|
Myopia In Animals
Some animals suffer from shortsightedness and have poor eyesight. In domestic animals, myopia, with or without astigmatism, occurs frequently. In rhinoceroses Whereas the rhinoceros may suffer from less-than-adequate eyesight, it generally survives by concentrating with its superior hearing and sense of smell. Some reports, however state that it can see better when focusing with one eye, particularly when walking, posturing, and combatting. Research Myopia, with or without astigmatism, is the most common eye condition in horses. Several types of occlusion myopia have been recorded in tree shrews, macaques, cats and rats, deciphered from several animal-inducing myopia models. Preliminary laboratory investigations using retinoscopy of 240 dogs found myopic problems with varying degrees of refraction errors depending on the breed. In cases involving German Shepherds, Rottweilers and Miniature horses, the refraction errors were indicative of myopia. Nuclear sclerosis of the crysta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
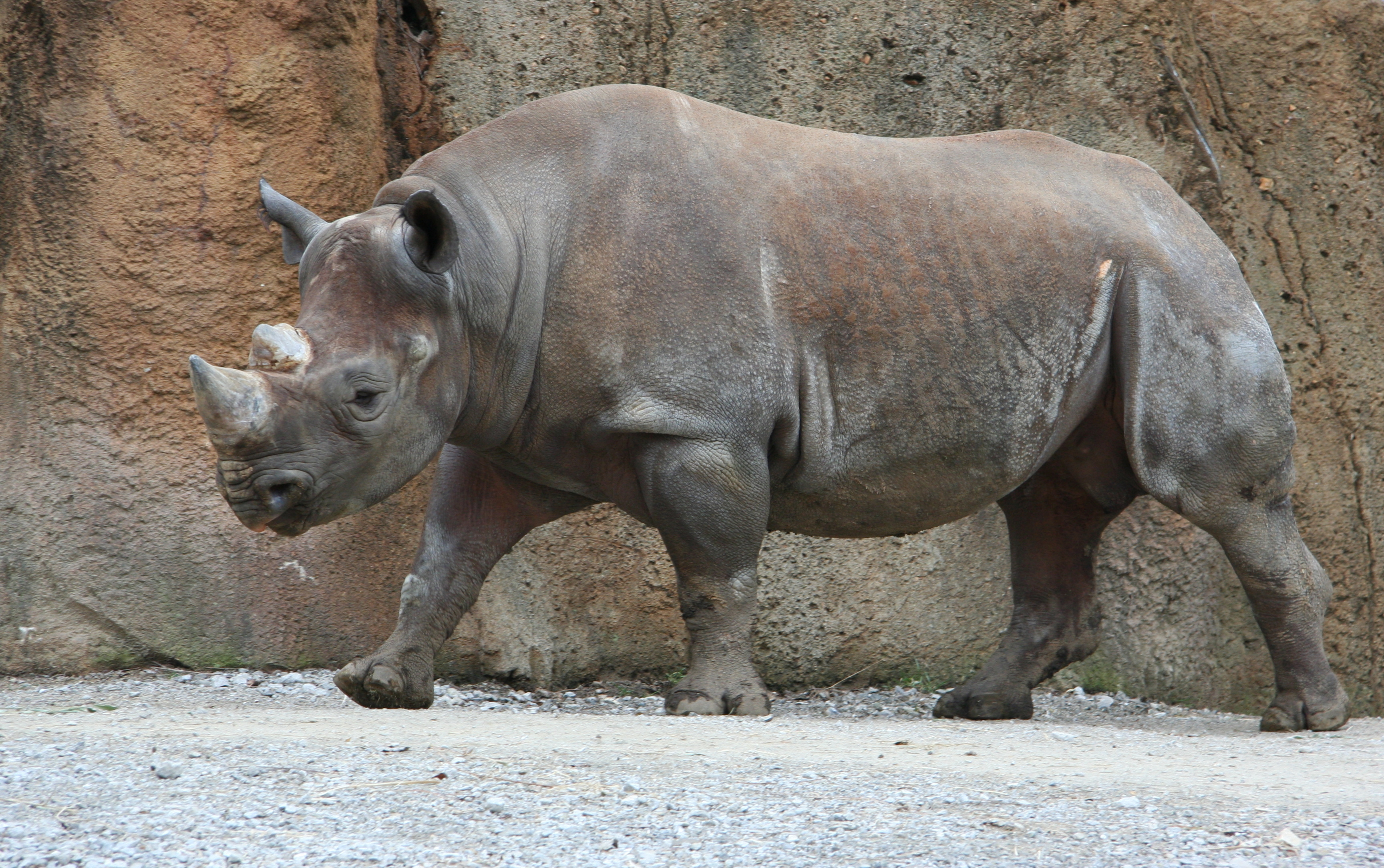
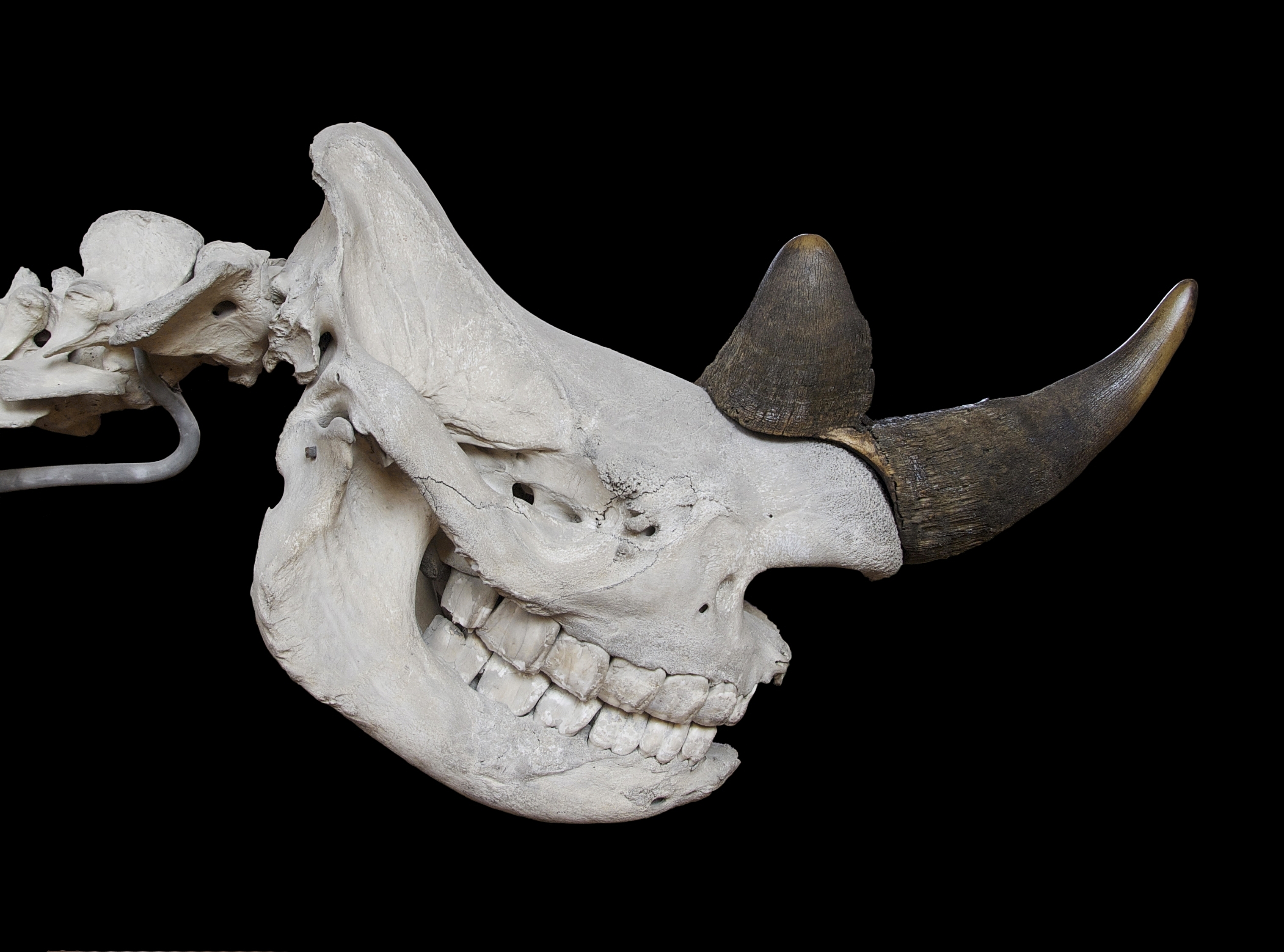
Diceros Bicornis
The black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis''), also called the black rhino or the hooked-lip rhinoceros, is a species of rhinoceros native to East and Southern Africa, including Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the species is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. It is the only extant species of the genus '' Diceros''. The other rhinoceros native to Africa is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' ( Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism (eye)
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors present can be corrected with simple glasses. In an eye with astigmatism, either the lens or the cornea is slightly egg-shaped, with higher curvature in one direction than the other. This gives distorted or blurred vision at any distance and requires corrective lenses that apply different optical powers at different rotational angles. Astigmatism can lead to symptoms that include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often is present at birth, but can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear, although it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Shrews
The treeshrews (also called tree shrews or banxrings) are small mammals native to the tropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. They make up the entire order Scandentia (from Latin ''scandere'', "to climb"), which split into two families: the Tupaiidae (19 species, "ordinary" treeshrews), and the Ptilocercidae (one species, the pen-tailed treeshrew). Though called 'treeshrews', and despite having previously been classified in Insectivora, they are not true shrews, and not all species live in trees. They are omnivores; among other things, treeshrews eat fruit. As fellow members of Euarchonta, treeshrews are closely related to primates, and have been used as an alternative to primates in experimental studies of myopia, psychosocial stress, and hepatitis. Description Treeshrews are slender animals with long tails and soft, greyish to reddish-brown fur. The terrestrial species tend to be larger than the arboreal forms, and to have larger claws, which they use for digging up i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macaques
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and Europe (in Gibraltar). Macaques are principally frugivorous (preferring fruit), although their diet also includes seeds, leaves, flowers, and tree bark. Some species such as the long-tailed macaque (''M. fascicularis''; also called the crab-eating macaque) will supplement their diets with small amounts of meat from shellfish, insects, and small mammals. On average, a southern pig-tailed macaque (''M. nemestrina'') in Malaysia eats about 70 large rats each year. All macaque social groups are arranged around dominant matriarchs. Macaques are found in a variety of habitats throughout the Asian continent and are highly adaptable. Certain species are synanthropic, having learned to live alongside humans, but they have become problematic in urban areas in Southeast Asia and are not suitable t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is a technique to obtain an objective measurement of the refractive error of a patient's eyes. How It Works The examiner uses a retinoscope to shine light into the patient's eye and observes the reflection (reflex) off the patient's retina. While moving the streak or spot of light through the pupil across the retina, the examiner observes the relative movement of the reflex or manually places lenses over the eye (using a phoropter or trial frame and trial lenses) to "neutralize" the reflex. Static Retinoscopy Static retinoscopy is a type of retinoscopy used in determining a patient's refractive error. It relies on Foucault knife-edge test, which states that the examiner should simulate optical infinity to obtain the correct refractive power. Hence, a power corresponding to the working distance is subtracted from the gross retinoscopy value to give the patient's refractive condition, the working distance lens being one which has a focal length of the examiner' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Shepherd
The German Shepherd, also known in Britain as an Alsatian, is a German Dog breed, breed of working dog of medium to large size. The breed was developed by Max von Stephanitz using various Old German herding dogs, traditional German herding dogs from 1899. It was originally bred as a herding dog, for herding sheep. It has since been used in many other types of work, including Assistance dog, disability assistance, search-and-rescue, Police dog, police work, and Dogs in warfare, warfare. It is commonly kept as a companion dog, and according to the Fédération Cynologique Internationale had the second-highest number of annual registrations in 2013. History During the 1890s, attempts were being made to standardise dog breeds. Dogs were being bred to preserve traits that assisted in their job of herding sheep and protecting their flocks from predators. In Germany this was practised within local communities, where shepherds selected and bred dogs. It was recognised that the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rottweiler
The Rottweiler (, , ) is a breed of domestic dog, regarded as medium-to-large or large. The dogs were known in German as , meaning Rottweil butchers' dogs, because their main use was to herd livestock and pull carts laden with butchered meat to market. This continued until the mid-19th century when railways replaced droving. Although still used to herd stock in many parts of the world, Rottweilers are now also used as search and rescue dogs, guard dogs, and police dogs.Adolf Pienkoss, ''The Rottweiler'', 3rd ed., Borken, Germany: Internationale Föderation der Rottweilerfreunde, 2008. History According to the FCI Standard, the Rottweiler is considered to be one of the oldest surviving dog breeds. Its origin goes back to Roman times. These dogs were kept as herder or driving dogs. They marched over the Alps with the Roman legions, protecting the humans and driving their cattle. In the region of Rottweil, these dogs met and mixed with the native dogs in a natural crossing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
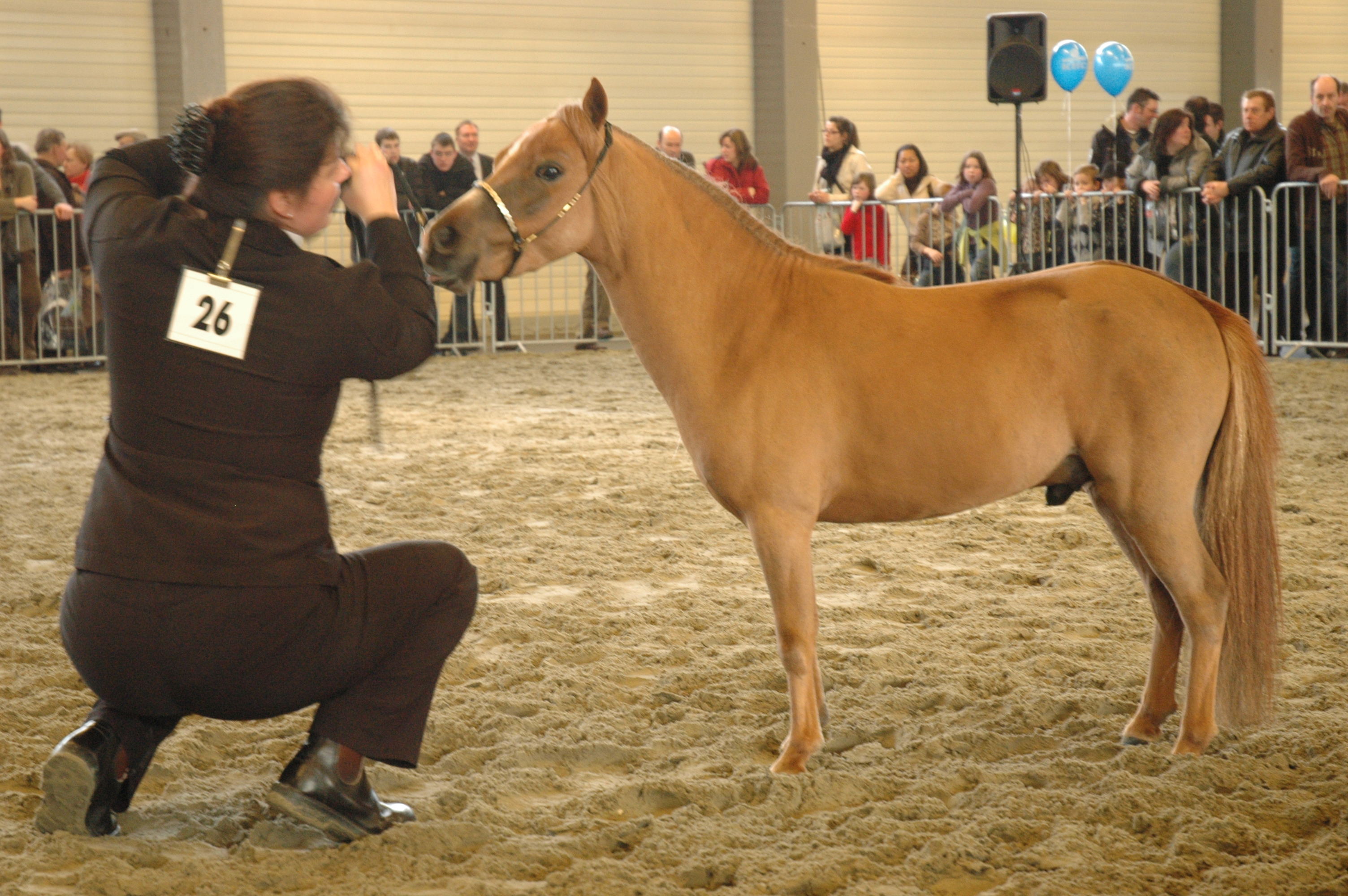
Miniature Horse
A miniature horse is a breed or type of horse characterised by its small size. Usually it has been bred to display in miniature the physical characteristics of a full-sized horse, but to be little over in height, or even less. Although such horses have the appearance of small horses, they are genetically much more similar to pony breeds such as the Shetland. They have various colors and coat patterns. Miniature horses are present in several countries, including Argentina, Australia, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Ireland, Namibia, the Philippines, the United Kingdom and the United States. In some countries they have the status of a breed; these include the Falabella of Argentina, the Dutch Miniature or , the South African Miniature Horse and the American Miniature Horse. They are commonly kept as companion animals, or for sporting activities such as driving or other competitive horse show events. A few have been trained as guide horses for blind people. History Minia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Sclerosis
Nuclear sclerosis is an age-related change in the density of the crystalline lens nucleus that occurs in all older animals. It is caused by compression of older lens fibers in the nucleus by new fiber formation. The denser construction of the nucleus causes it to scatter light. Although nuclear sclerosis may describe a type of early cataract in human medicine,Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. in veterinary medicine the term is also known as lenticular sclerosis and describes a bluish-grey haziness at the nucleus that usually does ''not'' affect vision, except for unusually dense cases. Immature senile cataract has to be differentiated with nuclear sclerosis while making its diagnosis. Veterinary medicine In veterinary practice, nuclear sclerosis is a consistent finding in dogs greater than six years old. Nuclear sclerosis appears as a bilateral bluish-grey haziness at the nucleus, or center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystalline Lens
The lens, or crystalline lens, is a Transparency and translucency, transparent Biconvex lens, biconvex structure in most land vertebrate eyes. Relatively long, thin fiber cells make up the majority of the lens. These cells vary in architecture and are arranged in concentric layers. New layers of cells are recruited from a thin epithelium at the front of the lens, just below the basement membrane surrounding the lens. As a result the vertebrate lens grows throughout life. The surrounding lens membrane referred to as the lens capsule also grows in a systematic way, ensuring the lens maintains an optically suitable shape in concert with the underlying fiber cells. Thousands of suspensory ligaments are embedded into the capsule at its largest diameter which suspend the lens within the eye. Most of these lens structures are derived from the epithelium of the embryo before birth. Along with the cornea, aqueous humour, aqueous, and vitreous humours, the lens Refraction, refracts light, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macaque
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and Europe (in Gibraltar). Macaques are principally frugivorous (preferring fruit), although their diet also includes seeds, leaves, flowers, and tree bark. Some species such as the long-tailed macaque (''M. fascicularis''; also called the crab-eating macaque) will supplement their diets with small amounts of meat from shellfish, insects, and small mammals. On average, a southern pig-tailed macaque (''M. nemestrina'') in Malaysia eats about 70 large rats each year. All macaque social groups are arranged around dominant matriarchs. Macaques are found in a variety of habitats throughout the Asian continent and are highly adaptable. Certain species are synanthropic, having learned to live alongside humans, but they have become problematic in urban areas in Southeast Asia and are not suitabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron, an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |