|
Monoprinting
Monoprinting is a type of printmaking where the intent is to make unique prints, that may explore an image serially. Other methods of printmaking create editioned multiples, the monoprint is editioned as 1 of 1. There are many techniques of mono-printing, in particular the monotype. Printmaking techniques which can be used to make mono-prints include lithography, woodcut, and etching. Types A monoprint is a single impression of an image made from a reprintable block. Materials such as metal plates, litho stones or wood blocks are used for etching upon. Rather than printing multiple copies of a single image, only one impression may be produced, either by painting or making a collage on the block. Etching plates may also be inked in a way that is expressive and unique in the strict sense, in that the image cannot be reproduced exactly. Monoprints may also involve elements that change, where the artist reworks the image in between impressions or after printing so that no two print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating work of art, artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine (Printer (computing), a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Prints are created by transferring ink from a Matrix (printing), matrix to a sheet of paper or other material, by a variety of techniques. Common types of matrices include: metal plates for engraving, etching and related intaglio printing techniques; stone, aluminum, or polymer for lithography; blocks of wood for woodcuts and wood engravings; and linoleum for linocuts. Screens made of silk or synthetic fabrics are used for the screen printing process. Other types of matrix substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotype
Monotyping is a type of printmaking made by drawing or painting on a smooth, non-absorbent surface. The surface, or matrix, was historically a copper etching plate, but in contemporary work it can vary from zinc or glass to acrylic glass. The image is then transferred onto a paper by pressing the two together, using a printing-press, brayer, baren or by techniques such as rubbing with the back of a wooden spoon or the fingers which allow pressure to be controlled selectively. Monotypes can also be created by inking an entire surface and then, using brushes or rags, removing ink to create a subtractive image, e.g. creating lights from a field of opaque colour. The inks used may be oil or water-based. With oil-based inks, the paper may be dry, in which case the image has more contrast, or the paper may be damp, in which case the image has a 10 percent greater range of tones. Monotyping produces a unique print, or monotype; most of the ink is removed during the initial pressin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotyping
Monotyping is a type of printmaking made by drawing or painting on a smooth, non-absorbent surface. The surface, or matrix (printing), matrix, was historically a copper etching plate, but in contemporary work it can vary from zinc or glass to acrylic glass. The image is then transferred onto a paper by pressing the two together, using a printing-press, brayer, Baren (printing tool), baren or by techniques such as rubbing with the back of a wooden spoon or the fingers which allow pressure to be controlled selectively. Monotypes can also be created by inking an entire surface and then, using brushes or rags, removing ink to create a subtractive image, e.g. creating lights from a field of opaque colour. The inks used may be oil or water-based. With oil-based inks, the paper may be dry, in which case the image has more contrast, or the paper may be damp, in which case the image has a 10 percent greater range of tones. Monotyping produces a unique print, or monotype; most of the ink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for sheet music, musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design''. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146, .Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. ''Typographic Design: Form and Communication'', Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 11. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for printmaking, fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Traditionally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking. An artist carves an image into the surface of a block of wood—typically with gouges—leaving the printing parts level with the surface while removing the non-printing parts. Areas that the artist cuts away carry no ink, while characters or images at surface level carry the ink to produce the print. The block is cut along the wood grain (unlike wood engraving, where the block is cut in the end-grain). The surface is covered with ink by rolling over the surface with an ink-covered roller ( brayer), leaving ink upon the flat surface but not in the non-printing areas. Multiple colours can be printed by keying the paper to a frame around the woodblocks (using a different block for each colour). The art of carving the woodcut can be called ''xylography'', but this is rarely used in English for images alone, although that term and ''xylographic'' are used in connection with block books, which are small books containing text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling, it is a crucial technique in modern technology, including circuit boards. In traditional pure etching, a metal plate (usually of copper, zinc or steel) is covered with a waxy ground which is resistant to acid. The artist then scratches off the ground with a pointed etching needle where the artist wants a line to appear in the finished piece, exposing the bare metal. The échoppe, a tool with a slanted oval section, is also used for "swelling" lines. The plate is then dipped in a bath of aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual arts, visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, Composition (visual art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collage
Collage (, from the , "to glue" or "to stick together") is a technique of art creation, primarily used in the visual arts, but in music too, by which art results from an assembly of different forms, thus creating a new whole. (Compare with pastiche, which is a "pasting" together.) Collage may refer to the technique as a whole, or more specifically to a two-dimensional work, assembled from flat pieces on a flat substrate, whereas Assemblage (art), assemblage typically refers to a three-dimensional equivalent. A collage may sometimes include Clipping (publications), magazine and newspaper clippings, ribbons, paint, bits of colored or handmade papers, portions of other artwork or texts, photographs and other found objects, glued to a piece of paper or canvas. The origins of collage can be traced back hundreds of years, but this technique made a dramatic reappearance in the early 20th century as an art form of novelty. The term ''Papier collé'' was coined by both Georges Braque a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, sometimes in combination. More modern tools include Stylus (computing), computer styluses with graphics tablets and gamepads in Virtual reality, VR drawing software. A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as Paperboard, cardboard, vellum, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and Lumber, board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. It is one of the simplest and most efficient means of communicating ideas. The wide availability of drawing instruments makes drawing one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
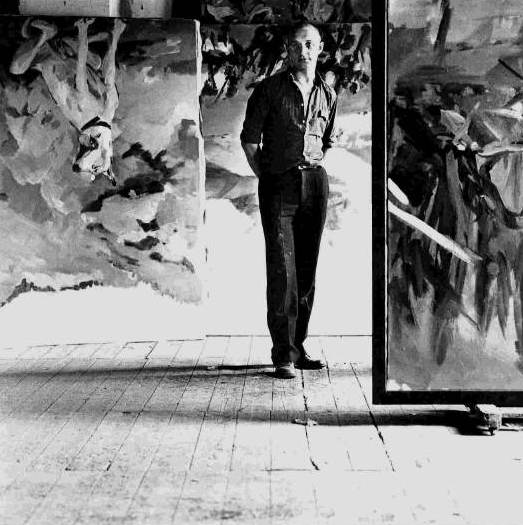
Georg Baselitz
Georg Baselitz (born 23 January 1938) is a German Painting, painter, Sculpture, sculptor and Graphic arts, graphic artist. In the 1960s he became well known for his Figurative art, figurative, expressive paintings. In 1969 he began painting his subjects upside down in an effort to overcome the Representation (arts), representational, content-driven character of his earlier work and stress the artifice of painting. Drawing from myriad influences, including art of History of the Soviet Union, Soviet era illustration art, the Mannerism, Mannerist period and African sculptures, he developed his own, distinct artistic language. He was born as Hans-Georg Kern in , Upper Lusatia, Germany. He grew up amongst the suffering and demolition of World War II, and the concept of destruction plays a significant role in his life and work. These biographical circumstances are recurring aspects of his entire oeuvre. In this context, the artist stated in an interview: "I was born into a destroyed or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Master Print
An old master print (also spaced masterprint) is a work of art produced by a printing process within the Western tradition (mostly by Old Masters). The term remains current in the art trade, and there is no easy alternative in English to distinguish the works of "fine art" produced in printmaking from the vast range of decorative, utilitarian and popular prints that grew rapidly alongside the artistic print from the 15th century onwards. Fifteenth-century prints are sufficiently rare that they are classed as old master prints even if they are of crude or merely workmanlike artistic quality. A date of about 1830 is usually taken as marking the end of the period whose prints are covered by this term. The main techniques used, in order of their introduction, are woodcut, engraving, etching, mezzotint and aquatint, although there are others. Different techniques are often combined in a single print. With rare exceptions printed on textiles, such as silk, or on vellum, old master print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |