|
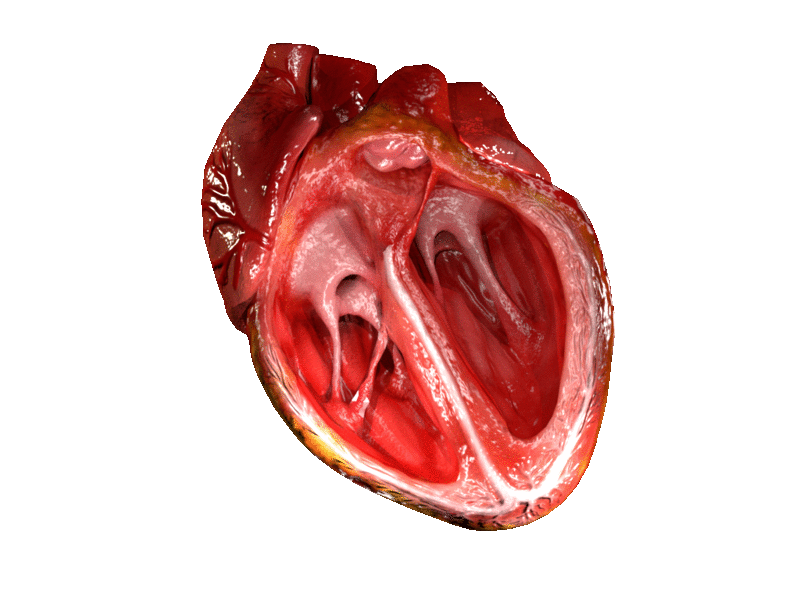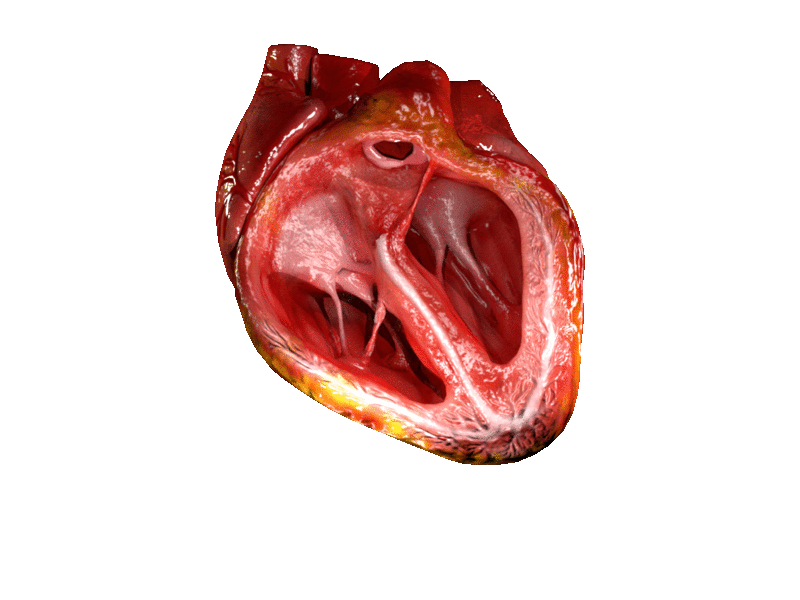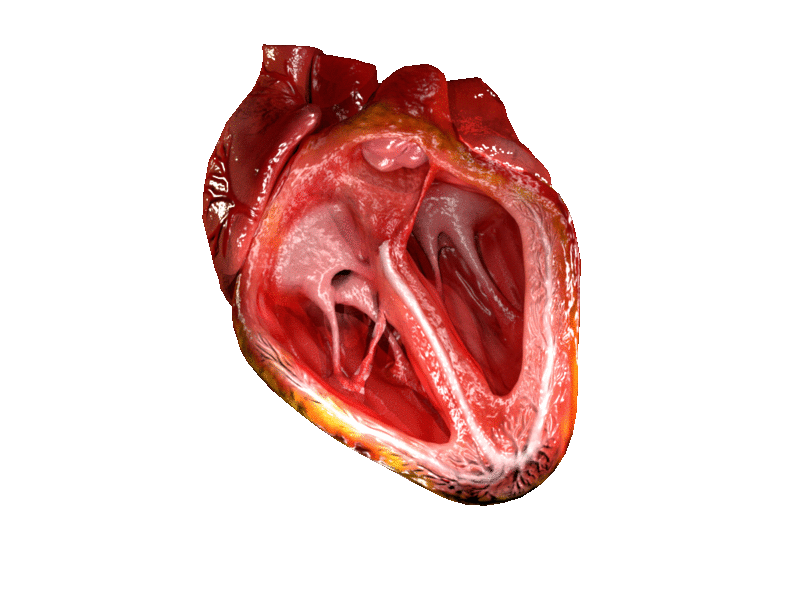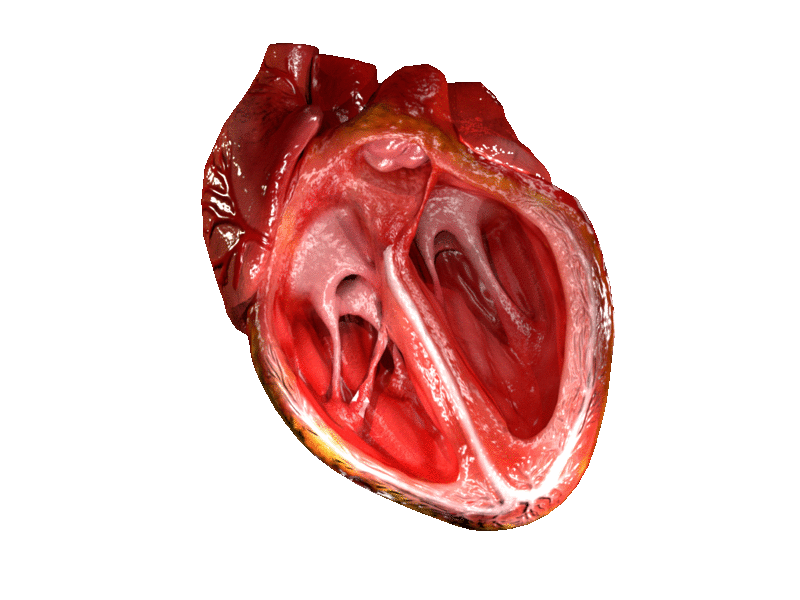
Myocardial Fibrosis
Cardiac fibrosis commonly refers to the excess deposition of extracellular matrix in the cardiac muscle, but the term may also refer to an abnormal thickening of the heart valves due to inappropriate proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts. Fibrotic cardiac muscle is stiffer and less compliant and is seen in the progression to heart failure. The description below focuses on a specific mechanism of valvular pathology but there are other causes of valve pathology and fibrosis of the cardiac muscle. Fibrocyte cells normally secrete collagen, and function to provide structural support for the heart. When over-activated this process causes thickening and fibrosis of the valve, with white tissue building up primarily on the tricuspid valve, but also occurring on the pulmonary valve. The thickening and loss of flexibility eventually may lead to valvular dysfunction and right-sided heart failure. Types Following are types of myocardial fibrosis: * Interstitial fibrosis, which is unspecific, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Management Of Parkinson's Disease
In the management of Parkinson's disease, due to the chronic nature of Parkinson's disease (PD), a broad-based program is needed that includes patient and family education, support-group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, no cure for the disease is known, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms. While many medications treat Parkinson's, none actually reverses the effects of the disease. Furthermore, the gold-standard treatment varies with the disease state. People with Parkinson's, therefore, often must take a variety of medications to manage the disease's symptoms. Several medications currently in development seek to better address motor fluctuations and nonmotor symptoms of PD. However, none is yet on the market with specific approval to treat Parkinson's. Medication The main families of drugs useful for treating motor symptoms are levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors. The most commonly used treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dopamine Receptor
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein (dopamine receptor-interacting proteins) interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors. Dopamine receptors are implicated in many neurological processes, including motivational and incentive salience, cognition, memory, learning, and fine motor control, as well as modulation of neuroendocrine signaling. Abnormal dopamine receptor signaling and dopaminergic nerve function is implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Thus, dopamine receptors are common neurologic drug targets; antipsychotics are often dopamine receptor antagonists while psychostimulants are typically indirect agonists of dopamine receptors. Subtypes The existence of multiple types of receptors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Methysergide
Methysergide, sold under the brand names Deseril and Sansert, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline and lysergamide groups which is used in the prophylaxis and treatment of migraine and cluster headaches. It has been withdrawn from the market in the United States and Canada due to safety concerns. It is taken by mouth. The drug is a prodrug of methylergometrine (methylergonovine), which circulates at levels about 10times higher than those of methysergide during treatment with methysergide. Whereas methysergide is a mixed agonist of some serotonin receptors (e.g., the 5-HT1 receptors) and antagonist of other serotonin receptors (e.g., the 5-HT2 receptors), methylergonovine is a non-selective agonist of most of the serotonin receptors, including of both the serotonin 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptor subgroups. Methysergide and methylergometrine are ergolines and lysergamides and are related to the ergot alkaloids. Previously thought to be an exclusively synthetic compound, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ergotamine
Ergotamine, sold under the brand name Ergomar among others, is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally and biochemically closely related to ergoline. It is structurally similar to several neurotransmitters, and it acts as a vasoconstrictor. It is used for acute migraines, sometimes with caffeine as the combination ergotamine/caffeine. The drug is a non-selective modulator or agonist of serotonin receptors and other receptors. It is peripherally selective and crosses into the brain in minimal amounts. Medicinal use of ergot fungus began in the 16th century, for the induction of childbirth; but dosage uncertainty discouraged its use. It has been used to prevent post-partum hemorrhage (bleeding after childbirth). It was first isolated from the ergot fungus by Arthur Stoll, at Sandoz in 1918, and was marketed as Gynergen in 1921. Medical uses Ergotamine is indicated as therapy to abort or prevent vascular headache. Available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue (fibrosis) in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present with lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, deep vein thrombosis, and other obstructive symptoms. It is named after John Kelso Ormond, who rediscovered the condition in 1948. Causes The association of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis with various immune-related conditions and response to immunosuppression led to a search for an autoimmune cause of idiopathic RPF. Many of these previously idiopathic cases can now be attributed to IgG4-related disease, an autoimmune disorder proposed in 2003. Otherwise, one-third of cases are secondary to malignancy, medication ( methysergide, hydralazine, beta blockers), prior radiotherapy, or certain infections. However, emerging evidence suggests that occupational exposure to asbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Raynaud's Phenomenon
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rarely, the nose, ears, nipples, or lips are affected. The episodes classically result in the affected part turning white and then blue. Often, numbness or pain occurs. As blood flow returns, the area turns red and burns. The episodes typically last minutes but can last several hours. The condition is named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862. Episodes are typically triggered by cold or emotional stress. Primary Raynaud's is idiopathic (spontaneous and of unknown cause) and not correlated with another disease. Secondary Raynaud's is diagnosed given the presence of an underlying condition and is associated with an older age of onset. In comparison to primary Raynaud's, ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antimigraine
Antimigraine drugs are medications intended to reduce the effects or intensity of migraine headache. They include drugs for the treatment of acute migraine symptoms as well as drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks. Treatment of acute symptoms Examples of specific antimigraine drug classes include triptans (first line option), ergot alkaloids, ditans and gepants. Migraines can also be treated with unspecific analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen. Opioids are not recommended for treatment of migraines. Triptans The triptan drug class includes 1st generation sumatriptan (which has poor bioavailability), and second generation zolmitriptan. Due to their safety, efficacy and selectivity, triptans are considered first line agents for abortion of migraines. These medications are selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists with some activity at 5-HT1F. They produce an antimigraine effect by vasoconstriction of the vessels in the brain, as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual. According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units. The cause is often unknown. Risk factors include a family history, prior pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs), HIV/AIDS, sickle cell disease, cocaine use, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, living at high altitudes, and problems with the mitral valve. The underlying mechanism typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
4-Methylaminorex
4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR, 4-MAX) is a stimulant drug of the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline group that was first synthesized in 1960 by McNeil Laboratories. It is also known by its street name "U4Euh" ("Euphoria"). It is banned in many countries as a stimulant. 4-Methylaminorex has effects comparable to methamphetamine but with a longer duration. Chemistry 4-Methylaminorex exists as four stereoisomers : (±)-''cis'' and (±)-''trans''. The (±)-''cis'' isomers are the form used recreationally. Synthesis The (±)-''cis'' isomers acemate (1:1-mixture) of the (4''R'',5''S'')-isomer and the enantiomeric (4''S'',5''R'')-isomergenerally synthesized from dl-phenylpropanolamine in one step by cyclization with cyanogen bromide (sometimes prepared ''in situ'' by reacting sodium cyanide with bromine). Alternate synthesis routes generally involve more steps, such as replacing cyanogen bromide with sodium or potassium cyanate to form an intermediate and then reacting it with concentrated hydroch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aminorex
Aminorex, sold under the brand names Menocil and Apiquel among others, is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension (PPH). In the United States, aminorex is a Schedule I controlled substance. Aminorex, in the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline group, was developed by McNeil Laboratories in 1962. It is closely related to 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR). Aminorex has been shown to have locomotor-stimulant effects, lying midway between dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine. Aminorex effects have been attributed to the release of catecholamines. It can be produced as a metabolite of the deworming medication levamisole, which is sometimes used as a cutting agent of illicitly produced cocaine. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Aminorex is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). Its values for induction of monoamine release are 26.4nM for norepinephrine, 49.4nM for dopamine, and 193nM fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phentermine
Phentermine, sold under the brand name Adipex-P among others, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is available by itself or as the combination phentermine/topiramate. Phentermine is taken by mouth. Common side effects include a fast heart beat, high blood pressure, trouble sleeping, dizziness, and restlessness. Serious side effects may include abuse, but do not include pulmonary hypertension or valvular heart disease, as the latter complications were caused by the fenfluramine component of the " fen-phen" combination. Phentermine is a norepinephrine and dopamine releasing agent (NDRA) and produces stimulant, rewarding, and appetite suppressant effects. Chemically, it is a substituted amphetamine. Phentermine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1959. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 149th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |