|
Moral Foundations Theory
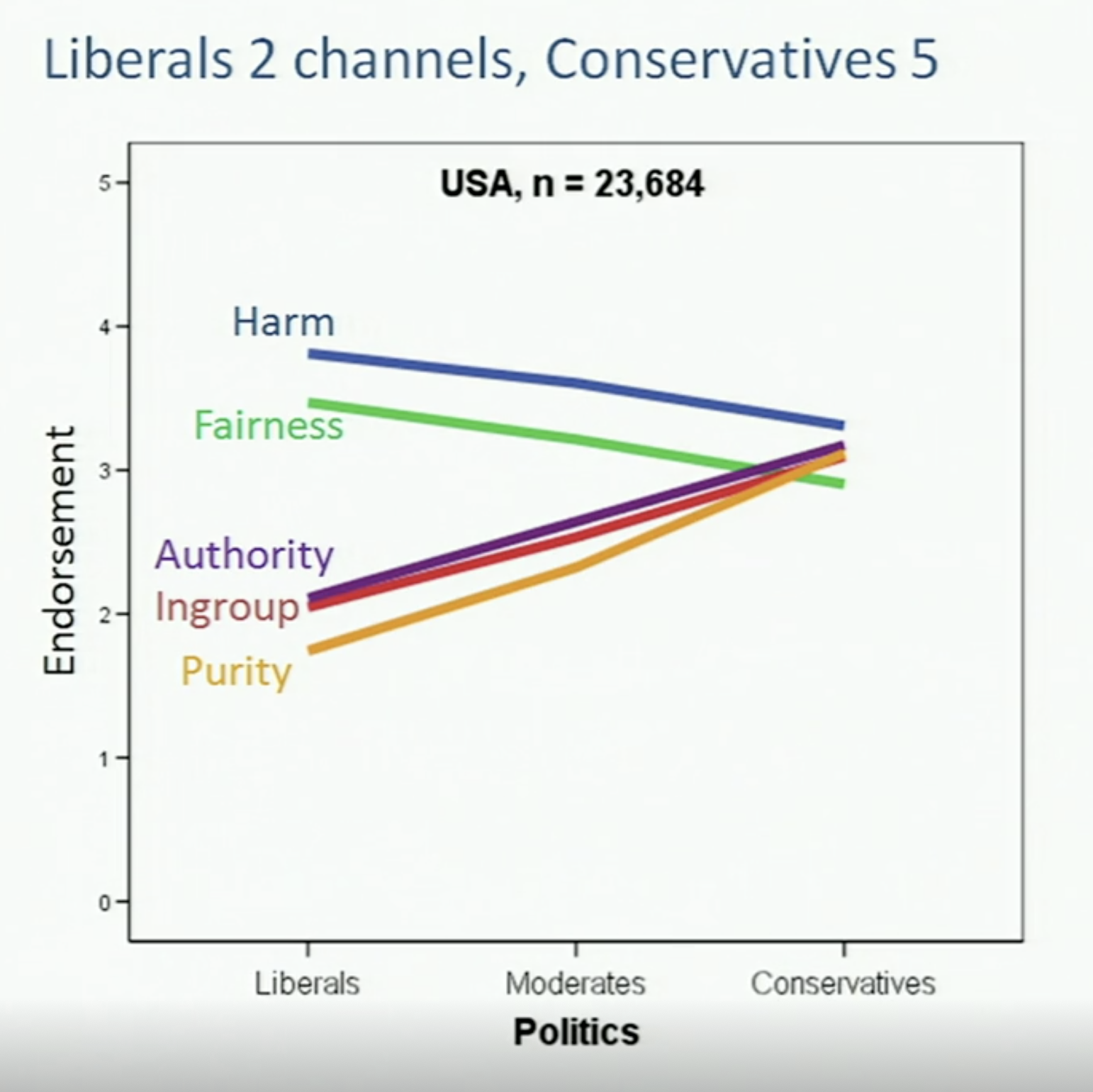
Moral foundations theory is a social psychological theory intended to explain the origins of and variation in human moral reasoning on the basis of innate, modular foundations. It was first proposed by the psychologists Jonathan Haidt, Craig Joseph, and Jesse Graham, building on the work of cultural anthropologist Richard Shweder. More recently, Mohammad Atari, Jesse Graham, and Jonathan Haidt have revised some aspects of the theory and developed new measurement tools. The theory has been developed by a diverse group of collaborators and popularized in Haidt's book '' The Righteous Mind''. The theory proposes that morality is "more than one thing", first arguing for five foundations, and later expanding for six foundations (adding Liberty/Oppression): * Care/harm * Fairness/cheating * Loyalty/betrayal * Authority/subversion * Sanctity/degradation * Liberty/oppression. Its authors remain open to the addition, subtraction, or modification of the set of foundations. Although the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychological
Social psychology is the methodical study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of sociology, psychological social psychology places more emphasis on the individual, rather than society; the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspects of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daedalus (journal)
''Dædalus'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that was established in 1846 as the ''Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences'', obtaining its current title in 1958. The journal is published by MIT Press on behalf of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other ... and only accepts submissions on invitation. In January 2021, the journal moved to an open access model. References External links * {{humanities-journal-stub Academic journals established in 1846 MIT Press academic journals Quarterly journals English-language journals Multidisciplinary humanities journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies 1955 establishments in Massachusetts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Formerly applied primarily to Economy, economic, Political philosophy, political, or Religion, religious theories and policies, in a tradition going back to Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, more recent use treats the term as mainly condemnatory. The term was coined by Antoine Destutt de Tracy, a French Enlightenment aristocrat and philosopher, who conceived it in 1796 as the "science of ideas" to develop a rational system of ideas to oppose the irrational impulses of the mob. In political science, the term is used in a Linguistic description, descriptive sense to refer to List of political ideologies, political belief systems. Etymology The term ''ideology'' originates from French language, French , itself coined from combining (; close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Module
A cognitive module in cognitive psychology is a specialized tool or sub-unit that can be used by other parts to resolve cognitive tasks. It is used in theories of the modularity of mind and the closely related society of mind theory and was developed by Jerry Fodor. It became better known throughout cognitive psychology by means of his book, ''The Modularity of Mind'' (1983). The nine aspects he lists that make up a mental module are domain specificity, mandatory operation, limited central accessibility, fast processing, informational encapsulation, "shallow" outputs, fixed neural architecture, characteristic and specific breakdown patterns, and characteristic ontogenetic pace and sequencing. Not all of these are necessary for the unit to be considered a module, but they serve as general parameters. The question of their existence and nature is a major topic in cognitive science and evolutionary psychology. Some see cognitive modules as an independent part of the mind. Others als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparedness (learning)
In psychology, preparedness is a concept developed to explain why certain associations are learned more readily than others. For example, phobias related to survival, such as snakes, spiders, and heights, are much more common and much easier to induce in the laboratory than other kinds of fears. According to Martin Seligman, this is a result of our evolutionary history. The theory states that organisms which learned to fear environmental threats faster had a survival and reproductive advantage. Consequently, the innate predisposition to fear these threats became an adaptive human trait. The concept of preparedness has also been used to explain why taste aversions are learned so quickly and efficiently compared with other kinds of classical conditioning Classical conditioning (also respondent conditioning and Pavlovian conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent Stimulus (physiology), stimulus (e.g. food, a puff of air on the eye, a potential rival) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Evolution
''Homo sapiens'' is a distinct species of the hominid family of primates, which also includes all the great apes. Over their evolutionary history, humans gradually developed traits such as Human skeletal changes due to bipedalism, bipedalism, dexterity, and complex language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins (a tribe of the Homininae, African hominid subfamily), indicating that human evolution was not linear but weblike. The study of the origins of humans involves Interdisciplinary, several scientific disciplines, including Biological anthropology, physical and evolutionary anthropology, paleontology, and genetics; the field is also known by the terms anthropogeny, anthropogenesis, and anthropogony—with the latter two sometimes used to refer to the related subject of hominization. Primate evolution, Primates diverged from other mammals about (Myr, mya), in the Late Cretaceous period, with their earliest fossils appearing over 55 mya, during the Paleocene. Prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Basic Human Values
The theory of basic human values is a theory of cross-cultural psychology and Universal value, universal values developed by Shalom H. Schwartz. The theory extends previous cross-cultural communication frameworks such as Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory. Schwartz identifies ten basic human values, distinguished by their underlying motivation or goals, and explains how people in all cultures recognize them. There are two major methods for measuring these ten basic values: the Schwartz Value Survey and the Portrait Values Questionnaire. In value theory, individual values may align with, or conflict against one another, often visualised in a circular diagram where opposing poles indicate values that are in conflict. An expanded framework of 19 distinct values was presented from Schwartz and colleagues in a 2012 publication, creating on the theory of basic values. These values are conceptualized as "guiding principles" that influence the behaviors and decisions of individuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalom Schwartz
Shalom H. Schwartz () is a social psychologist, cross-cultural researcher and creator of the Theory of Basic Human Values (universal values as latent motivations and goals). He also developed value scales to measure both individual and national/cultural values that have been translated into 50+ languages and applied in over 90 societies. Biography ; Knafo, A., Roccas, S., & Sagiv, L. (2011). The value of values in cross-cultural research: A special issue in honor of Shalom Schwartz ditorial Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 42(2), 178–185. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022110396863 After completing his master's degree in social psychology and group development at Columbia University and completing his rabbinical studies, Schwartz received his Ph.D. in social psychology from the University of Michigan in 1967. Subsequently he taught in the sociology department of the University of Wisconsin–Madison, becoming a full professor in 1973. From 1971 to 73, Schwartz was a visit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relational Models Theory
Relational models theory (RMT) is a theory of interpersonal relationships, authored by anthropologist Alan Fiske and initially developed from his fieldwork in Burkina Faso. RMT proposes that all human interactions can be described in terms of just four "relational models", or elementary forms of human relations: communal sharing, authority ranking, equality matching and market pricing (to these are added the limiting cases of asocial and null interactions, whereby people do not coordinate with reference to any shared principle). RMT influenced Jonathan Haidt's moral foundations theory and Steven Pinker's theory of indirect speech. The theory First proposed in Fiske's doctoral dissertation in 1985, relational models theory proposes four relational models which are each argued to be innate, intrinsically motivated, and culturally universal (though with culture-specific implementations) ways of cooperating and coordinating social interactions. The four relational models The four re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |