 |
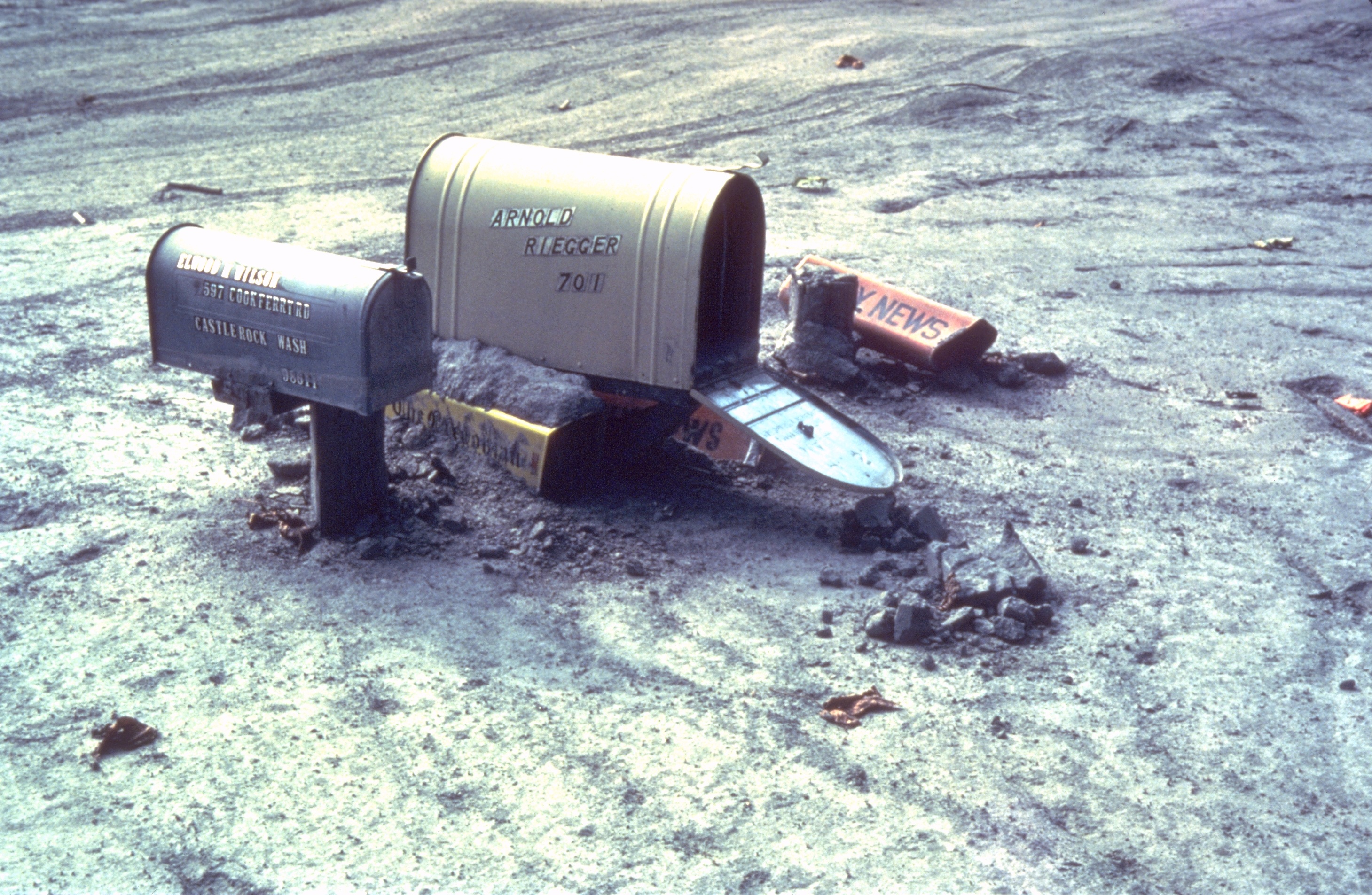
Mudslide
A mudflow, also known as mudslide or mud flow, is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris and dirt that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/second. Mudflows contain a significant proportion of clay, which makes them more fluid than debris flows, allowing them to travel farther and across lower slope angles. Both types of flow are generally mixtures of particles with a wide range of sizes, which typically become sorted by size upon deposition. Mudflows are often called mudslips, a term applied indiscriminately by the mass media to a variety of mass wasting events. Mudflows often start as slides, becoming flows as water is entrained along the flow path; such events are often called mud failures. Other types of mudflows include lahars (involving fine-grained pyroclastic deposits on the flanks of volcanoes) and jökulhlaups (outbursts from under glaciers or icecaps). A statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
List Of Landslides
This list of landslides is a list of notable landslides and mudflows divided into sections by date and type. This list may be incomplete as there is no central catalogue for landslides, although it does exist for some for individual countries or areas. Volumes of landslides are recorded in the scientific literature using cubic kilometres (km3) for the largest and millions of cubic metres (MCM) for most events. Prehistoric landslides Note: km3 = cubic kilometre(s) Submarine landslides Note: MCM = million cubic metres; km3 = cubic kilometre(s) Pre-20th-century historic landslides Note: km3 = cubic kilometre(s); MCM = million cubic metres 20th-century landslides 1901–1950 Note: km3 = cubic kilometre(s); MCM = million cubic metres 1951–1975 Note: km3 = cubic kilometre(s); MCM = million cubic metres 1976–2000 Note: MCM = million cubic metres 21st-century landslides 2001–2010 Note: m3 = cubic metre(s); MCM = million cubic metres 2011–2020 Note: MCM = million cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Landslides
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides. Gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, but there are other factors affecting slope stability that produce specific conditions that make a slope prone to failure. In many cases, the landslide is triggered by a specific event (such as heavy rainfall, an earthquake, a slope cut to build a road, and many others), although this is not always identifiable. Landslides are frequently made worse by human development (such as urban sprawl) and resource exploitation (such as mining and deforestation). Land degradation frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides. Gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, but there are other factors affecting slope stability that produce specific conditions that make a slope prone to failure. In many cases, the landslide is triggered by a specific event (such as heavy rainfall, an earthquake, a slope cut to build a road, and many others), although this is not always identifiable. Landslides are frequently made worse by human development (such as urban sprawl) and resource exploitation (such as mining and deforestation). Land degradation freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
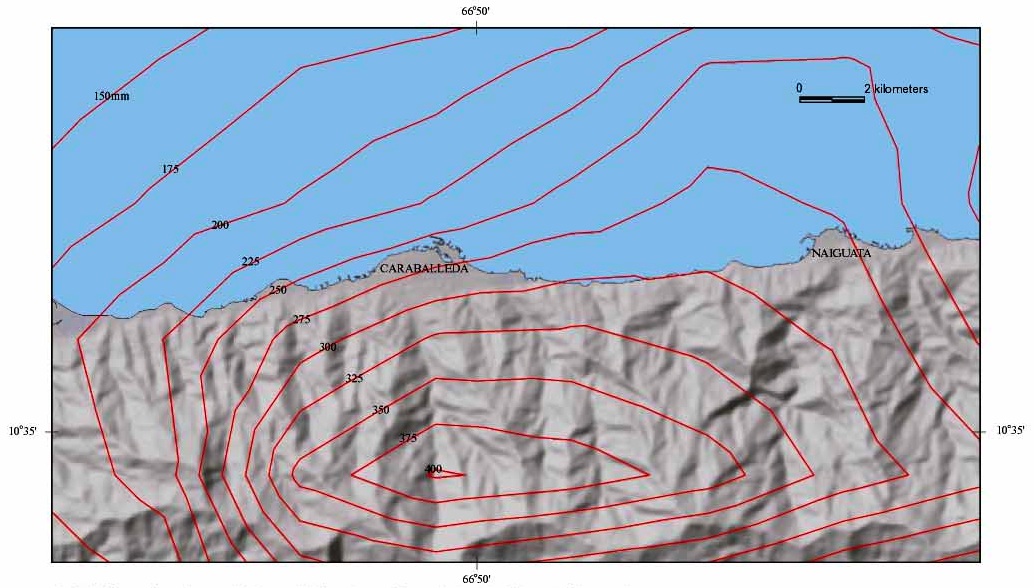 |
Vargas Tragedy
The Vargas tragedy was a natural disaster that occurred in Vargas State, Venezuela on 15 December 1999 (over the course of 10 days), when torrential rains caused flash floods and debris flows that killed tens of thousands of people, destroyed thousands of homes, and led to the complete collapse of the state's infrastructure. According to relief workers, the neighborhood of Los Corales was buried under of mud and a high percentage of homes were simply swept into the ocean. Entire towns including Cerro Grande and Carmen de Uria completely disappeared. As much as 10% of the population of Vargas died during the event. A deadlier natural disaster would not occur until the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Background The coastal area of Vargas State has long been subject to mudslides and flooding. Deposits preserved on the alluvial fan deltas here show that geologically similar catastrophes have occurred with regularity since prehistoric times. Since the 17th century, at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Vargas, Venezuela
La Guaira State (), known until 2019 as Vargas State (, ), is one of the 23 states of Venezuela. Formerly named after Venezuela's first civilian president, José María Vargas, the state comprises a coastal region in the north of Venezuela, bordering Aragua to the west, Miranda to the east, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Capital District to the south. It is home to both the country's largest seaport and airport. The state capital and largest city is La Guaira followed by Catia La Mar and Maiquetía. The Litoral Varguense conurbation is the principal urban agglomeration in the state, which is part of the Greater Caracas Area. In 1999, the geographic center of the state suffered major floods and landslides, known as (the Vargas tragedy), causing major losses of life and property, and resulting in forced population movements, including the virtual disappearance of some small towns. Thousands died, and many more fled the area to other states. The state's name was chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Debris Flow
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented Rock (geology), rock flow down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. They generally have bulk density, bulk densities comparable to those of rock avalanche, rockslides and other types of landslide classification, landslides (roughly 2000 kilograms per cubic meter), but owing to widespread sediment liquefaction caused by high pore pressure, pore-fluid pressures, they can flow almost as fluidly as water. Debris flows descending steep channels commonly attain speeds that surpass 10 m/s (36 km/h), although some large flows can reach speeds that are much greater. Debris flows with volumes ranging up to about 100,000 cubic meters occur frequently in mountainous regions worldwide. The largest prehistoric flows have had volumes exceeding 1 billion cubic meters (i.e., 1 cubic kilometer). As a result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lahar
A lahar (, from ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of Pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a valley, river valley. Lahars are often extremely destructive and deadly; they can flow tens of metres per second, they have been known to be up to deep, and large flows tend to destroy any structures in their path. Notable lahars include those at Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines and Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia, the latter of which killed more than 20,000 people in the Armero tragedy. Etymology The word ''lahar'' is of Javanese language, Javanese origin. Berend George Escher introduced it as a geological term in 1922. Description The word ''lahar'' is a general term for a flowing mixture of water and pyroclastic debris. It does not refer to a particular rheology or sediment concentration. Lahars can occur as normal stream flows (sediment concentration of less than 30%), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Landslide Classification
There have been known various classifications of landslides. Broad definitions include forms of mass movement (geology), mass movement that narrower definitions exclude. For example, the ''McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science and Technology'' distinguishes the following types of landslides: *fall (by undercutting) *fall (by toppling) *Slump (geology), slump *rockslide *earthflow *sinkholes, mountain side *rockslide that develops into rock avalanche Influential narrower definitions restrict landslides to slumps and translational slides in rock and regolith, not involving fluidisation. This excludes falls, topples, lateral spreads, and mass flows from the definition.Varnes D. J., Slope movement types and processes. In: Schuster R. L. & Krizek R. J. Ed., Landslides, analysis and control. Transportation Research Board Sp. Rep. No. 176, Nat. Acad. oi Sciences, pp. 11–33, 1978.Hungr O, Evans SG, Bovis M, and Hutchinson JN (2001) Review of the classification of landslides of the flow type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Avalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a Grade (slope), slope, such as a hill or mountain. Avalanches can be triggered spontaneously, by factors such as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, other animals, and earthquakes. Primarily composed of flowing snow and air, large avalanches have the capability to capture and move ice, rocks, and trees. Avalanches occur in two general forms, or combinations thereof: slab avalanches made of tightly packed snow, triggered by a collapse of an underlying weak snow layer, and loose snow avalanches made of looser snow. After being set off, avalanches usually accelerate rapidly and grow in mass and volume as they capture more snow. If an avalanche moves fast enough, some of the snow may mix with the air, forming a powder snow avalanche. Though they appear to share similarities, avalanches are distinct from slush flows, Mudflow, mudslides, Landslide#Debris landslide, rock slides, and serac collap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, transports it to another location where it is deposit (geology), deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by Solvation, dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and Wind wave, waves; glacier, glacial Plucking (glaciation), plucking, Abrasion (geology), abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; Aeolian processes, wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and Mass wastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, cultural center of Southern California. With an estimated 3,878,704 residents within the city limits , it is the List of United States cities by population, second-most populous in the United States, behind only New York City. Los Angeles has an Ethnic groups in Los Angeles, ethnically and culturally diverse population, and is the principal city of a Metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area of 12.9 million people (2024). Greater Los Angeles, a combined statistical area that includes the Los Angeles and Riverside–San Bernardino metropolitan areas, is a sprawling metropolis of over 18.5 million residents. The majority of the city proper lies in Los Angeles Basin, a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
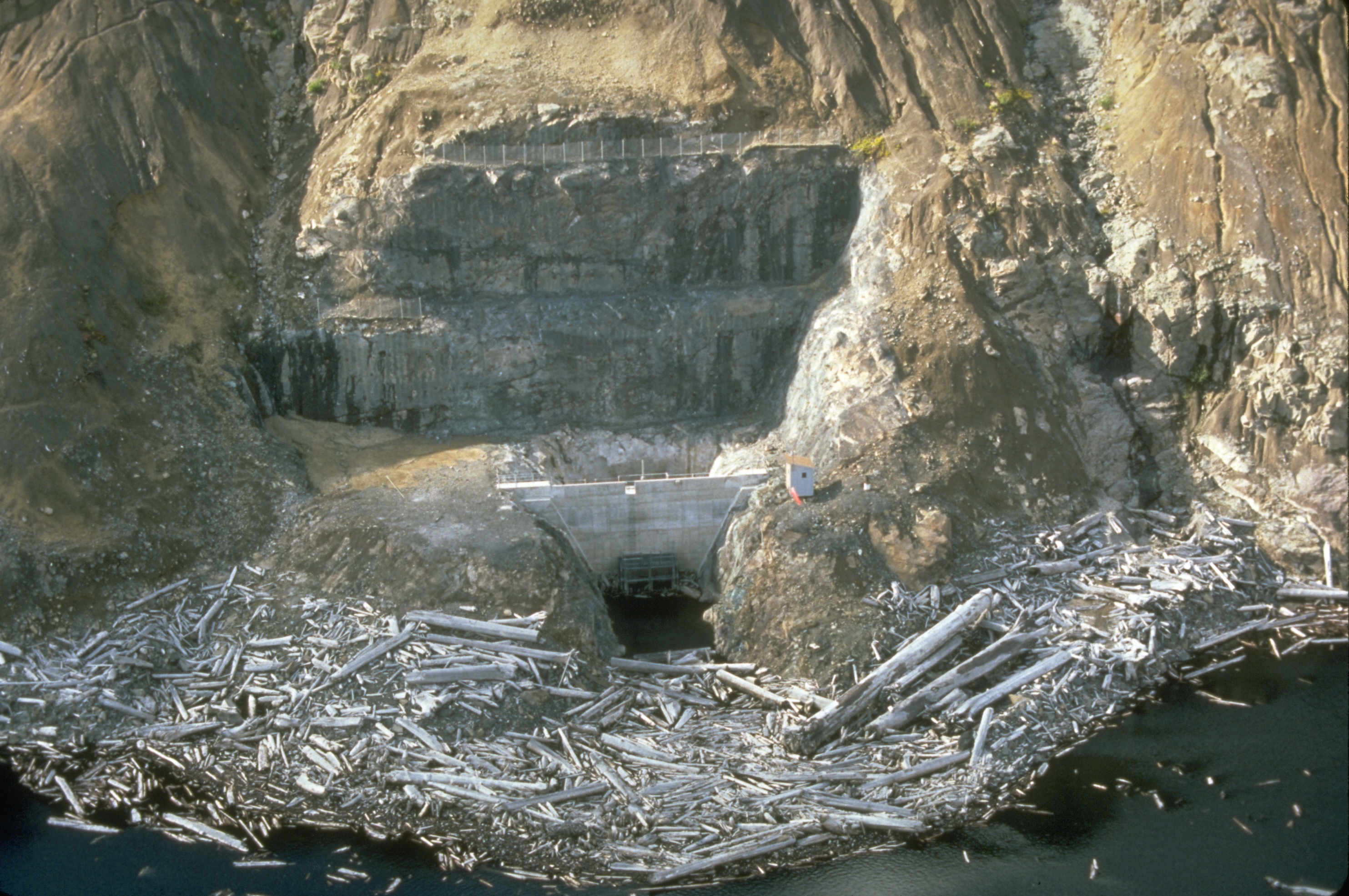 |
Spirit Lake (Washington)
Spirit Lake is a lake in Skamania County, Washington, United States, located north of Mount St. Helens. It was a popular tourist destination for many years until Mount St. Helens erupted in 1980. Previously there had been six camps on the shore of Spirit Lake: Boy Scout ( Camp Spirit Lake), the Girl Scout Camp at Spirit Lake, two YMCA camps ( Camp Loowit, and Portland YMCA camp), Harmony Fall Lodge, and another for the general public. There were also several lodges accessible to visitors, including Spirit Lake Lodge and Mt. St. Helens Lodge. The latter was owned and operated by Harry R. Truman, a noted victim of the volcano's 1980 eruption. Human history The body of water was named "Spirit" by settlers after histories from Native American people in the area spoke of haunting spirits at the lake. The spirits, telling a story of life and death, formed out of the mists into various shapes of trees and animals, foretelling impending doom but good fortune in the afterlife. Any pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |