapiens''). It follows the early expansions of hominins out of Africa, accomplished by ''Homo erectus'' and then ''Neanderthal, Homo neanderthalensis''. The model proposes a "monogenism, single origin" of ''Human, Homo sapiens'' in the taxonomic sense, precluding parallel evolution in other regions of traits considered anatomically modern humans, anatomically modern, but not precluding multiple Archaic human admixture with modern humans, admixture between ''H. sapiens'' and archaic humans in Europe and Asia. ''H. sapiens'' most likely developed in the Horn of Africa between 300,000 and 200,000 years ago, although an alternative hypothesis argues that diverse morphological features of ''H. sap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bun
An occipital bun, also called an occipital spur, occipital knob, chignon hook or inion hook, is a prominent bulge or projection of the occipital bone at the back of the human skull, skull. It is important in scientific descriptions of classic Neanderthal crania. It is found among Archaic humans, archaic ''Homo'' species (including Neanderthals), as well as Late Pleistocene, Upper Pleistocene ''Human, Homo sapiens'' and present-day human populations. Occipital buns in Neanderthals The occipital bun is a protuberance of the occipital bone. Its size and shape has been compared to that of a dinner roll. It is a quintessential trait of Neanderthals, though it is a trend in archaic ''Homo'' species. The true purpose of the occipital bun has not yet been defined. However, some studies have found possible evolutionary purposes. In a study published in ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B'', the occipital bun has been attributed to the enlargement of the visual cortex; this is hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neander Valley
The Neandertal (, also , ; sometimes called "the Neander Valley" in English) is a small valley of the river Düssel in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located about east of Düsseldorf, the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia. The valley lies within the limits of the towns of Erkrath and Mettmann. In August 1856, the area became famous for the discovery of Neanderthal 1, one of the first specimens of ''Homo neanderthalensis'' to be found. The Neandertal was originally a limestone canyon widely known for its rugged scenery, waterfalls and caves. However, industrial quarrying during the 19th and 20th centuries removed most of the limestone and dramatically changed the shape of the valley. It was during such a quarrying operation that the bones of the original Neanderthal man were found in a cave known as Kleine Feldhofer Grotte. Neither the cave nor the cliff in which the bones were located still exist. During the 19th century, the valley was called (Neander' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |