|
Multiple-barrel
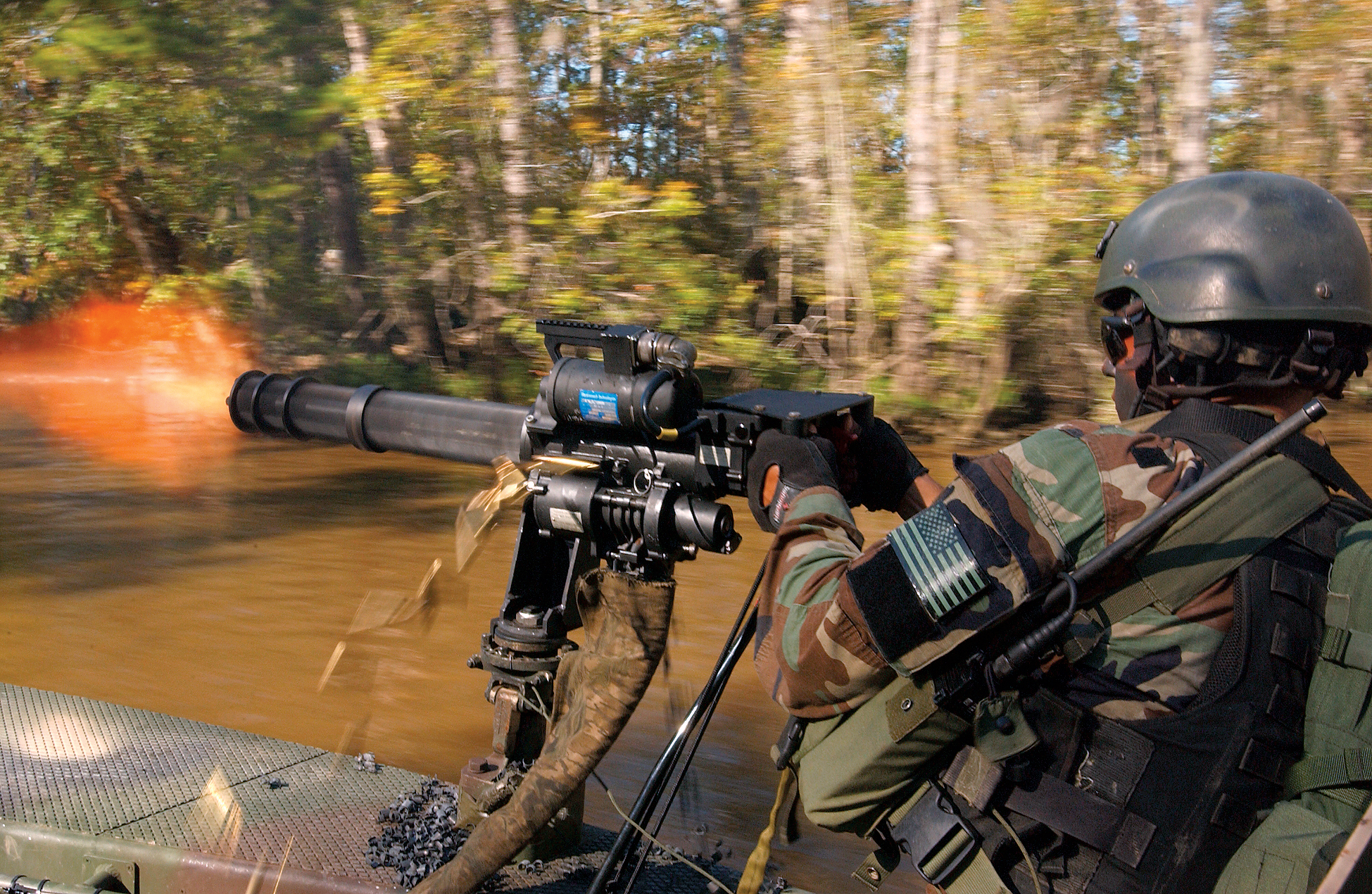
A multiple-barrel firearm is any type of firearm with more than one gun barrel, usually to increase the rate of fire or hit probability and to reduce barrel erosion/overheating. History Volley gun Multiple-barrel firearms date back to the 14th century, when the first primitive volley guns were developed. They are made with several single-shot barrels assembled together for firing a large number of shots, either simultaneously or in quick succession. These firearms were limited in firepower by the number of barrels bundled, and needed to be manually prepared, ignited and reloaded for each firing. In practice the large volley guns were not particularly more useful than a cannon firing canister shot or grapeshot. Since they were still mounted on a carriage, they could be as hard to aim and move around as a heavy cannon, and the many barrels took as long (if not longer) to reload.Matthew Sharpe "Nock's Volley Gun: A Fearful Discharge" ''American Rifleman'' December 2012 pp.50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many centuries passed before multi-shot repeater designs became commonplace. Compared to repeating firearms, single-shot designs have no moving parts (other than the trigger and hammer/ firing pin or frizzen) and thus do not need a sizable receiver behind the barrel, and are much less complex than revolvers or magazine/ belt-fed firearms. Although largely disappeared from military usage due to the slow rates of fire, single-shot designs are still produced by many manufacturers in both cartridge- and non-cartridge varieties, from zip guns to the highest-quality hunting and match guns. History Pre-cartridge era The vast majority of firearms before the introduction of metallic cartridges from the 1860s onwards, were single-shot muzzleload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Colt
Samuel Colt (; July 19, 1814 – January 10, 1862) was an American inventor, industrialist, and businessman who established Colt's Patent Fire-Arms Manufacturing Company (now Colt's Manufacturing Company) and made the mass production of revolvers commercially viable. Colt's first two business ventures were producing firearms in Paterson, New Jersey, and making underwater mines; both ended in disappointment. His business affairs improved rapidly after 1847, when the Texas Rangers ordered 1,000 revolvers during the American war with Mexico. Later, his firearms were used widely during the settling of the western frontier. Colt died in 1862 as one of the wealthiest men in America. Colt's manufacturing methods were sophisticated. His use of interchangeable parts helped him become one of the first to use the assembly line efficiently. Moreover, his innovative use of art, celebrity endorsements, and corporate gifts to promote his wares made him a pioneer of advertising, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
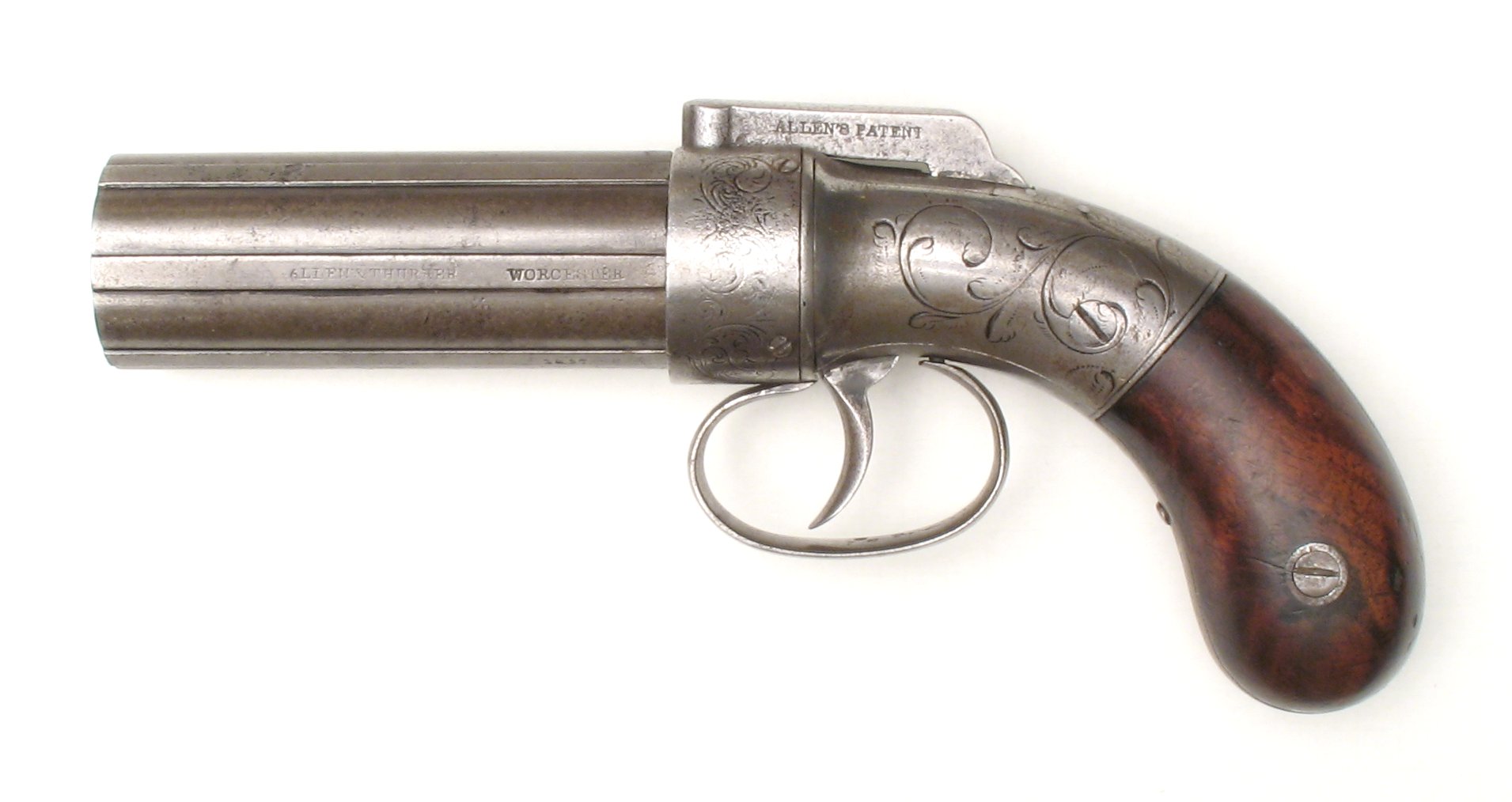
Pepperbox Gun Tula
The pepper-box revolver or simply pepperbox (also "pepper-pot", from its resemblance to the household pepper shakers) is a multiple-barrel firearm, mostly in the form of a handgun, that has three or more gun barrels in a coaxially revolving mechanism. Each barrel holds a single shot, and the shooter can manually rotate the whole barrel assembly to sequentially index each barrel into alignment with the lock or hammer, similar to rotation of a revolver's cylinder. Pepperbox guns have existed for all types of firelock firearms and metal cased ammunition systems used in breechloading firearms: matchlock, wheellock, flintlock, snaplock, caplock, pinfire, rimfire and centerfire. While they are usually sidearms, a few long guns were also made. For example, Samuel Colt owned a three-barrel pepperbox matchlock musket from British India, and an eight-barrel pepperbox shotgun was designed in 1967 but never went into production. Early years This type of firearm was popular in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Forces Gatling Gun
Special or specials may refer to: Policing * Specials, Ulster Special Constabulary, the Northern Ireland police force * Specials, Special Constable, an auxiliary, volunteer, or temporary; police worker or police officer Literature * ''Specials'' (novel), a novel by Scott Westerfeld * ''Specials'', the comic book heroes, see ''Rising Stars'' (comic) Film and television * Special (lighting), a stage light that is used for a single, specific purpose * ''Special'' (film), a 2006 scifi dramedy * ''The Specials'' (2000 film), a comedy film about a group of superheroes * ''The Specials'' (2019 film), a film by Olivier Nakache and Éric Toledano * Television special, television programming that temporarily replaces scheduled programming * ''Special'' (TV series), a 2019 Netflix Original TV series * ''Specials'' (TV series), a 1991 TV series about British Special Constables * ''The Specials'' (TV series), an internet documentary series about 5 friends with learning disabilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinfire
A pinfire cartridge is an obsolete type of metallic firearm cartridge in which the priming compound is ignited by striking a small pin which protrudes radially from just above the base of the cartridge. Invented by Frenchman Casimir Lefaucheux in the 1830s but not patented until 1835, it was one of the earliest practical designs of a metallic cartridge. Its history is closely associated with the development of the breechloader which replaced muzzle-loading weapons. History The Swiss gun maker Samuel Joannes Pauly patented the first breechloading cartridge in 1812. This was for use in a shotgun with fixed barrels which was loaded by lifting a breech block on the top. French gun maker Henri Roux attempted to improve this cartridge in the 1820s but a constantly primed cartridge was felt by many to be too dangerous and many breechloading guns reverted to using an unprimed cartridge. This was fired by a separate percussion cap which was used on the still dominant muzzle-loading gun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engholm King
{{Surname ...
Engholm is a surname of: * Björn Engholm (born 1939), German SPD politician. He was Minister-President of Schleswig-Holstein from 1988 to 1993 * Harry Engholm, British screenwriter * Johan Engholm (1820-1918), Swedish gunsmith * Maria Prytz (born 1976; née Engholm), Swedish curler *Christian Engholm Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass-produced
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods. The term ''mass production'' was popularized by a 1926 article in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' supplement that was written based on correspondence with Ford Motor Company. ''The New York Times'' used the term in the title of an article that appeared before publication of the ''Britannica'' article. The concepts of mass production are applied to various kinds of products: from fluids and particulates handled in bulk (food, fuel, chemicals and mined minerals), to parts and assemblies of parts ( household appliances and automobiles). Some mass production techniques, such as standardized sizes and production lines, predate the Industrial Revolution by many centuries; however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Forsyth
Alexander John Forsyth (28 December 1768 – 11 June 1843) was a Scottish Church of Scotland minister who first successfully used fulminating (or 'detonating') chemicals to prime gunpowder in fire-arms thereby creating what became known as percussion ignition. Life He was born in the manse at Belhelvie the son of Rev James Forsyth (d.1790), and his wife, Isabella Syme. He studied at King's College, Aberdeen graduating MA in 1786. He succeeded his father as minister of his home town in 1791. Forsyth took out a British patent for locks utilising fulminates in 1807. Despite the patent being in force, several British gunsmiths, most notably Joseph Manton, invented other forms of detonating gunlocks ignition in order to evade Forsyth's patent, which would not expire until 1821. Forsyth continually protected his patent between 1807 and 1821 in Britain with legal action. He fought cases against Joseph Egg, Collinson Hall, Isaac Riviere, Joseph Vicars, and Joseph Manton (twice). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Cap
The percussion cap or percussion primer, introduced in the early 1820s, is a type of single-use percussion ignition device for muzzle loader firearm locks enabling them to fire reliably in any weather condition. This crucial invention gave rise to the cap lock mechanism or percussion lock system using percussion caps struck by the hammer to set off the gunpowder charge in percussion guns including percussion rifles and cap and ball firearms. Any firearm using a caplock mechanism is a percussion gun. Any long gun with a cap-lock mechanism and rifled barrel is a percussion rifle. Cap and ball describes cap-lock firearms discharging a single bore-diameter spherical bullet with each shot. Description The percussion cap is a small cylinder of copper or brass with one closed end. Inside the closed end is a small amount of a shock-sensitive explosive material such as mercuric fulminate (discovered in 1800; it was the only practical detonator used from about 1850 to the early 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Match
A match is a tool for starting a fire. Typically, matches are made of small wooden sticks or stiff paper. One end is coated with a material that can be ignited by friction generated by striking the match against a suitable surface. Wooden matches are packaged in matchboxes, and paper matches are partially cut into rows and stapled into matchbooks. The coated end of a match, known as the match "head", consists of a bead of active ingredients and binder (material), binder, often colored for easier inspection. There are two main types of matches: safety matches, which can be struck only against a specially prepared surface, and strike-anywhere matches, for which any suitably frictional surface can be used. Because of the substance used to coat each match, this makes them non-biodegradable. Etymology Historically, the term ''match'' referred to lengths of rope, cord (later cambric) impregnated with chemicals, and allowed to burn continuously. These were used to light fires and fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammer
A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal (as with a forge), or to crush rock. Hammers are used for a wide range of driving, shaping, breaking and non-destructive striking applications. Traditional disciplines include carpentry, blacksmithing, warfare, and percussive musicianship (as with a gong). Hammering is use of a hammer in its strike capacity, as opposed to prying with a secondary claw or grappling with a secondary hook. Carpentry and blacksmithing hammers are generally wielded from a stationary stance against a stationary target as gripped and propelled with one arm, in a lengthy downward planar arc—downward to add kinetic energy to the impact—pivoting mainly around the shoulder and elbow, with a small but brisk wrist rotation shortly before impact; for extreme i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |