|
Myometrium
The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes) but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions. Structure The myometrium is located between the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterine wall) and the serosa or perimetrium (the outer uterine layer). The myometrium can be divided into three layers: * The inner one-third thickness is termed the ''junctional'' or ''sub-endometrial'' layer. In most mammals it is characterized by fibers oriented in a circular way. Humans, having a single uterus form the fusion of two Müllerian ducts, have the fibers forming two cones. Mice have an unfused uterus, so the arrangement is simply circular. * The middle layer occurs in both mice and humans. In mice it is a hard-to-spot mesh-like structure that probably helps coordinate the forces from the inner and outer layers. In humans there is also a mesh-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Contraction
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that can occur at various intensities in both the non-pregnant and pregnant uterine state. The non-pregnant uterus undergoes small, spontaneous contractions in addition to stronger, coordinated contractions during the menstrual cycle and orgasm. Throughout gestation, the uterus enters a state of uterine quiescence due to various neural and hormonal changes. During this state, the uterus undergoes little to no contractions, though spontaneous contractions still occur for the uterine myocyte cells to experience hypertrophy. The pregnant uterus only contracts strongly during orgasms, labour, and in the postpartum stage to return to its natural size. Throughout menstrual cycle Uterine contractions that occur throughout the menstrual cycle, also termed ''endometrial waves'' or ''contractile waves'', appear to involve only the sub- endometrial layer of the myometrium. Follicular and luteal phase In the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
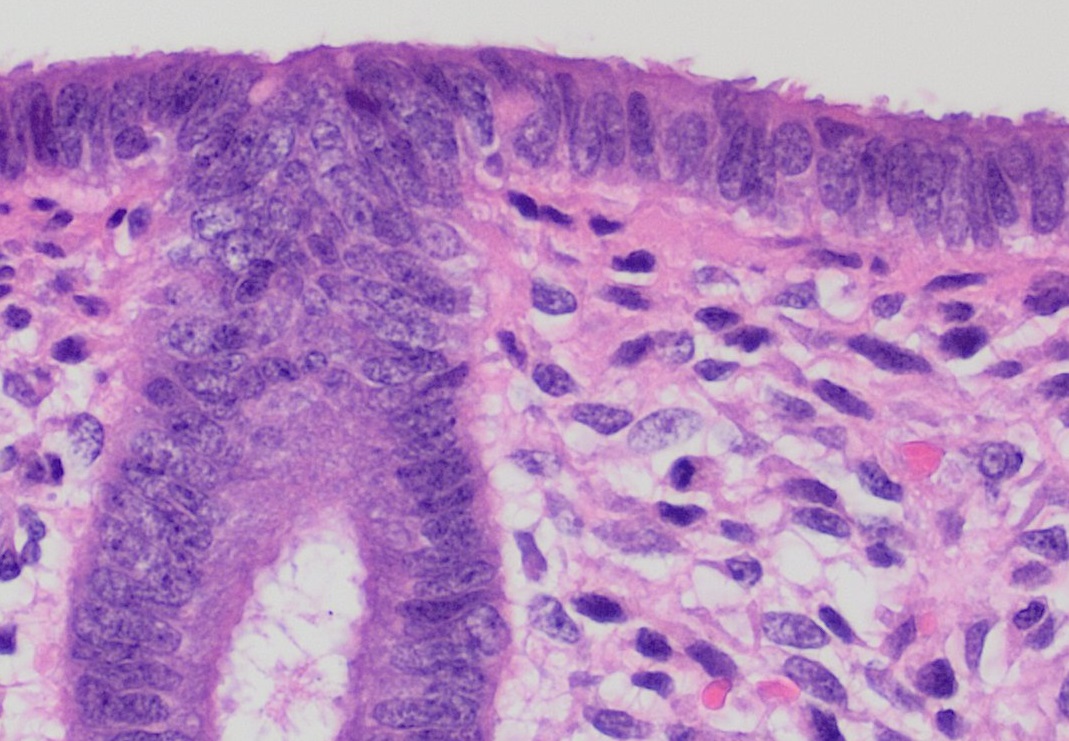
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including other apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferguson Reflex
The Ferguson reflex (also called the fetal ejection reflex) is the neuroendocrine reflex comprising the self-sustaining cycle of uterine contractions initiated by pressure at the cervix, more precisely, the internal end of cervix, or vaginal walls. It is an example of positive feedback in biology. The Ferguson reflex occurs in mammals. Mechanism Upon application of pressure to the internal end of the cervix, oxytocin is released (therefore increase in contractile proteins), which stimulates uterine contractions, which in turn increases pressure on the cervix (thereby increasing oxytocin release, etc.), until the baby is delivered. Sensory information regarding mechanical stretch of the cervix is carried in a sensory neuron, which synapses in the dorsal horn before ascending to the brain in the anterolateral columns (ipsilateral and contralateral routes). Via the medial forebrain bundle, the efferent reaches the PVN and SON of the hypothalamus. The posterior pituitary relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Wave Potential
A slow-wave potential is a rhythmic electrophysiological event in the gastrointestinal tract. The normal conduction of slow waves is one of the key regulators of gastrointestinal motility. Slow waves are generated and propagated by a class of pacemaker cells called the interstitial cells of Cajal, which also act as intermediates between nerves and smooth muscle cells. Slow waves generated in interstitial cells of Cajal spread to the surrounding smooth muscle cells and control motility. Description In the human enteric nervous system, the slow-wave threshold is the slow-wave potential which must be reached before a slow wave can be propagated in smooth muscle of the gut wall. When the amplitude of slow waves in smooth muscle cells reaches the slow-wave threshold — the L-type Ca2+ channels are activated, resulting in calcium influx and initiation of motility. Slow waves are generated at unique intrinsic frequencies by the interstitial Cajal cells, even within the same organ. Ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efflux (microbiology)
An efflux pump is an Active transport, active transporter in cells that moves out unwanted material. Efflux pumps are an important component in bacteria, particularly in their ability to remove antibiotics. The efflux process can also involve the movement of heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites, and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that encode efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species, the most concerning being antibiotic resistance, as microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual ( endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
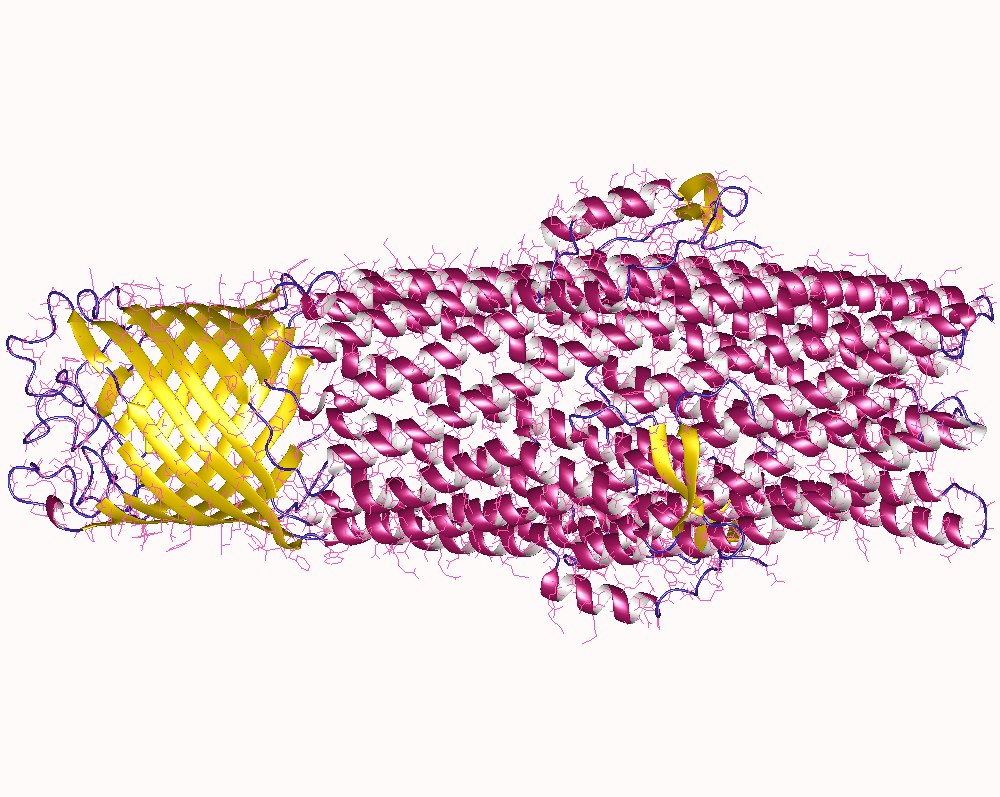
Potassium Channel
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracellular Space
Intracellular space is the interior space of the plasma membrane The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr .... It contains about two-thirds of TBW. Cellular rupture may occur if the intracellular space becomes dehydrated, or if the opposite happens, where it becomes too bloated. Thus it is important for the liquid to stay in optimal quantity. See also * Extracellular space References {{Cellular structures Cell anatomy Cell biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |