|
Multi-spectral Camouflage
Multi-spectral camouflage is the use of counter-surveillance techniques to Stealth technology, conceal objects from detection across several parts of the electromagnetic spectrum at the same time. While traditional military camouflage attempts to hide an object in the visible spectrum, multi-spectral camouflage also tries to simultaneously hide objects from detection methods such as infrared signature, infrared, radar cross-section, radar, and extremely high frequency, millimetre-wave radar imaging. Among animals, both insects such as the Smerinthus ocellatus, eyed hawk-moth, and vertebrates such as tree frogs possess camouflage that works in the infra-red as well as in the visible spectrum. History The English zoologist Hugh Cott, in his 1940 book ''Adaptive Coloration in Animals'', wrote that some caterpillars such as the eyed hawk-moth ''Smerinthus ocellatus'', and tree frogs such as the red-snouted treefrog ''Scinax ruber, Hyla coerulea'', are coloured so as to blend with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marder 1A5 Mobile Camouflage System Barracuda
Marder may refer to: German military vehicles * A series of World War II tank destroyers: ** Marder I ** Marder II ** Marder III * Marder (IFV), a modern infantry fighting vehicle * Marder (submarine), a World War II midget submarine People with the surname * Arthur Marder (1910–1980), American historian * Barry Marder, American stand-up comedian * Darius Marder, American film director and screenwriter * Eve Marder, American neuroscientist * Janet Marder, American female rabbi * Larry Marder, American cartoonist * Malerie Marder, American photographer * Marlene Marder, Swiss guitarist * Maureen Marder, exotic dancer and welder whose life was the basis of ''Flashdance'' * Michael Marder, Basque contemporary philosopher * Rebecca Marder, French actress * Seth Marder, American chemist * Steven Marder, dotcom executive Other uses * Marder (Zoids), ''Marder'' (Zoids), a zoid from Zoids See also * Marten (other), "Marder" is German for the animal marten {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organ (biology), organs, cell (biology), cells, and biomolecules carry out chemistry, chemical and physics, physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into clinical physiology, medical physiology, Zoology#Physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysics, biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostasis, homeostatic control mechanisms, and cell signaling, communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathology, pathological state'' refers to abnormality (behavior), abnormal conditions, including human diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
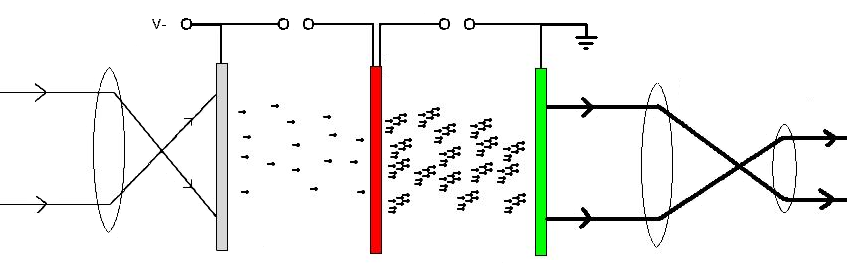
Image Intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in X-rays or gamma rays ( X-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night-vision goggles. Introduction Image intensifier tubes (IITs) are optoelectronic devices that allow many devices, such as night vision devices and medical imaging devices, to function. They convert low levels of light from various wavelengths into visible quantities of light at a single wavelength. Operation Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
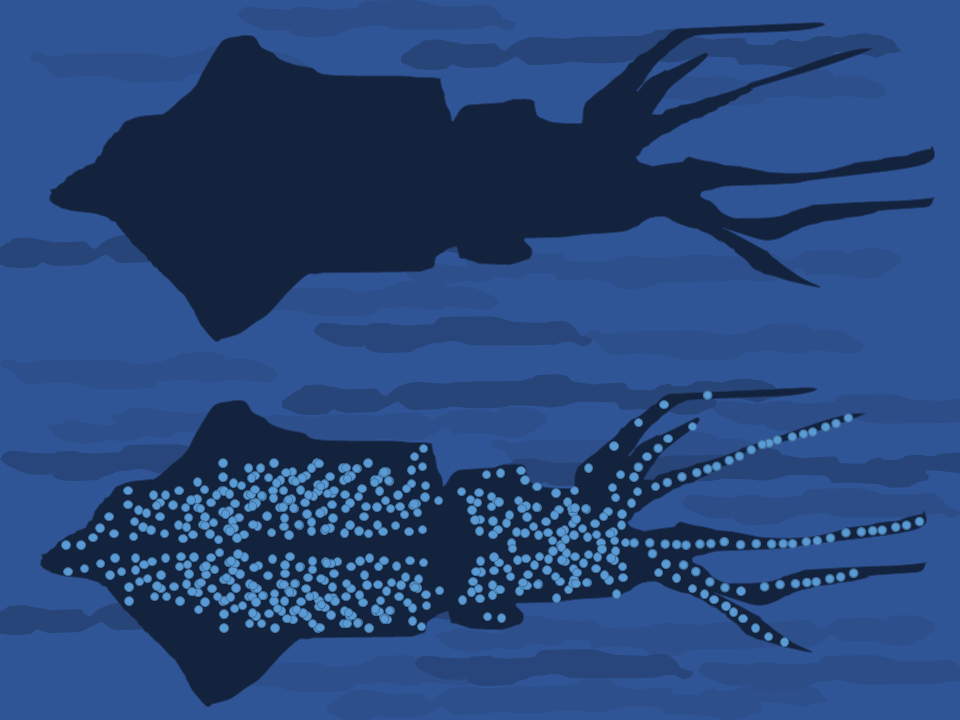
Counter-illumination
Counter-illumination is a method of active camouflage seen in marine animals such as firefly squid and midshipman fish, and in military prototypes, producing light to match their backgrounds in both brightness and wavelength. Marine animals of the mesopelagic (mid-water) zone tend to appear dark against the bright water surface when seen from below. They can camouflage themselves, often anti-predator adaptation, from predators but also from their prey, by producing light with bioluminescence, bioluminescent photophores on their downward-facing surfaces, reducing the contrast of their silhouettes against the background. The light may be produced by the animals themselves, or by mutualism (biology), symbiotic bacteria, often ''Aliivibrio fischeri''. Counter-illumination differs from countershading, which uses only pigments such as melanin to reduce the appearance of shadows. It is one of the dominant types of aquatic camouflage, along with transparency and silvering (camouflage), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared (with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies), called collectively '' optical radiation''. In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarization. Its speed in vacuum, , is one of the fundamental constants of nature. All electromagnetic radiation exhibits some properties of both particles and waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be emitted and received by antenna (radio), antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most building materials. Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon energies and the shortest wavelengths—much smaller than an atomic nucleus. Gamma rays, X-rays, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic-aperture Radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target during the period when the target scene is illuminated creates the large ''synthetic'' antenna aperture (the ''size'' of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. For a fixed antenna size and orientation, objects which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamaterial
A metamaterial (from the Greek word μετά ''meta'', meaning "beyond" or "after", and the Latin word ''materia'', meaning "matter" or "material") is a type of material engineered to have a property, typically rarely observed in naturally occurring materials, that is derived not from the properties of the base materials but from their newly designed structures. Metamaterials are usually fashioned from multiple materials, such as metals and plastics, and are usually arranged in repeating patterns, at scales that are smaller than the wavelengths of the phenomena they influence. Their precise shape, geometry, size, orientation, and arrangement give them their "smart" properties of manipulating electromagnetic, acoustic, or even seismic waves: by blocking, absorbing, enhancing, or bending waves, to achieve benefits that go beyond what is possible with conventional materials. Appropriately designed metamaterials can affect waves of electromagnetic radiation or sound in a manner n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IIT Kanpur
The Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (IIT- Kanpur or IIT-K) is a public institute of technology located in Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. As an Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), it was declared an Institute of National Importance by the Government of India under the Institutes of Technology Act. IIT Kanpur has been occasionally ranked among the best academic institutions in India. As of January 2025, at least 17 Padma Shri, 4 Padma Bhushan, 1 Padma Vibhushan, and 33 Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize recipients have been affiliated with IIT Kanpur as alumni or faculty members. History IIT Kanpur was established by an Act of Parliament in 1960 by the Government of India. The institute was started in December 1959 in a room in the canteen building of the Harcourt Butler Technological University at Agricultural Gardens in Kanpur. In 1963, the institute moved to its present location, on the Grand Trunk Road near Kalyanpur locality in Kanpur district. The campus, which is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |