 |
Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome. Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder. A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA. About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Alpha-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein (aSyn) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. It is a neuronal protein involved in the regulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking and the release of neurotransmitters. Alpha-synuclein is abundant in the brain, with smaller amounts present in the heart, muscles, and other tissues. Within the brain, it is primarily localized to the axon terminals of presynaptic neurons. There, it interacts with phospholipids and other proteins. Presynaptic terminals release neurotransmitters from specialized compartments called synaptic vesicles, a process essential for neuronal communication and normal brain function. In Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies, abnormal, insoluble forms of alpha-synuclein accumulate within neurons as inclusion bodies, inclusions known as Lewy body, Lewy bodies. Mutations in the ''SNCA'' gene are linked to familial forms of Parkinson's disease. During the process of seeded nucleation, alpha-synuclein adopts a cross-be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Midodrine
Midodrine, sold under the brand names ProAmatine and Orvaten among others, is an antihypotensive medication used to treat orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure when standing) and urinary incontinence. It is taken oral administration, by mouth. Side effects of midodrine include hypertension (high blood pressure), paresthesia, pruritus, itching, goosebumps, chills, urinary urgency, urinary retention, and urinary frequency. Midodrine is a prodrug of its active metabolite desglymidodrine. This metabolite acts as a binding selectivity, selective agonist of the alpha-1 adrenergic receptor, α1-adrenergic receptor. This in turn results in vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. Midodrine was discovered by 1971 and was introduced for medical use in the United States in 1996. Medical uses Midodrine is indicated for the treatment of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension. It can reduce dizziness and faints by about a third, but can be limited by troublesome goose bumps, prur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Glen Drager
A glen is a valley, typically one that is long and bounded by gently sloped concave sides, unlike a ravine, which is deep and bounded by steep slopes. The word is Goidelic in origin: ''gleann'' in Irish and Scottish Gaelic, ''glion'' in Manx. The designation "glen" also occurs often in place names. Glens are appreciated by tourists for their tranquility and scenery. Etymology The word is Goidelic in origin: ''gleann'' in Irish and Scottish Gaelic, ''glion'' in Manx. In Manx, ''glan'' is also to be found meaning glen. It is cognate with Welsh ''glyn''. Whittow defines it as a "Scottish term for a deep valley in the Highlands" that is "narrower than a strath". Examples in Northern England, such as Glenridding, Westmorland, or Glendue, near Haltwhistle, Northumberland, are thought to derive from the aforementioned Cumbric cognate, or another Brythonic equivalent. This likely underlies some examples in Southern Scotland. As the name of a river, it is thought to derive fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Milton Shy
Milton may refer to: Names * Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname) ** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet * Milton (given name) Places Australia * Milton, New South Wales * Milton, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane ** Milton Courts, a tennis centre ** Milton House, Milton, a heritage-listed house ** Milton railway station, Brisbane ** Milton Reach, a reach of the Brisbane River ** Milton Road, an arterial road in Brisbane Canada * Milton, Newfoundland and Labrador * Milton, Nova Scotia in the Region of Queens Municipality * Milton, Ontario ** Milton line, a commuter train line ** Milton GO Station * Milton (federal electoral district), Ontario ** Milton (provincial electoral district), Ontario * Beaverton, Ontario a community in Durham Region and renamed as Beaverton in 1835 * Rural Municipality of Milton No. 292, Saskatchewan New Zealand * Milton, New Zealand United Kingdom England * Milton, Cambridgeshire, a village nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Inferior Olivary Nucleus
The inferior olivary nucleus (ION) is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus.Gado, Thomas A. Woolsey; Joseph Hanaway; Mokhtar H. (2003). The brain atlas a visual guide to the human central nervous system (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 206. . In vertebrates, the ION is known to coordinate signals from the spinal cord to the cerebellum to regulate motor coordination and learning.Schweighofer N, Lang EJ, Kawato M. Role of the olivo-cerebellar complex in motor learning and control. ''Frontiers in Neural Circuits''. 2013;7:94. . These connections have been shown to be tightly associated, as degeneration of either the cerebellum or the ION results in degeneration of the other. Neurons of the ION are glutamatergic and receive inhibitory input via GABA receptors. There are two distinct GABAα receptor populations that are spatially organized within each neuron present in the ION. The GABAα receptor make-up varies based on where the rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor control, motor movements, procedural memory, procedural learning, habituation, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main functional components of the basal ganglia include the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as visual perception, vision, hearing, and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing that information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective segmentation (biology), body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a brain vesicle, vesicular enlargement at the rostral (anatomical term), rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Autonomic Dysfunction
Dysautonomia, autonomic failure, or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This condition may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and blood vessels. Dysautonomia has many causes, not all of which may be classified as neuropathic. A number of conditions can feature dysautonomia, such as Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, dementia with Lewy bodies, Ehlers–Danlos syndromes, autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy and autonomic neuropathy, HIV/AIDS, mitochondrial cytopathy, pure autonomic failure, autism, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Diagnosis is made by functional testing of the ANS, focusing on the affected organ system. Investigations may be performed to identify underlying disease processes that may have led to the development of symptoms or autonomic neuropathy. Symptomatic treatment is available for many symptoms associated with dysautono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), Rigidity (neurology), rigidity, and balance disorder, postural instability. Both hypokinetic features (bradykinesia and akinesia) and hyperkinetic features (cogwheel rigidity and tremors at rest) are displayed in parkinsonism. These are the four Parkinson's disease#Motor, motor signs that are found in Parkinson's disease (PD)after which Parkinsonism is namedand in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD), and many other conditions. This set of signs occurs in a wide range of conditions and may have many causes, including neurodegenerative conditions, drugs, toxins, metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions other than Parkinson's disease. Signs and symptoms Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by the four Parkinson's disease#Motor, motor signs that are found in Parkinson's disease: tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), Rigidity (neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
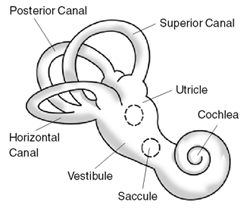 |
Postural Instability
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness, or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating. Balance is the result of several body systems working together: the visual system (eyes), vestibular system (ears) and proprioception (the body's sense of where it is in space). Degeneration or loss of function in any of these systems can lead to balance deficits. Signs and symptoms Cognitive dysfunction (disorientation) may occur with vestibular disorders. Cognitive deficits are not just spatial in nature, but also include non-spatial functions such as object recognition memory. Vestibular dysfunction has been shown to adversely affect processes of attention and increased demands of attention can worsen the postural sway associated with vestibular disorders. Recent MRI studies also show that humans with bilateral vestibular damage (damage to bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |