|
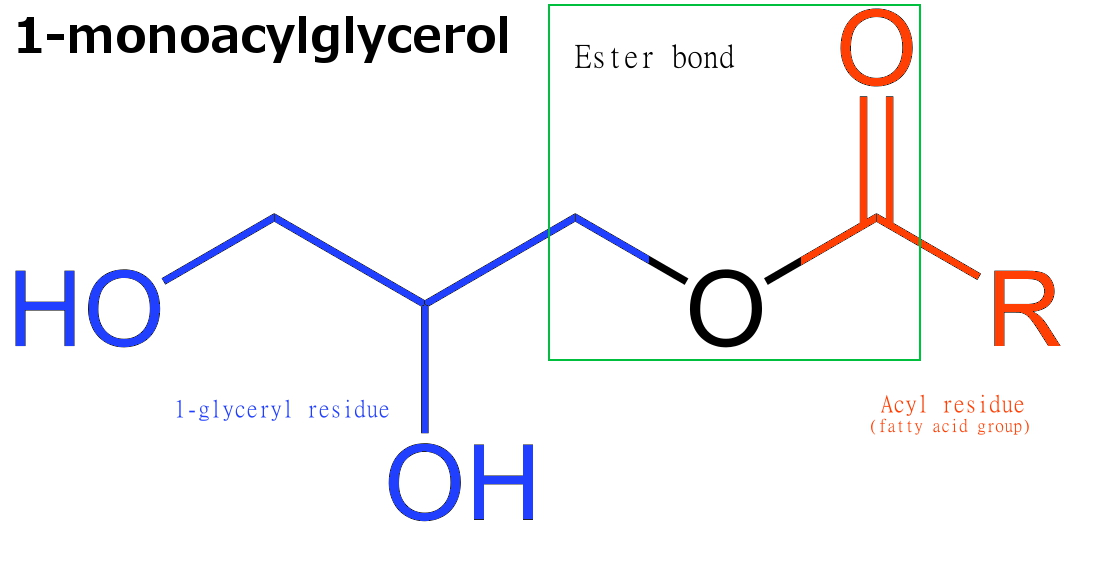
Monoacylglycerol
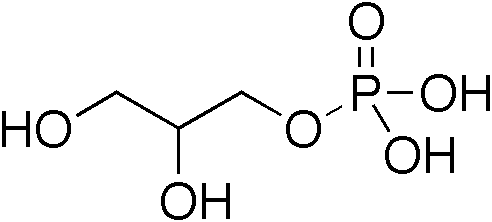
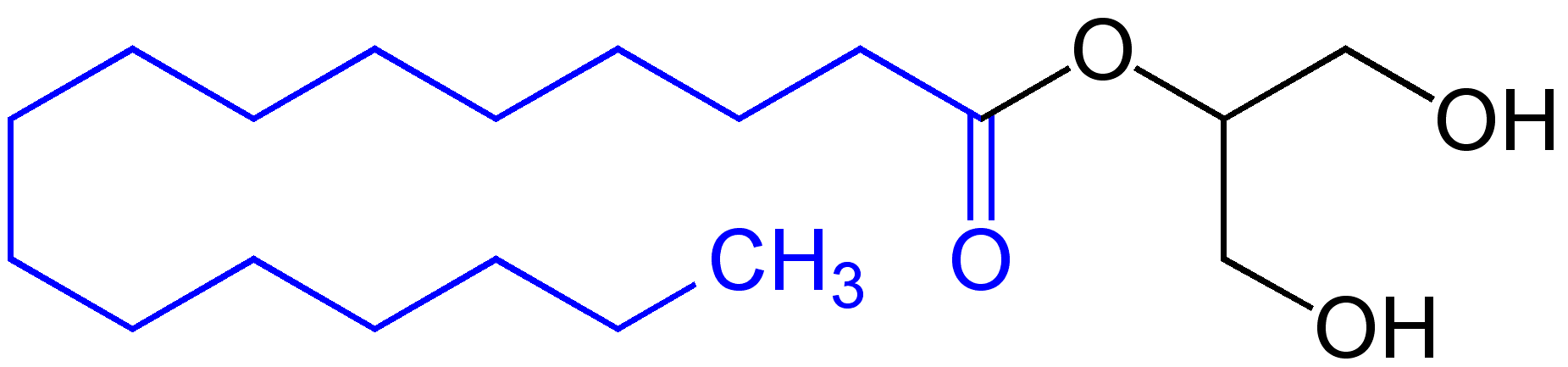
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol. Synthesis Monoglycerides are produced both biologically and industrially. They are naturally present at very low levels (0.1-0.2%) in some seed oils such as olive oil, rapeseed oil and cottonseed oil. They are biosynthesized by the enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase and the enzymatic hydrolysis of diglycerides by diacylglycerol lipase; or as an intermediate in the alkanoylation of glycerol to form fats. Several monoglycerides are pharmacologically active (e.g. 2-oleoylglycerol, 2-arachidonoylglycerol). Industrial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacylglycerol Lipase
Diacylglycerol lipase, also known as DAG lipase, DAGL, or DGL, is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of diacylglycerol, releasing a free fatty acid and monoacylglycerol:diacylglycerol + H2O ⇌ monoacylglycerol + free fatty acidDAGL has been studied in multiple domains of life, including bacteria, fungi, plants, insects, and mammals. By searching with BLAST for the previously sequenced microorganism DAGL, Bisogno et al discovered two distinct mammalian isoforms, designated DAGLα () and DAGLβ (). Most animal DAGL enzymes cluster into the DAGLα and DAGLβ isoforms. Mammalian DAGL is a crucial enzyme in the biosynthesis of 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), the most abundant endocannabinoid in tissues. The endocannabinoid system has been identified to have considerable involvement in the regulation of homeostasis and disease. As a result, much effort has been made toward investigating the mechanisms of action and the therapeutic potential of the system's receptors, endogenous li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-arachidonoylglycerol
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is an endocannabinoid, an endogenous agonist of the CB1 receptor and the primary endogenous ligand for the CB2 receptor. It is an ester formed from the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid and glycerol. It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system, with cannabinoid neuromodulatory effects. It has been found in maternal bovine and human milk. The chemical was first described in 1994–1995, although it had been discovered some time before that. The activities of phospholipase C (PLC) and diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) mediate its formation. 2-AG is synthesized from arachidonic acid-containing diacylglycerol (DAG). Occurrence 2-AG, unlike anandamide (another endocannabinoid), is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system; it is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in mouse and rat brain (~5–10 nmol/g tissue). Detection of 2-AG in brain tissue is complicated by the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diglyceride
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoprotein Lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-soluble enzyme that hydrolyzes triglycerides in lipoproteins, such as those found in chylomicrons and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), into two free fatty acids and one monoacylglycerol molecule: : triacylglycerol + H2O = diacylglycerol + a carboxylate It is also involved in promoting the cellular uptake of chylomicron remnants, cholesterol-rich lipoproteins, and free fatty acids. LPL requires ApoC-II as a cofactor. LPL is attached to the luminal surface of endothelial cells in capillaries by the protein glycosylphosphatidylinositol HDL-binding protein 1 ( GPIHBP1) and by heparan sulfated peptidoglycans. It is most widely distributed in adipose, heart, and skeletal muscle tissue, as well as in lactating mammary glands. Synthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diglycerides
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
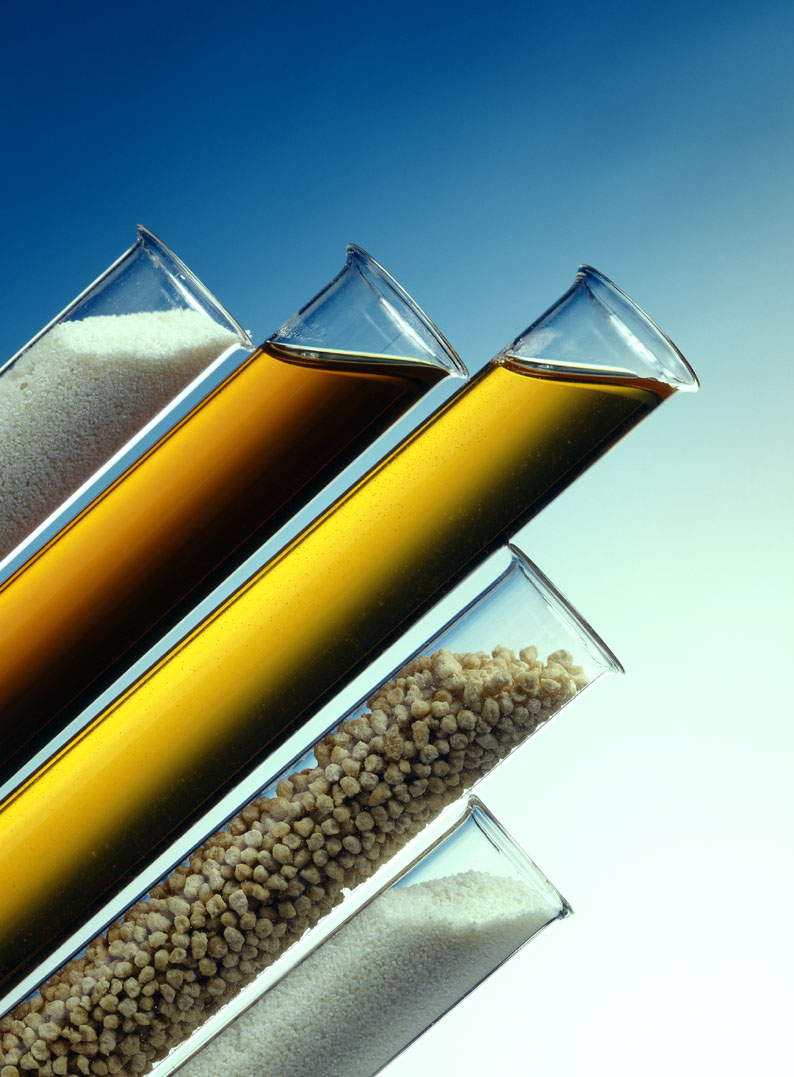
Mono- And Diglycerides Of Fatty Acids
Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids ( E471) are a naturally occurring class of food additive composed of diglycerides and monoglycerides used as an emulsifier in foods such as infant formula, fresh pasta, jams and jellies, chocolate, creams, baked goods, and more. It is also used as a fruit coating agent. This mixture is also sometimes referred to as partial glycerides. Synthesis Monoglycerides and diglycerides are types of glycerides both naturally present in food fats, including various seed oils; however, their concentration is usually low and industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides (fats/oils) and glycerol, followed by purification via solvent-free molecular distillation. The raw materials of mono- and diglycerides may be either vegetable or animal fats and oils. Dietary aspects E471 is mainly produced from vegetable oils (such as soybean, grapeseed, canola, sunflower, cottonseed, coconut, and palm oil) and plant p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets, and wines. With the advent of ultra-processed foods in the late 20th century, many additives having both natural and artificial origin were introduced. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process through packaging, storage or transport. In Europe and internationally, many additives are designated with E numbers, while in the United States, additives in amounts deemed safe for human consumption are designated as GRAS. Identification To regulate these additives and inform consumers each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cream
Ice cream is a frozen dessert typically made from milk or cream that has been flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as Chocolate, cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit, such as strawberries or peaches. Food colouring is sometimes added in addition to Food stabilizer, stabilizers. The mixture is cooled below the freezing point of water and stirred to incorporate air spaces and prevent detectable ice crystals from forming. It can also be made by Whisk, whisking a flavoured cream base and liquid nitrogen together. The result is a smooth, semi-solid foam that is solid at very low temperatures (below ). It becomes more Ductility, malleable as its temperature increases. Ice cream may be served in dishes, eaten with a spoon, or licked from edible wafer Ice cream cone, ice cream cones held by the hands as finger food. Ice cream may be served with other desserts—such as cake or pie—or used as an ingredient in cold dishes—like ice cream floats, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulsifiers
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms ''colloid'' and ''emulsion'' are sometimes used interchangeably, ''emulsion'' should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the dispersed phase) is dispersed in the other (the continuous phase). Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions. As an example, oil and water can form, first, an oil-in-water emulsion, in which the oil is the dispersed phase, and water is the continuous phase. Second, they can form a water-in-oil emulsion, in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the continuous phase. Multiple emulsions are also pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word ''surfactant'' is a Blend word, blend of "surface-active agent", coined in 1950. As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt. Surfactants are among the most widespread and commercially important chemicals. Private households as well as many industries use them in large quantities as detergent, detergents and cleaning agents, but also for example as emulsion#Emulsifiers, emulsifiers, wetting agents, foaming agents, Antistatic agent, antistatic additives, or dispersants. Surfactants occur naturally in traditional plant-based detergents, e.g. Aesculus, horse chestnuts or Sapindus, soap nuts; they can also be found in the secretions of some caterpillars. Today one of the most commonly used anionic surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Fat
Animal fats are lipids derived from animals which are used by the animal for a multitude of functions, or can be used by humans for dietary, sanitary, and cosmetic purposes. Depending on the temperature of the fat, it can change between a solid state and a liquid ( oil) state. Chemically, both fats and oils are composed of triglycerides. Although many animal parts and secretions may yield oil, in commercial practice, oil is extracted primarily from rendered tissue fats from livestock animals like pigs, chickens and cows. Dairy products yield animal fat and oil products such as butter. Chemical structure Animal fats are composed of triglycerides, which are a type of ester molecule in which glycerol is bonded to three fatty acids. The three fatty acids that bond to the glycerol will determine the complexity and type of the triglyceride. If the three fatty acids are the same, then the triglyceride will be considered a simple triglyceride. However, most triglycerides contain diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |