|
NForce3
The nForce3 chipset was created by Nvidia as a Media and Communications Processor. Specifically, it was designed for use with the Athlon 64 processor. Features of the nForce3 When the Athlon 64 was launched, the Nvidia nForce3 Pro150 and VIA K8T800 were the only two chipsets available. The 150 chipset was widely criticized at launch for using a 600 MHz HyperTransport interface, when VIA had implemented the full AMD specification at 800 MHz, even though overall performance of the 150 was still good. Later revisions fixed this omission, and using a HyperTransport interface, the nForce3 chipset is able to communicate at up to 8 GB/s with the CPU. This reduces system bottlenecks when using high-bandwidth devices. For example, the Gigabit Ethernet transmits at 125 MB/s; if the Ethernet were not on the chipset, a saturated gigabit Ethernet link would use 93% of the bandwidth of the shared 133 MB/s PCI bus. The 150 also noticeably lacked features. Subsequent revisions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Nvidia Chipsets
This is a comparison of chipsets designed by Nvidia. Nvidia stopped producing chipsets in 2009. Nvidia codenames its chipsets MCPs (Media and Communications Processors). nForce nForce nForce Southbridges nForce2 nForce2 nForce2 Southbridges nForce3 The memory controller is integrated into the CPU, the supported memory types depend on the CPU and socket used. nForce4 For AMD processors The memory controller is integrated into the CPU, the supported memory types depend on the CPU and socket used. For Intel processors (LGA 775) nForce 400 ( GeForce 6000) The memory controller is integrated into the CPU, the supported memory types depend on the CPU and socket used. List is incomplete because multiple variants of 410 and 430 exist. nForce 500 Series For AMD processors The memory controller is integrated into the CPU, the supported memory types depend on the CPU and socket used. For Intel processors nForce 600 (GeForce 7000) Series F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NForce4
The nForce4 is a motherboard chipset released by Nvidia in October 2004. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors (Socket 939, Socket AM2 and Socket 754) and Intel Pentium 4 LGA 775 processors. Models nForce4/nForce4-4x nForce4 is the second evolution of the Media Communications Processor (MCP) and incorporates both Northbridge and Southbridge on a single die (the first was nForce3). The Socket 754 version of the board has the HyperTransport link clocked to 800 MHz (6.4 GB/s transfer rate). Motherboards based on early revisions are mostly referred to as "nForce4-4x" (relating with their ability to handle HT speeds of 4x). *Support for up to 20 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes (up to 38-40 lanes for the nForce4 SLI x16). Reference boards are set up with one x16 slot and three x1 slots, leaving 1 lane unused. *Support for up to 10 USB 2.0 ports. *Support for 4 SATA and 4 PATA drives, which can be linked together in any combination of SATA and PATA to form a RAID 0, 1, or 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ActiveArmor
The nForce4 is a motherboard chipset released by Nvidia in October 2004. The chipset supports AMD64, AMD 64-bit processors (Socket 939, Socket AM2 and Socket 754) and Intel Corporation, Intel Pentium 4 LGA 775 processors. Models nForce4/nForce4-4x nForce4 is the second evolution of the Media Communications Processor (MCP) and incorporates both Northbridge (computing), Northbridge and Southbridge (computing), Southbridge on a single Die (integrated circuit), die (the first was nForce3). The Socket 754 version of the board has the HyperTransport link clocked to 800 Hertz, MHz (6.4 GB/s transfer rate). Motherboards based on early revisions are mostly referred to as "nForce4-4x" (relating with their ability to handle HT speeds of 4x). *Support for up to 20 PCI Express (PCIe) lanes (up to 38-40 lanes for the nForce4 SLI x16). Reference boards are set up with one x16 slot and three x1 slots, leaving 1 lane unused. *Support for up to 10 Universal Serial Bus, USB 2.0 ports. *Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth, low-Memory latency, latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001. The HyperTransport Consortium is in charge of promoting and developing HyperTransport technology. HyperTransport is best known as the system bus architecture of AMD central processing units (CPUs) from Athlon 64 through AMD FX and the associated motherboard chipsets. HyperTransport has also been used by IBM and Apple Inc., Apple for the Power Mac G5 machines, as well as a number of modern MIPS architecture, MIPS systems. The current specification HTX 3.1 remained competitive for 2014 high-speed (2666 and 3200 megatransfer, MT/s or about 10.4 GB/s and 12.8 GB/s) DDR4 RAM and slower (around 1 GB/similar to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SoundStorm
SoundStorm is a brand by Nvidia referring to a SIP block integrating 5.1 surround sound technology found on the die of their nForce and nForce2 chipsets for x86 CPUs. It is also the name of a certification to be obtained from Nvidia when complying with their specifications. Certification The SoundStorm certification ensured that many manufacturers produced solutions with high quality sound output. To achieve SoundStorm certification, a motherboard had to use the nForce or nForce2 chipsets and also include the specified discrete outputs. It was also necessary to meet certain sound quality levels as tested by Dolby Digital sound labs. At the time SoundStorm was the only available solution capable of outputting Dolby Digital Live, coveted in home theater PCs. Hardware The SoundStorm SIP block is said to consist of a series of fixed-function and general-purpose processing units. A fully programmable, Motorola 56300-based digital signal processor (DSP) is provided for effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NForce2
The Nvidia nForce2 chipset was released by Nvidia in July 2002 as a refresh to the original nForce product offering. The nForce2 chipset was a platform for motherboards supporting AMD's Socket A CPUs along with DDR SDRAM. There were multiple variations of the chipset including one with an integrated GeForce4 MX graphics processor (IGP), and one without. Refresh In 2003, Nvidia released a refreshed nForce2, called "nForce2 Ultra 400". The nForce2 Ultra 400 and nForce2 400 presented official support for a 200 MHz FSB and PC-3200 DDR SDRAM, whereas the older nForce2 only supported a maximum of 166 MHz FSB. Ultra 400 offered dual-channel support, while the plain 400 was single-channel PC-3200-capable. Both performed very similarly because neither had the IGP. Athlon XP did not benefit significantly from the added bandwidth because the Athlon XP's bus was only capable of bandwidth matching a single channel of PC-3200. The new chipset was partnered with several different southb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northbridge (computing)
In computing, a northbridge (also host bridge, or memory controller hub) is a microchip that comprises the core logic chipset architecture on motherboards to handle high-performance tasks, especially for older personal computers. It is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB), and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. Historically, separation of functions between CPU, northbridge, and southbridge chips was necessary due to the difficulty of integrating all components onto a single chip die. However, as CPU speeds increased over time, a bottleneck emerged due to limitations caused by data transmission between the CPU and its support chipset. The trend for integrated northbridges began near the end of the 2000s for example, the Nvidia GeForce 320M GPU in the 2010 MacBook Air was a northbridge/southbridge/GPU combo chip. On older Intel based PCs, the northbridge was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
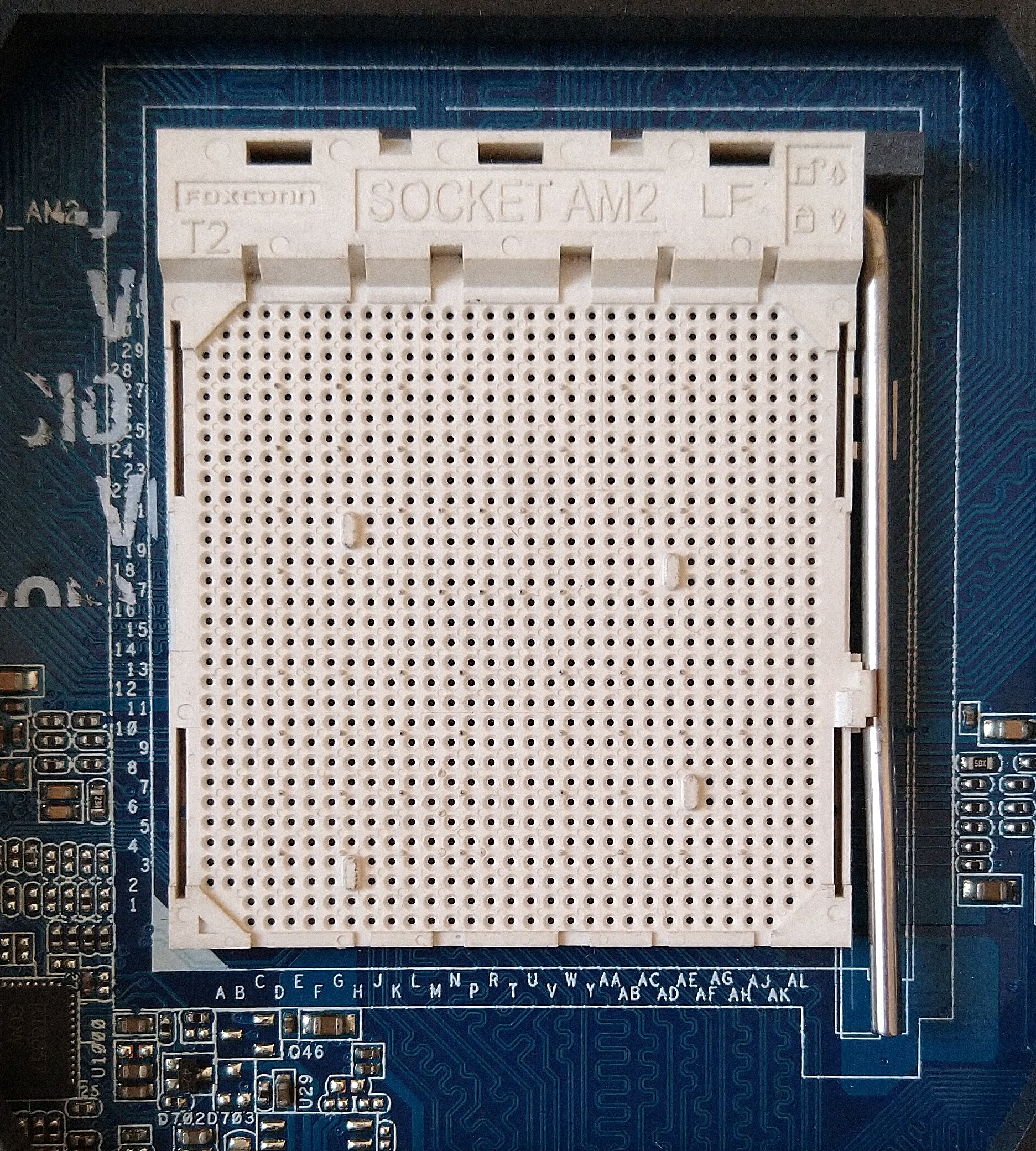
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as a replacement for Socket 939. Technical specifications AM2 processors are incompatible with 939 motherboards and vice versa, and although it has 940 pins, it is incompatible with Socket 940. Socket AM2 supports DDR2 SDRAM memory but not DDR memory, which the previous Socket 939 supported. ''AnandTech'' reported that Socket AM2 system performance was only about 7% faster than Socket 939 equivalents, with most applications about 2% faster, despite having over 30% greater memory bandwidth due to DDR2 support. The first processor cores to support socket AM2 were the single-core Orleans (Athlon 64) and Manila (Sempron), and the dual-core Windsor ( Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon 64 FX). Most processors on Socket AM2 include SSE3 instructions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Graphics Port
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is a parallel expansion card standard, designed for attaching a video card to a computer system to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP was progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe), which is serial, as opposed to parallel; by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express. Advantages over PCI AGP is a superset of the PCI standard, designed to overcome PCI's limitations in serving the requirements of the era's high-performance graphics cards. The primary advantage of AGP is that it doesn't share the PCI bus, providing a dedicated, point-to-point pathway between the expansion slot(s) and the motherboard chipset. The direct connection also allows higher clock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform. Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 under the codename "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it feature creep, gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redundant Array Of Independent Disks
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This is in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives known as ''single large expensive disk'' (''SLED''). Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as RAID levels, depending on the required level of redundancy and performance. The different schemes, or data distribution layouts, are named by the word "RAID" followed by a number, for example RAID 0 or RAID 1. Each scheme, or RAID level, provides a different balance among the key goals: reliability, availability, performance, and capacity. RAID levels greater than RAID 0 provide protection against unrecoverable sector read errors, as well as against failures of whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then released by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |