|
National Symbols Of Croatia
The national symbols of Croatia are insignia, icons, or cultural expressions that are emblematic, representative, or otherwise characteristic of the Republic of Croatia, Croatian people The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They also f ..., or the Croatian culture. They are being implemented within the country and abroad as a form of representation for the nation's statehood or its unique cultural aspects. State insignia Iconography Culture Architecture Food and drink People Flora and fauna References {{Europe topic, National symbols of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Italy to the west. Its capital and largest city, Zagreb, forms one of the country's Administrative divisions of Croatia, primary subdivisions, with Counties of Croatia, twenty counties. Other major urban centers include Split, Croatia, Split, Rijeka and Osijek. The country spans , and has a population of nearly 3.9 million. The Croats arrived in modern-day Croatia, then part of Illyria, Roman Illyria, in the late 6th century. By the 7th century, they had organized the territory into Duchy of Croatia, two duchies. Croatia was first internationally recognized as independent on 7 June 879 during the reign of Duke Branimir of Croatia, Branimir. Tomislav of Croatia, Tomis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavonia
Slavonia (; ) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria County, Istria, one of the four Regions of Croatia, historical regions of Croatia. Located in the Pannonian Plain and taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Counties of Croatia, Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina County, Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja County, Osijek-Baranja, Požega-Slavonia County, Požega-Slavonia, Virovitica-Podravina County, Virovitica-Podravina, and Vukovar-Syrmia County, Vukovar-Syrmia, although the territory of the counties includes Baranya (region), Baranya, and the definition of the western extent of Slavonia as a region varies. The counties cover or 22.2% of Croatia, inhabited by 806,192—18.8% of Croatia's population. The largest city in the region is Osijek, followed by Slavonski Brod and Vinkovci. Slavonia is located in the Pannonian Basin, largely bordered by the Danube, Drava, and Sava rivers. In the west, the region consists of the Sava and Drava valleys and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Glagolitic
Angular Glagolitic is a style of Glagolitic book hand, developing from the earlier Rounded Glagolitic. Many letters present in Rounded Glagolitic were gradually abandoned: ⱏ, ⱐ, ⱔ, ⱘ, ⱙ, ⱚ, ⱛ and to a large extent ⰿ (replaced with ⱞ) and ⱗ. Others were introduced, like ⱜ. Glagolitic became the main script among Istrian Slavs in the 11th and 12th centuries, It already had some of the traits that would later make it distinct in form from Rounded Glagolitic, but over time under the influence of multiple waves of monastic exposure to Latinic hands like Beneventan and Blackletter it took on a stable angular shape it would hold for centuries. Intensified literary activity in the March of Istria and on Frankopan family domains in the 13th century secured for Angular Glagolitic the status of this Uncial script over a wide area, and although a chancery hand soon complemented it, not all notaries and chancellors adopted it immediately, with some using Angular Glagol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missale Romanum Glagolitice
''Missale Romanum Glagolitice'' (, ) is a Croatian missal and incunabulum printed in 1483. It is written in Glagolitic script and is the first printed Croatian book. It is the first missal in Europe not published in Latin script. Its ''editio princeps'', unique in the achieved typographic artistry, was published 28 years after the Gutenberg Bible's 42-lines, which bore witness of high cultural influence of Croatian Glagolites at the time.Hercigonja: 1984 "''Because of the importance of Glagolitic printing in the period from 1483 to 1561...as indisputably the highest attainment of Croatian medieval literature and a crucial event in our entire cultural tradition.''"; "''In the fifteenth century the Croatian Glagolitism reached the highest point in its development, the era of the full maturity of its literary endeavourings. The most prominent results of these endeavourings were indisputably the appearance of the editio princeps of the Croatian Glagolitic Missal on the 22nd February 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Croatia
Northern Croatia or North Croatia (, ) refers to the northern parts of Croatia, encompassing Zagreb County, Zagreb, Varaždin County, Varaždin, Međimurje County, Međimurje, Krapina-Zagorje County, Zagorje and Koprivnica-Križevci County, Koprivnica-Križevci counties, including the cities of Zagreb, Varaždin, Čakovec, Krapina, Koprivnica and Križevci, Croatia, Križevci. The region is home to the Kajkavian dialect, which some consider to be a separate language of its own. The region borders Hungary to its north-east and Slovenia to its north-west. Status The term had not been used in official capacity until recently. Until 2012, the region's borders coincided with the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS-2 region ''Northwest Croatia'' (''Sjeverozapadna Hrvatska'' in Croatian). This NUTS-2 region was then merged with ''Central and Eastern Croatia'' (''Središnja i Istočna Hrvatska'') forming the NUTS-2 region Continental Croatia. As of 2021, the NUTS-2 regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lika
Lika () is a traditional region of Croatia proper, roughly bound by the Velebit mountain from the southwest and the Plješevica mountain from the northeast. On the north-west end Lika is bounded by Ogulin-Plaški basin, and on the south-east by the Malovan pass. Today most of the territory of Lika (Brinje, Donji Lapac, Gospić, Lovinac, Otočac, Perušić, Plitvička Jezera, Udbina and Vrhovine) is part of Lika-Senj County. Josipdol, Plaški and Saborsko are part of Karlovac County and Gračac is part of Zadar County, and it takes up about 12% of Croatia, Croatia's land area. Major towns include Gospić, Otočac, and Gračac, most of which are located in the karst poljes of the rivers of Lika (river), Lika, Gacka and others. The Plitvice Lakes National Park and Northern Velebit National Park are also in Lika. History Antiquity Since the first millennium BC the region was inhabited by the Iapodes, an ancient people related to Illyrians. During the Gallic invasion of the Balk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvarner
The Kvarner Gulf (, or ; ; or ) sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal waters. The largest islands within the Kvarner are Cres, Krk, Pag, Rab and Lošinj. A portion of the Kvarner Bay, located between Cres, Krk, Rab and Pag is also called (literally "little Kvarner"; or ), and the portion east of Krk and Rab is called Senj Channel (after the mainland town of Senj). The bay is notable for its depth (more than 100 meters), which allows for the city of Rijeka at its northernmost point to have a sea port that can accommodate Capesize ships. Environment The bay is home to many beaches and tourist locations because of its beautiful waters and warm climate. Important Bird Area Collectively, the islands of the Kvarner Gulf form the Kvarner Islands Important Bird Area (IBA), designated as such by BirdLife International because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first letters were invented in Ancient Egypt to serve as an aid in writing Egyptian hieroglyphs; these are referred to as Egyptian uniliteral signs by lexicographers. This system was used until the 5th century AD, and fundamentally differed by adding pronunciation hints to existing hieroglyphs that had previously carried no pronunciation information. Later on, these phonemic symbols also became used to transcribe foreign words. The first fully phonemic script was the Proto-Sinaitic script, also descending from Egyptian hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
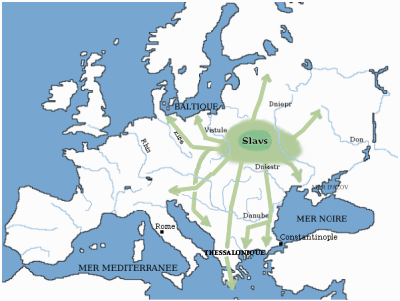
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glagolitic Script
The Glagolitic script ( , , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed that it was created in the 9th century for the purpose of translating liturgical texts into Old Church Slavonic by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzantine Emperor Michael III in 863 to Great Moravia after an invitation from Rastislav of Moravia to spread Christianity there. After the deaths of Cyril and Methodius, their disciples were expelled and they moved to the First Bulgarian Empire instead. The Early Cyrillic alphabet, which developed gradually in the Preslav Literary School by Greek alphabet scribes who incorporated some Glagolitic letters, gradually replaced Glagolitic in that region. Glagolitic remained in use alongside Latin in the Kingdom of Croatia and alongside Cyrillic until the 14th century in the Second Bulgarian Empire and the Serbian Empire, and later mainly for cryptographic purposes. Glagolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metonym
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something associated with that thing or concept. For example, the word "wikt:suit, suit" may refer to a person from groups commonly wearing business attire, such as salespeople or attorneys. Etymology The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come ; , a suffix that names figures of speech, . Background Metonymy and related figures of speech are common in everyday speech and writing. Synecdoche and metalepsis are considered specific types of metonymy. Polysemy, the capacity for a word or phrase to have multiple meanings, sometimes results from relations of metonymy. Both metonymy and metaphor involve the substitution of one term for another. In metaphor, this substitution is based on some specific analogy between two things, whereas in metonymy the substitution is based on some understood association or Contiguity (psychology), contiguity. American literary theorist Kenneth Burke considers metonymy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |