|
Myxopyronin
Myxopyronins (Myx) are a group of alpha-pyrone antibiotics, which are inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP). They target switch 1 and switch 2 of the RNAP "switch region". Rifamycins and fidaxomicin also target RNAP, but target different sites in RNAP. Myxopyronins do not have cross-resistance with any other drugs so myxopyronins may be useful to address the growing problem of drug resistance in tuberculosis. They also may be useful in treatment of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). They are in pre-clinical development and has not yet started clinical trial Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...s. Myxopyronin was first isolated in 1983 from a soil bacterium by Werner Kohl and Herbert Irschik at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrone
Pyrones or pyranones are a class of heterocyclic chemical compounds. They contain an unsaturated six-membered ring, which has one oxygen atom and a carbonyl functional group. There are two isomers, denoted as 2-pyrone and 4-pyrone. The 2-pyrone (or α-pyrone) structure is a lactone and is found in nature as part of the coumarin ring system. The 4-pyrone (or γ-pyrone) structure is an ether–ketone found in some natural chemical compounds such as chromone, maltol and kojic acid. See also * Furanone 2-Furanone is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is also known as γ-crotonolactone (GCL), as it is formally the lactone derived from γ-hydroxy isocrotonic acid. The chemical is colloquially called "butenolide", and is the parent structure for ..., which has one fewer carbon atom in the ring. * Pyridones, which contain a nitrogen in place of the oxygen that is part of the ring References {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifamycin
The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium '' Amycolatopsis rifamycinica'' or artificially. They are a subclass of the larger family of ansamycins. Rifamycins are particularly effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used to treat tuberculosis, leprosy, and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections. The rifamycin group includes the classic rifamycin drugs as well as the rifamycin derivatives rifampicin (or rifampin), rifabutin, rifapentine, rifalazil and rifaximin. Rifamycin, sold under the trade name Aemcolo, is approved in the United States for treatment of travelers' diarrhea in some circumstances. The name "rifamycin" (originally "rifomycin") was derived from the 1955 French film ''Rififi''. Bacterium ''Streptomyces mediterranei'' was first isolated in 1957 from a soil sample collected near the beach-side town of St Raphael in southern France. The name was originally given by two microbiologists wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fidaxomicin
Fidaxomicin, sold under the brand name Dificid (by Merck) among others, is the first member of a class of narrow spectrum macrocyclic antibiotic drugs called tiacumicins. It is a fermentation product obtained from the actinomycete '' Dactylosporangium aurantiacum'' subspecies ''hamdenesis''. Fidaxomicin is minimally absorbed into the bloodstream when taken orally, is bactericidal, and selectively eradicates pathogenic ''Clostridioides difficile'' with relatively little disruption to the multiple species of bacteria that make up the normal, healthy intestinal microbiota. The maintenance of normal physiological conditions in the colon may reduce the probability of recurrence of ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection. It is marketed by Merck, which acquired Cubist Pharmaceuticals in 2015, and had in turn bought the originating company, Optimer Pharmaceuticals. It is used for the treatment of ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection, which is also known as ''Clostridioides dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-resistance
Cross-resistance is when something develops resistance to several substances that have a similar mechanism of action. For example, if a certain type of bacteria develops antimicrobial resistance to one antibiotic, that bacteria will also have resistance to several other antibiotics that target the same protein or use the same route to get into the bacterium. A real example of cross-resistance occurred for nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin, which are both quinolone antibiotics. When bacteria developed resistance to ciprofloxacin, they also developed resistance to nalidixic acid because both drugs inhibit topoisomerase, a key enzyme in DNA replication. Due to cross-resistance, antimicrobial treatments like phage therapy can quickly lose their efficacy against bacteria. This makes cross-resistance an important consideration in designing evolutionary therapies. Definition Cross-resistance is the idea is that the development of resistance to one substance subsequently leads to resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
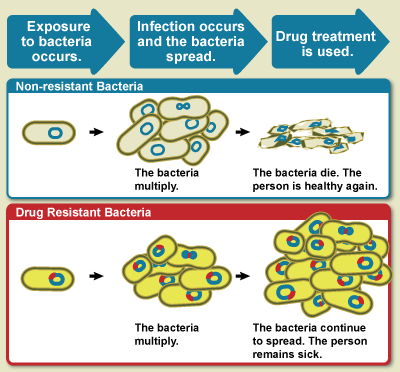
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans – leading to development of super-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths worldwide attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through mutation) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA infection is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-clinical Development
In drug development, preclinical development (also termed preclinical studies or nonclinical studies) is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials (testing in humans) and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data are collected, typically in laboratory animals. The main goals of preclinical studies are to determine a starting, safe dose for first-in-human study and assess potential toxicity of the product, which typically include new medical devices, prescription drugs, and diagnostics. Companies use stylized statistics to illustrate the risks in preclinical research, such as that on average, only one in every 5,000 compounds that enters drug discovery to the stage of preclinical development becomes an approved drug. Types Each class of product may undergo different types of preclinical research. For instance, drugs may undergo pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body) (PD), pharmacokinetics (what the body does to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard H
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include " Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Ander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog, also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a chemical compound, compound having a chemical structure, structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronicity, isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analog (chemistry), functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is virtual screening, screened for structural analogs of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |