|
Mycorrhizal
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is normally mutualistic. In particular species, or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus in the form of sugars or lipids, while the fungus supplies the plant with water and mineral nutrients, such as phosphorus, taken from the soil. Mycorrhiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectomycorrhiza
An ectomycorrhiza (from Greek ἐκτός ', "outside", μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; ectomycorrhizas or ectomycorrhizae, abbreviated EcM) is a form of symbiotic relationship that occurs between a fungal symbiont, or mycobiont, and the roots of various plant species. The mycobiont is often from the phyla Basidiomycota and Ascomycota, and more rarely from the Zygomycota. Ectomycorrhizas form on the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pine and rose families. Research on ectomycorrhizas is increasingly important in areas such as ecosystem management and restoration, forestry and agriculture. Unlike other mycorrhizal relationships, such as arbuscular mycorrhiza and ericoid mycorrhiza, ectomycorrhizal fungi do not penetrate their host's cell walls. Instead they form an entirely intercellular interface known as the Hartig net, consisting of highly branched hyphae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
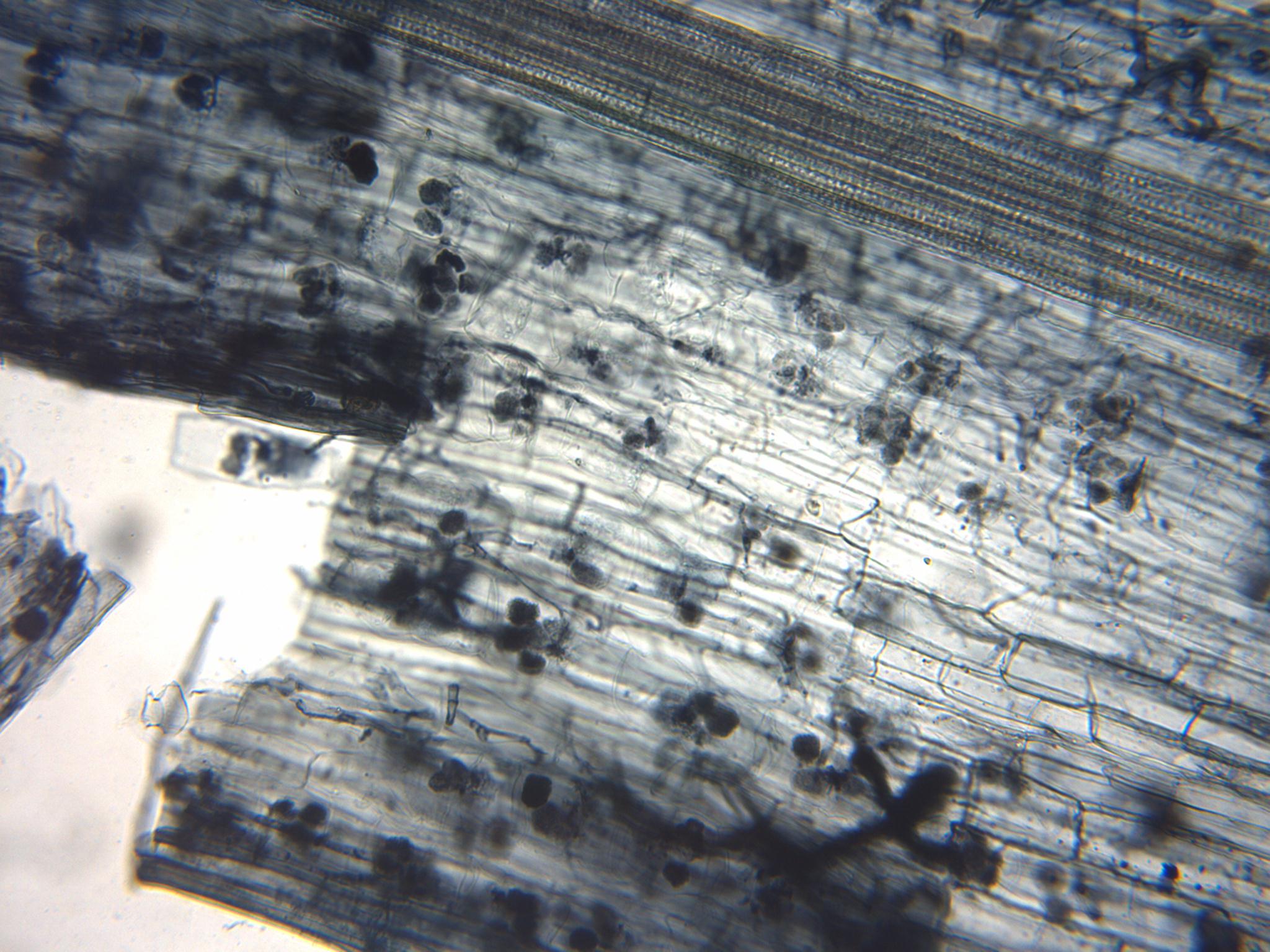
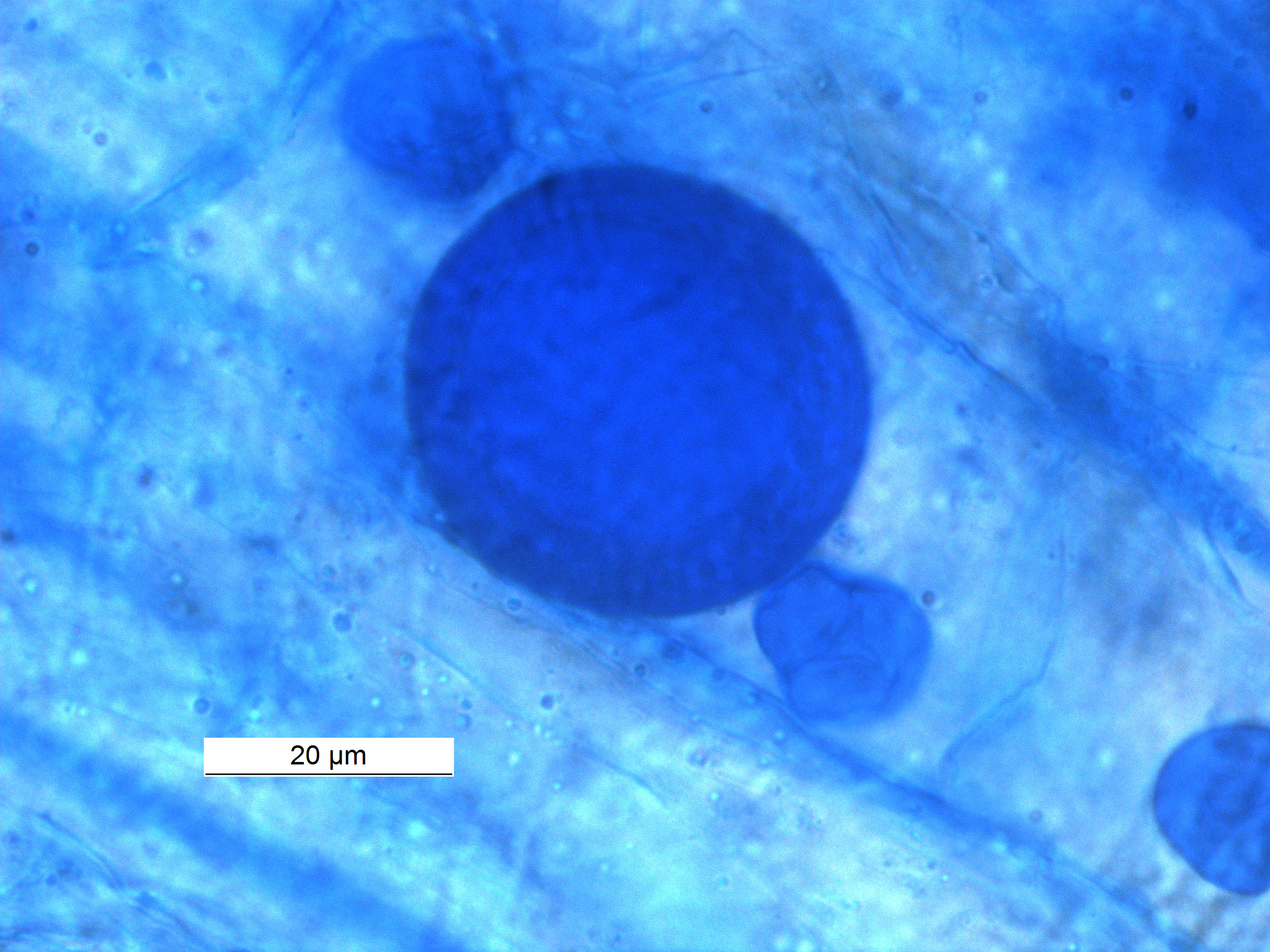
Arbuscular Mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of endomycorrhiza along with ericoid mycorrhiza and orchid mycorrhiza (not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza). They are characterized by the formation of unique tree-like structures, the arbuscules. In addition, globular storage structures called vesicles are often encountered. Arbuscular mycorrhizae are formed by fungi in the subphylum Glomeromycotina. This subphylum, along with the Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina, form the phylum Mucoromycota, a sister clade of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi. AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis playe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiosis, symbiont fungus (''Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the Cortex (botany), cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of endomycorrhiza along with ericoid mycorrhiza and orchid mycorrhiza (not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza). They are characterized by the formation of unique tree-like structures, the arbuscules. In addition, globular storage structures called vesicles are often encountered. Arbuscular mycorrhizae are formed by fungi in the subphylum Glomeromycota, Glomeromycotina. This subphylum, along with the Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina, form the phylum Mucoromycota, a sister clade of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi. AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or Substrate (biology), substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Pore space in soil, Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed ''rhizodeposition'', and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed Root mucilage, root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycle, nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolism, metabolic products of symbiotic and Plant pathology, pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce Allelopathy, allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives. The ''rhizoplane'' refers to the root surface including it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological Biological interaction, interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of Ecology, ecological interaction. Prominent examples are: * the nutrient exchange between vascular plants and mycorrhizal fungi, * the Fertilisation, fertilization of flowering plants by pollinators, * the ways plants use fruits and edible seeds to encourage animal aid in seed dispersal, and * the way corals become photosynthetic with the help of the microorganism zooxanthellae. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and Cheating (biology), exploitation, and with parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. However, mutualism may evolve from interactions that began with imbalanced benefits, such as parasitism. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Life
Soil biology is the study of Soil microbiology, microbial and faunal activity and ecology in soil. Soil life, soil biota, soil fauna, or edaphon is a collective term that encompasses all organisms that spend a significant portion of their biological life cycle, life cycle within a soil profile, or at the soil-plant litter, litter interface. These organisms include earthworms, nematodes, protozoa, fungi, bacteria, different arthropods, as well as some reptiles (such as snakes), and species of burrowing mammals like gophers, mole (animal), moles and prairie dogs. Soil biology plays a vital role in determining many soil characteristics. The decomposition of soil organic matter, organic matter by soil organisms has an immense influence on soil fertility, plant development, plant growth, soil structure, and carbon cycle, carbon storage. As a relatively new science, much remains unknown about soil biology and its effect on soil ecosystems. Overview The soil is home to a large propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fly Agaric
''Amanita muscaria'', commonly known as the fly agaric or fly amanita, is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus ''Amanita''. It is a large white- gilled, white-spotted mushroom typically featuring a bright red cap covered with distinctive white warts. It is one of the most recognizable fungi in the world. ''A.muscaria'' exhibits complex genetic diversity that suggests it is a species complex rather than a single species. It is a widely distributed mushroom native to temperate and boreal forests of the Northern Hemisphere, now also naturalized in the Southern Hemisphere, forming symbiotic relationships with various trees and spreading invasively in some regions. Its name derives from its traditional use as an insecticide. It can cause poisoning, especially in children and those seeking its hallucinogenic effects, due to psychoactive compounds like muscimol and the ibotenic acid; however, fatal poisonings are extremely rare. Boiling it reduces toxicity by removing water-solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Nutrition
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite. This is in accordance with Justus von Liebig's law of the minimum. The total essential plant nutrients include seventeen different elements: carbon, oxygen and hydrogen which are absorbed from the air, whereas other nutrients including nitrogen are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants). Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from their growing medium: * The macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) * The micronutrients (or trace minerals): iron (Fe), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |