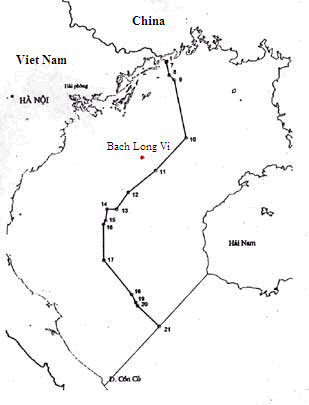
|
National Boundary Delimitation
In international law, national boundary delimitation (also known as national delimitation and boundary delimitation) is the process of legally establishing the outer limits ("borders") of a state within which full territorial or functional sovereignty is exercised. National delimitation involves negotiations surrounding the modification of a state's borders and often takes place as part of the negotiations seeking to end a conflict over resource control, popular loyalties, or political interests. Occasionally this is used when referring to the maritime boundaries, in which case it is called maritime delimitation. The term "maritime delimitation" is a form of national delimitation that can be applied to the disputes between nations over maritime claims. An example is found at Maritime Boundary Delimitation in the Gulf of Tonkin. In international politics, the Division for Ocean Affairs and the Law of the Sea ( Office of Legal Affairs, United Nations Secretariat) is responsible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Law
International law, also known as public international law and the law of nations, is the set of Rule of law, rules, norms, Customary law, legal customs and standards that State (polity), states and other actors feel an obligation to, and generally do, obey in their mutual relations. In international relations, actors are simply the individuals and collective entities, such as states, International organization, international organizations, and non-state groups, which can make behavioral choices, whether lawful or unlawful. Rules are formal, typically written expectations that outline required behavior, while norms are informal, often unwritten guidelines about appropriate behavior that are shaped by custom and social practice. It establishes norms for states across a broad range of domains, including war and diplomacy, Trade, economic relations, and human rights. International law differs from state-based List of national legal systems, domestic legal systems in that it operates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative division, subnational entities. Political borders can be established through warfare, colonization, or mutual agreements between the political entities that reside in those areas. Some borders—such as most states' internal administrative borders, or inter-state borders within the Schengen Area—are open border, open and completely unguarded. Most external political borders are partially or fully controlled, and may be crossed legally only at designated border checkpoints; adjacent Border control#Border zones, border zones may also be controlled. For the purposes of border control, airports and Port#Seaport, seaports are also classed as borders. Most countries have some form of border control to regulate or limit the movement of people, animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people and to change existing laws. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. ''De jure'' sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; '' de facto'' sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization. Etymology The term arises from the unattested Vulgar Latin *''superanus'' (itself a derived form of Latin ''super'' – "over") meaning "chief", "ruler". Its spellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Boundary
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boundaries Geodatabase General info retrieved 19 November 2010 encompassing maritime features, limits and zones.Geoscience Australia Maritime definitions retrieved 16 January 2023 Generally, a maritime boundary is delineated at a particular distance from a jurisdiction's coastline. Although in some countries the term ''maritime boundary'' represents borders of a maritime nation that are recognized by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, maritime borders usually serve to identify the edge of international waters. Maritime boundaries exist in the context of territorial waters, contiguous zones, and exclusive economic zones; however, the terminology does not encompass lake or river boundaries, which are considered within the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Delimitation
In international law, national boundary delimitation (also known as national delimitation and boundary delimitation) is the process of legally establishing the outer limits ("borders") of a state within which full territorial or functional sovereignty is exercised. National delimitation involves negotiations surrounding the modification of a state's borders and often takes place as part of the negotiations seeking to end a conflict over resource control, popular loyalties, or political interests. Occasionally this is used when referring to the maritime boundaries, in which case it is called maritime delimitation. The term "maritime delimitation" is a form of national delimitation that can be applied to the disputes between nations over maritime claims. An example is found at Maritime Boundary Delimitation in the Gulf of Tonkin. In international politics, the Division for Ocean Affairs and the Law of the Sea ( Office of Legal Affairs, United Nations Secretariat) is responsible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin ( northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern coastline of Vietnam down to the Cồn Cỏ district, in the north by China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, and to the east by the Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island. English sources from the People's Republic of China refer to the Gulf of Tonkin as Beibu Wan. Description and etymology The name ''Tonkin'', written "" in chữ Hán characters and in the Vietnamese alphabet, means "eastern capital", and is the former toponym for Hanoi, the present capital of Vietnam. It is not to be confused with Tokyo, which is also written "" and also means "eastern capital". During the French colonial era, the northern region of today’s Vietnam was called ''Tonkin''. ''Bắc Bộ'' is the native Vietnamese name of Tonkin, which is the nowad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division For Ocean Affairs And The Law Of The Sea
Division may refer to: Mathematics *Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication *Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division Military *Division (military), a formation typically consisting of 10,000 to 25,000 troops ** Divizion, a subunit in some militaries *Division (naval), a collection of warships Science *Cell division, the process in which biological cells multiply *Continental divide, the geographical term for separation between watersheds *Division (taxonomy), used differently in botany and zoology *Division (botany), a taxonomic rank for plants or fungi, equivalent to phylum in zoology *Division (horticulture), a method of vegetative plant propagation, or the plants created by using this method * Division, a medical/surgical operation involving cutting and separation, see ICD-10 Procedure Coding System Technology *Beam compass, a compass with a beam and sliding sockets for drawing and dividing circles larger than those made by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Office Of Legal Affairs
The United Nations Office of Legal Affairs (OLA) is a United Nations office currently administered by Under-Secretary-General for Legal Affairs and Legal Counsel of the United Nations Elinor Hammarskjöld. History Established in 1946, the United Nations Office of Legal Affairs provides a unified central legal service for the Secretariat and the principal and other organs of the United Nations and contributes to the progressive development and codification of international public and trade law. Pursuant to Article 102 of the UN Charter, OLA registers, publishes, and serves as a depository of international treaties. The office also functions to promote the strengthening and development as well as the effective implementation of the international legal order for the seas and ocean Units The Office consists of six Division (business), divisions: * Office of the Legal Counsel (OLC) * General Legal Division (GLD) * Codification Division (COD) * Division for Ocean Affairs and the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Secretariat
The United Nations Secretariat is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), The secretariat is the UN's executive arm. The secretariat has an important role in setting the agenda for the deliberative and decision-making bodies of the UN (i.e., the General Assembly, Economic and Social Council, and Security Council), and the implementation of the decision of these bodies. The secretary-general, who is appointed by the General Assembly, is the head of the secretariat. The mandate of the secretariat is a wide one. Dag Hammarskjöld, the UN's second secretary-general, described its power as follows: "The United Nations is what member nations made it, but within the limits set by government action and government cooperation, much depends on what the secretariat makes it. It has creative capacity. It can introduce new ideas. It can, in proper forms, take initiatives. It can put before member governments findings which will influence their actions". The United Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Delimitation In The Soviet Union
In the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), national delimitation was the process of specifying well-defined national territorial units (Soviet socialist republics [SSR], autonomous Soviet socialist republics [ASSR], autonomous oblasts [provinces], raions [districts] and ''okrugs'' [circuits]) from the ethnic diversity of the USSR and its subregions. The Russian-language term for this Soviet state policy was ''razmezhevanie'' (, ''natsionalno-territorialnoye razmezhevaniye''), which is variously translated in English-language literature as "national-territorial delimitation" (NTD), "demarcation", or "partition". National delimitation formed part of a broader process of changes in administrative-territorial division, which also changed the boundaries of territorial units, but was not necessarily linked to national or ethnic considerations. National delimitation in the USSR was distinct from nation-building (), which typically referred to the policies and actions implemented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nation-building
Nation-building is constructing or structuring a national identity using the power of the state. Nation-building aims at the unification of the people within the state so that it remains politically stable and viable. According to Harris Mylonas, "Legitimate authority in modern national states is connected to popular rule, to majorities. Nation-building is the process through which these majorities are constructed." In Mylonas's framework, "state elites employ three nation-building policies: accommodation, assimilation, and exclusion." Nation builders are those members of a state who take the initiative to develop the national community through government programs, including military conscription and national content mass schooling. Nation-building can involve the use of propaganda or major infrastructure development to foster social harmony and economic growth. According to Columbia University sociologist Andreas Wimmer, three factors tend to determine the success of nation-buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |