|
Myogenic Hyperuricemia
The myogenic mechanism is how arteries and arterioles react to an increase or decrease of blood pressure to keep the blood flow constant within the blood vessel. Myogenic response refers to a contraction initiated by the myocyte itself instead of an outside occurrence or stimulus such as nerve innervation. Most often observed in (although not necessarily restricted to) smaller resistance arteries, this 'basal' myogenic tone may be useful in the regulation of organ blood flow and peripheral resistance, as it positions a vessel in a preconstricted state that allows other factors to induce additional constriction or dilation to increase or decrease blood flow. The smooth muscle of the blood vessels reacts to the stretching of the muscle by opening ion channels, which cause the muscle to depolarize, leading to muscle contraction. This significantly reduces the volume of blood able to pass through the lumen, which reduces blood flow through the blood vessel. Alternatively when the sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic scale, macroscopic level, and histology, microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic circulation, systemic arteries, carrying blood from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch-activated Ion Channel
Mechanosensitive channels (MSCs), mechanosensitive ion channels or stretch-gated ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are present in the membranes of organisms from the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. They are the sensors for a number of systems including the senses of touch, hearing and balance, as well as participating in cardiovascular regulation and osmotic homeostasis (e.g. thirst). The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes. All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
In the renal physiology, physiology of the kidney, tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) is a feedback system inside the kidneys. Within each nephron, information from the nephron#Renal tubule, renal tubules (a downstream area of the tubular fluid) is signaled to the Glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus (an upstream area). Tubuloglomerular feedback is one of several mechanisms the kidney uses to regulate glomerular filtration rate (GFR). It involves the concept of purinergic signaling, in which an increased distal tubular sodium chloride concentration causes a basolateral release of adenosine from the macula densa cells. This initiates a cascade of events that ultimately brings GFR to an appropriate level. Background The kidney maintains the electrolyte concentrations, osmolality, and acid-base balance of blood plasma within the narrow limits that are compatible with effective cellular function; and the kidney participates in blood pressure regulation and in the maintenance of steady whole-org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow-wave Potential
A slow-wave potential is a rhythmic electrophysiological event in the gastrointestinal tract. The normal conduction of slow waves is one of the key regulators of gastrointestinal motility. Slow waves are generated and propagated by a class of pacemaker cells called the interstitial cells of Cajal, which also act as intermediates between nerves and smooth muscle cells. Slow waves generated in interstitial cells of Cajal spread to the surrounding smooth muscle cells and control motility. Description In the human enteric nervous system, the slow-wave threshold is the slow-wave potential which must be reached before a slow wave can be propagated in smooth muscle of the gut wall. When the amplitude of slow waves in smooth muscle cells reaches the slow-wave threshold — the L-type Ca2+ channels are activated, resulting in calcium influx and initiation of motility. Slow waves are generated at unique intrinsic frequencies by the interstitial Cajal cells, even within the same organ. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resting Membrane Potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential has a value of approximately −70 mV or −0.07 V. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Because the membrane pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
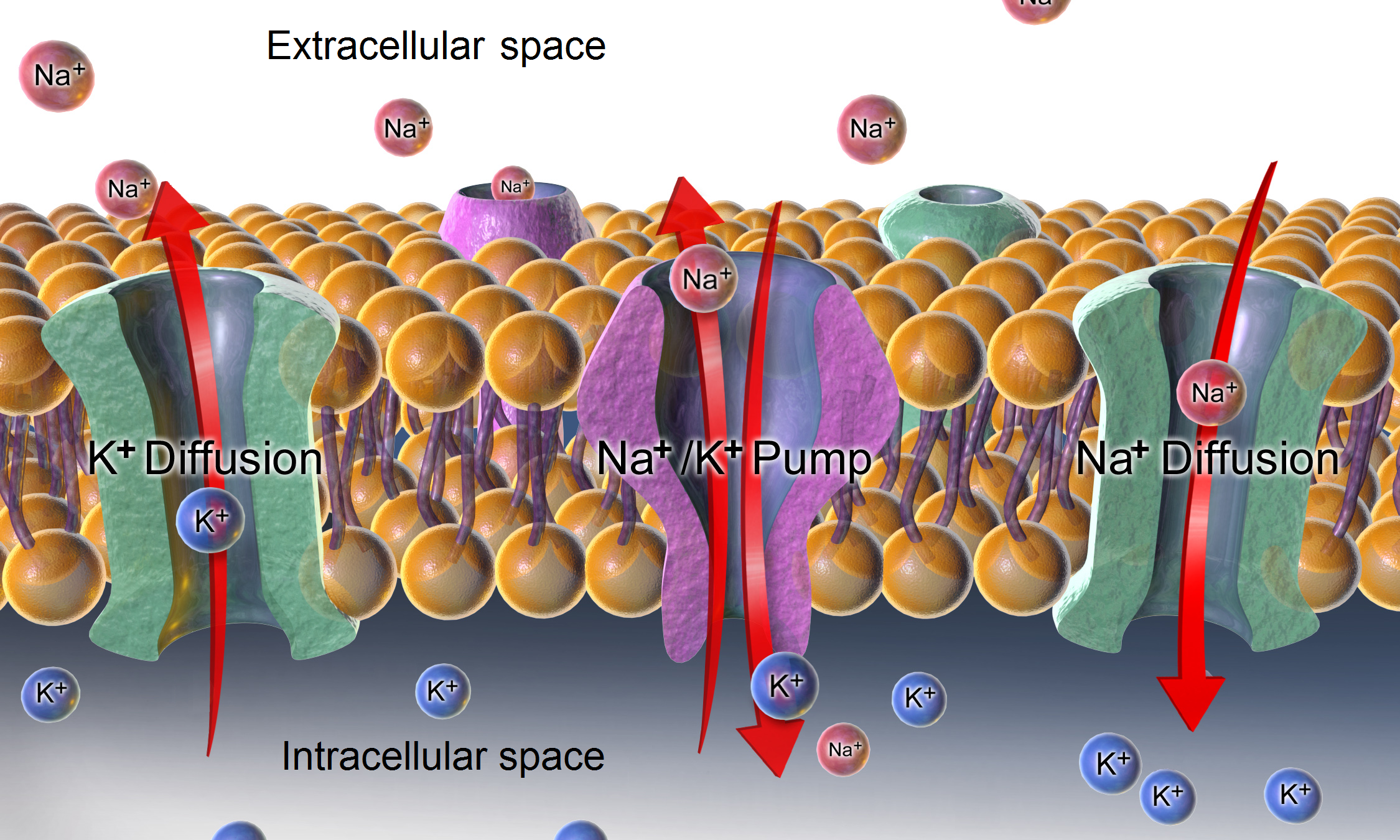
Cation Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: # The rate of ion transport thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride Channel
Chloride channels are a superfamily of poorly understood ion channels specific for chloride. These channels may conduct many different ions, but are named for chloride because its concentration ''in vivo'' is much higher than other anions. Several families of voltage-gated ion channel, voltage-gated channels and ligand-gated ion channel, ligand-gated channels (e.g., the CaCC families) have been characterized in humans. Voltage-gated chloride channels perform numerous crucial physiological and cellular functions, such as controlling pH, volume homeostasis, transporting organic solutes, regulating cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Based on sequence homology the chloride channels can be subdivided into a number of groups. General functions Voltage-gated chloride channels are important for setting cell resting membrane potential and maintaining proper cell volume. These channels conduct or other anions such as . The structure of these channels are not like other k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrine Signalling
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain. Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flow), and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic artery, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bayliss
Sir William Maddock Bayliss (2 May 1860 – 27 August 1924) was an English physiologist. Life He was born in Wednesbury, Staffordshire but shortly thereafter his father, a successful merchant of ornamental ironwork, moved his family to a house he had built on West Heath Road in Hampstead in north London, which he named St Cuthberts. It stood in four acres of gardens. William was his sole heir. He began to study medicine at University College London in 1880, but dropped out when he failed anatomy. Attracted to physiology, he studied under John Burdon Sanderson at Wadham College, Oxford, where he won a first class degree, investigating electrical changes occurring during salivary secretion. He returned to University College London in 1888 as an assistant to Edward Sharpey-Schafer. In 1890 he began to collaborate with Ernest Starling, who was at Guy's Hospital, on the electrical activity of the heart. They complemented each other in many ways: for instance, Bayliss dealt wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system functions to regulate the body's unconscious actions. The sympathetic nervous system's primary process is to stimulate the body's fight or flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basic level to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system is described as being antagonistic to the parasympathetic nervous system. The latter stimulates the body to "feed and breed" and to (then) "rest-and-digest". The SNS has a major role in various physiological processes such as blood glucose levels, body temperature, cardiac output, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by a single Ventricle (heart), ventricle of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula: :CO = HR \times SV Values for cardiac output are usually denoted as L/min. For a healthy individual weighing 70 kg, the cardiac output at rest averages about 5 L/min; assuming a heart rate of 70 beats/min, the stroke volume would be approximately 70 mL. Because cardiac output is related to the quantity of blood delivered to various parts of the body, it is an important com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |