|
Monoisotopic Mass
Monoisotopic mass (Mmi) is one of several types of molecular masses used in mass spectrometry. The theoretical monoisotopic mass of a molecule is computed by taking the sum of the accurate masses (including mass defect) of the most abundant naturally occurring stable isotope of each atom in the molecule. It is also called the exact (a.k.a. theoretically determined) mass. For small molecules made up of low atomic number elements the monoisotopic mass is observable as an isotopically pure peak in a mass spectrum. This differs from the nominal molecular mass, which is the sum of the mass number of the primary isotope of each atom in the molecule and is an integer. It also is different from the molar mass, which is a type of average mass. For some atoms like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur, the Mmi of these elements is exactly the same as the mass of its natural isotope, which is the lightest one. However, this does not hold true for all atoms. Iron's most common isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionization, ionized, for example by bombarding it with a Electron ionization, beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules, electrons, positrons, protons, antiprotons, and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected. Uses Everyday examples of gas ionization occur within a fluorescent lamp or other electrical discharge lamps. It is also used in radiation detectors such as the Geiger- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word: ''Atomgewicht'', "atomic weight"), also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approximately equal to the ''atomic'' (also known as ''isotopic'') mass of the atom expressed in daltons. Since protons and neutrons are both baryons, the mass number ''A'' is identical with the baryon number ''B'' of the nucleus (and also of the whole atom or ion). The mass number is different for each isotope of a given chemical element, and the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ''Z'' gives the number of neutrons (''N'') in the nucleus: . The mass number is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, the most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12, or , which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The full isotope symbol would also have the atomic number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quantity relative molecular mass is the unitless ratio of the mass of a molecule to the atomic mass constant (which is equal to one dalton). The molecular mass and relative molecular mass are distinct from but related to the ''molar mass''. The molar mass is defined as the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of the substance, and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). That makes the molar mass an ''average'' of many particles or molecules (weighted by abundance of the isotopes), and the molecular mass the mass of one specific particle or molecule. The molar mass is usually the more appropriate quantity when dealing with macroscopic (weigh-able) quantities of a substance. The definition of molecular weight is most authoritat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
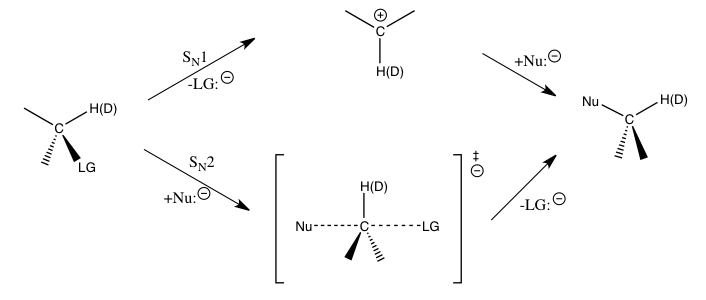
Kinetic Isotope Effect
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes. Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (''k'') and the heavy (''k'') isotopically substituted reactants ( isotopologues): KIE = ''k/k''. This change in reaction rate is a quantum effect that occurs mainly because heavier isotopologues have lower vibrational frequencies than their lighter counterparts. In most cases, this implies a greater energy input needed for heavier isotopologues to reach the transition state (or, in rare cases, dissociation limit), and therefore, a slower reaction rate. The study of KIEs can help elucidate reaction mechanisms, and is occasionally exploited in drug development to improve unfavorable pharmacokinetics by protecting metabolically vulnerable C-H bonds. Background KIE is considered one of the most essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine Sulphone
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. Methionine is also involved in angiogenesis and various processes related to DNA transcription, epigenetic expression, and gene regulation. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. It is encoded by the codon AUG. It was named by Satoru Odake in 1925, as an abbreviation of its structural description 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the protonated form un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Atomic Weight
The standard atomic weight of a chemical element (symbol ''A''r°(E) for element "E") is the weighted arithmetic mean of the relative isotopic masses of all isotopes of that element weighted by each isotope's abundance on Earth. For example, isotope 63Cu (''A''r = 62.929) constitutes 69% of the copper on Earth, the rest being 65Cu (''A''r = 64.927), so :A_\text\text(_\text\text)=0.69\times62.929+0.31\times64.927=63.55. Relative isotopic mass is dimensionless, and so is the weighted average. It can be converted into a measure of mass (with dimension ) by multiplying it with the atomic mass constant dalton. Among various variants of the notion of atomic weight (''A''r, also known as ''relative atomic mass'') used by scientists, the standard atomic weight is the most common and practical. The standard atomic weight of each chemical element is determined and published by the Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights (CIAAW) of the International Union of Pure and App ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Cyclotron Resonance
Ion cyclotron resonance is a phenomenon related to the movement of ions in a magnetic field. It is used for accelerating ions in a cyclotron, and for measuring the masses of an ionized analyte in mass spectrometry, particularly with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers. It can also be used to follow the kinetics of chemical reactions in a dilute gas mixture, provided these involve charged species. Definition of the resonant frequency An ion in a static and uniform magnetic field will move in a circle due to the Lorentz force. The angular frequency of this ''cyclotron motion'' for a given magnetic field strength ''B'' is given by : \omega = 2\pi f = \frac, where ''z'' is the number of positive or negative charges of the ion, ''e'' is the elementary charge and ''m'' is the mass of the ion. An electric excitation signal having a frequency ''f'' will therefore resonate with ions having a mass-to-charge ratio ''m/z'' given by : \frac = \frac. The circular motion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
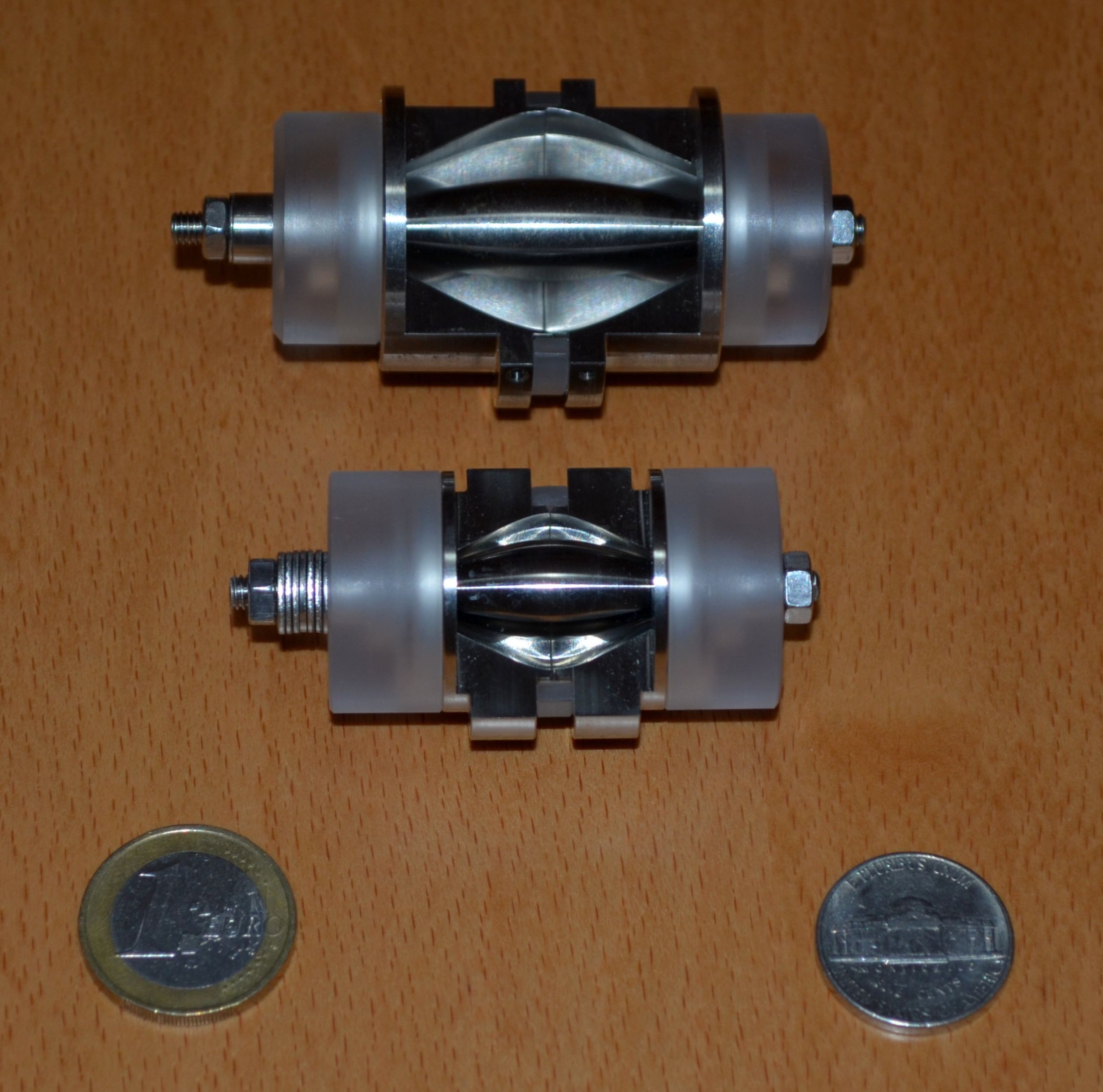
Orbitrap
In mass spectrometry, Orbitrap is an ion trap mass analyzer consisting of an outer barrel-like electrode and a coaxial inner spindle-like electrode that traps ions in an orbital motion around the spindle. The image current from the trapped ions is detected and converted to a mass spectrum by first using the Fourier transform of time domain of the harmonic to create a frequency signal which is converted to mass. History The concept of electrostatically trapping ions in an orbit around a central spindle was developed by Kenneth Hay Kingdon in the early 1920s. The Kingdon trap consists of a thin central wire and an outer cylindrical electrode. A static applied voltage results in a radial logarithmic potential between the electrodes. In 1981, Knight introduced a modified outer electrode that included an axial quadrupole term that confines the ions on the trap axis. Neither the Kingdon nor the Knight configurations were reported to produce mass spectra. In 1986, Professor Yuri Konst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |