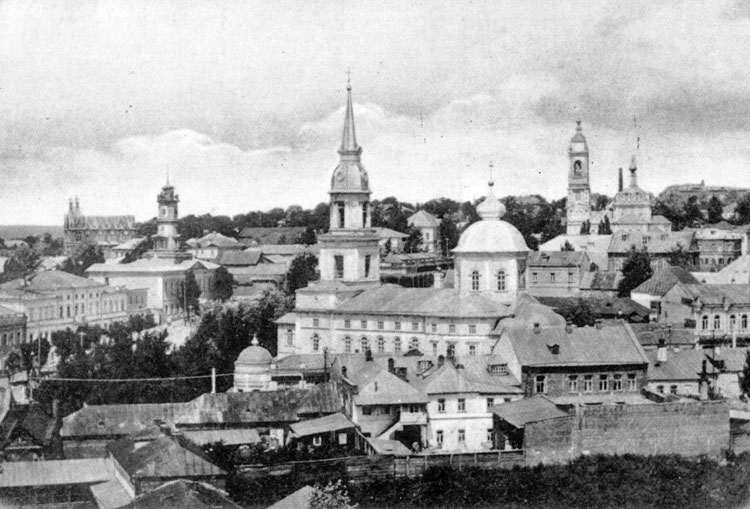|
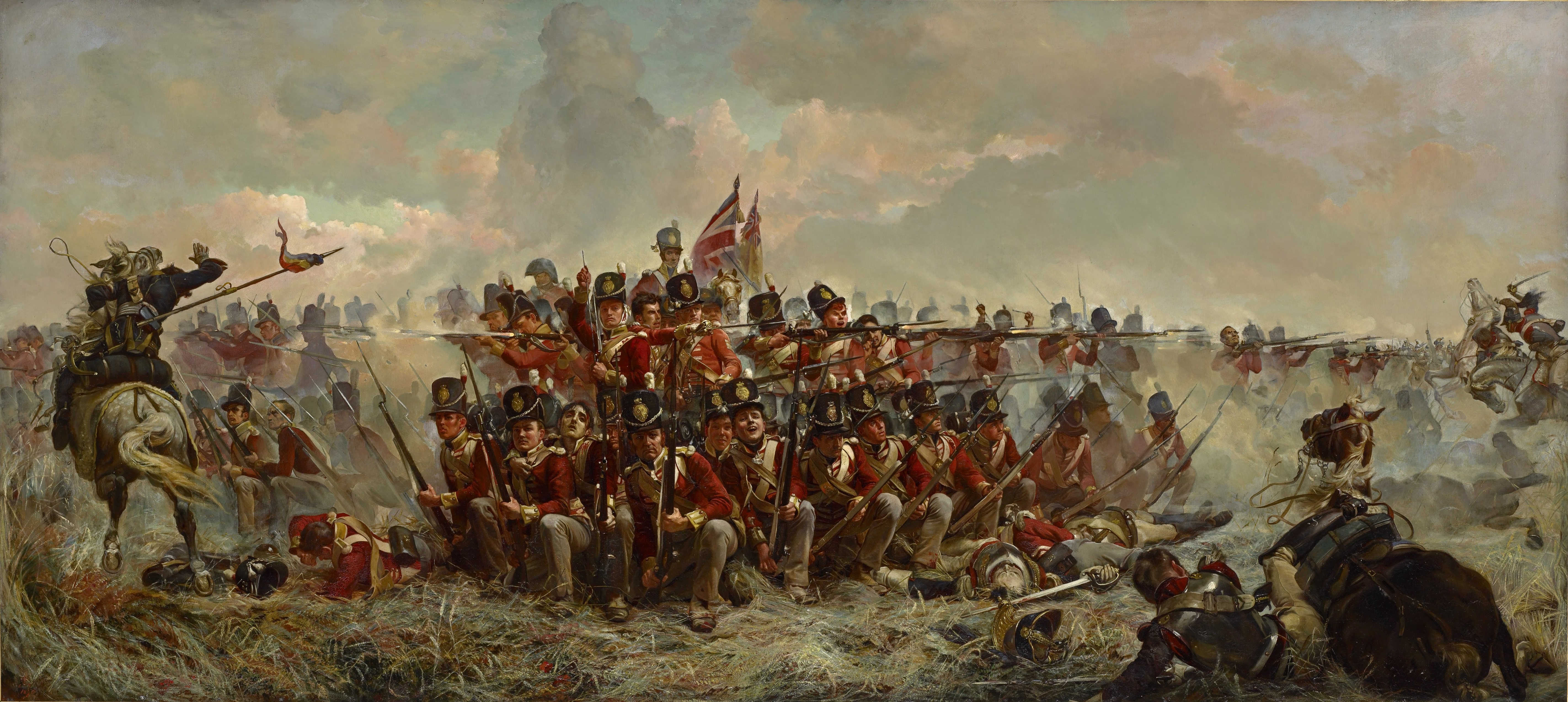
Mobile Defense
Mobile defense is a manoeuvre by military units that repulses an attack by the use of well-planned counter-attacks by the defender, which seeks to avoid a pitched battle. History One modern example of mobile defense was during World War II during the Third Battle of Kharkov. The German commander, Generalfeldmarschall, Field Marshal Erich von Manstein, used II SS Panzer Corps to launch an attack to the rear of the Soviet spearhead force and to encircle it. The success led to the stabilization of the German Army Group South. Manstein became a proponent of the use of a strategy of mobile defense on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front as a whole. Manstein came to the conclusion that Germany could not defeat the Soviet Union in the traditional static defensive system used in World War I and that the only chance to achieve a draw was to wear down the Soviet Army in costly mobile battles. Manstein formulated a plan for the summer of 1943 in which he argued all mechanized for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrams Kicks Up Dust 140821-A-SF231-268
Abrams may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Abrams (surname), a list of notable people with the surname Places United States * Abrams, Wisconsin, a town * Abrams (community), Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Abrams Mountain, Colorado * Abrams Creek (Tennessee) * Abrams Creek (Virginia) * Abrams Run, West Virginia, a stream Elsewhere * Mount Abrams, Graham Land, Antarctica Other uses * M1 Abrams, the main battle tank of the United States Army * '' Abrams v. United States'', 250 U.S. 616 (1919), a U.S. Supreme Court decision regarding free speech during times of war * Abrams Air Craft Corporation, an American aircraft manufacturer * Abrams Books, U.S. publishing house * ''Abrams Discoveries'', a non-fiction book series published by Harry N. Abrams * The Abrams, a Canadian country music band See also * Abrams Planetarium, the planetarium on the campus of Michigan State University * Abram (other) * Abramson (surname) * Abrahams (surname) Abrahams is a surname. Notable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kursk
Kursk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur (Kursk Oblast), Kur, Tuskar, and Seym (river), Seym rivers. It has a population of Kursk is the oldest city in the oblast, recorded in 1032 as part of the Kievan Rus'. It became the seat of a small eponymous principality in the 13th century, before passing to Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuanian rule in the Late Middle Ages, late medieval period, and then to Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow in the early modern period. Kursk has served as the seat of regional administration since 1779. The area around Kursk was the site of a turning point in the Soviet–German struggle during World War II and the site of the Battle of Kursk, single largest battle in history. Geography Urban layout Kursk was originally built as a fortress city on a hill dominating the plain. The settlement was surrounded on three sides by the Kur (Kursk Oblast), K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (Russia)
The Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation (; MOD) is the governing body of the Russian Armed Forces. The President of Russia is the Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, Commander-in-Chief of the forces and directs the activity of the ministry. The Minister of Defence (Russia), Minister of Defence exercises day-to-day administrative and operational authority over the forces. The General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, General Staff of the Armed Forces executes the instructions and orders of the president and the defence minister. The ministry is headquartered in the General Staff Building (Moscow), General Staff building, built-in 1979–1987 on Arbatskaya Square, near Arbat Street in Moscow. Other buildings of the ministry are located throughout Moscow. The supreme body responsible for the ministry's management and supervision of the Armed Forces and the centralization of the Armed Forces' command is the National De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Rogozin
Dmitry Olegovich Rogozin (; born 21 December 1963) is a Russian nationalist politician serving as the senator from the Russian-occupied Zaporozhye Oblast since 23 September 2023. He previously served as General Director of Roscosmos from 2018 to July 2022, as deputy prime minister in charge of the defense industry from 2011 to 2018, and as Russia's ambassador to NATO from 2008 to 2011. He was co-founder of the far-right Rodina political party, which was created in 2003. Parts of the party later merged with other parties to form A Just Russia in 2006. Early life and education Rogozin was born in Moscow to the family of a Soviet military scientist. He graduated from Moscow State University in 1986 with a degree in journalism, and in 1988 he graduated from the University of Marxism–Leninism under the Moscow City Committee of the CPSU with a degree in economics. His thesis on "Philosophy and Theory of Wars" earned him a Doctor of Philosophy while a Doctor of Technical Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area Defense
Area defense is a method of positional defensive warfare described in the U.S. Army's combat manuals of the 1960s and 1970s. After 1982 the term "positional defense" replaced it. Basic provisions Area defense consisted of stubbornly holding tactically advantageous positions with careful equipping of defense lines, engineering barriers, and the fullest possible use of all available firepower of the troops. As a rule, area defense was used to cause the maximum damage to the enemy and to preserve the integrity of the defensive belt in conditions of inadequate depth of defense and in types of terrain which limited the maneuvering of forces. The use of units that were inferior in mobility to enemy troops was considered advisable for district defense, and district defense could also be used in combination with Mobile Defense techniques, especially at the operational level. American military theorists consider this method of warfare a classic. When defending an area, an American mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterattack
A counterattack is a tactic employed in response to an attack, with the term originating in "Military exercise, war games". The general objective is to negate or thwart the advantage gained by the enemy during attack, while the specific objectives typically seek to regain lost ground or destroy the attacking enemy (this may take the form of an opposing sports team or Military organization#Commands.2C formations.2C and units, military units). A counter-offensive is a broad-scale counterattack. The counter-offensive is executed after exhausting the enemy's front line, frontline troops and after the enemy Military reserve, reserves had been committed to combat and proven incapable of breaching defenses, but ''before'' the enemy has had the opportunity to assume new defensive positions. Sometimes the counter-offensive can be of a more limited operational maneuver nature, with more limited objectives rather than those seeking attainment of a Strategic goal (military), strategic goal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Tactics
Infantry tactics are the combination of military concepts and methods used by infantry to achieve tactical objectives during combat. The role of the infantry on the battlefield is, typically, to close with and engage the enemy, and hold territorial objectives; infantry tactics are the means by which this is achieved. Infantry commonly makes up the largest proportion of an army's fighting strength, and consequently often suffers the heaviest casualties. Throughout history, infantrymen have sought to minimise their losses in both attack and defence through effective tactics. (''For a wider view of battle and theater tactics see: Military strategy)'' Infantry tactics are the oldest method of warfare and span all eras. In different periods, the prevailing technology of the day has had an important impact on infantry tactics. In the opposite direction, tactical methods can encourage the development of particular technologies. Similarly, as weapons and tactics evolve, so do the tactic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon Of Mass Destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a biological, chemical, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natural structures (e.g., mountains), or the biosphere. The scope and usage of the term has evolved and been disputed, often signifying more politically than technically. Originally coined in reference to aerial bombing with chemical explosives during World War II, it has later come to refer to large-scale weaponry of warfare-related technologies, such as biological, chemical, radiological, or nuclear warfare. Early usage The first use of the term "weapon of mass destruction" on record is by Cosmo Gordon Lang, Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1937 in reference to the bombing of Guernica, Spain: At the time, nuclear weapons had not been developed fully. Japan conducted research on biological weapons, and chemical weapons had seen wide battlefield use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voenizdat
Voenizdat () was a publishing house in Moscow, Russia that was one of the first and largest publishing houses in USSR. The name is a Russian abbreviation for Voennoe Izdatelstvo (), meaning "Military Publishing House". Voenizdat was established by the Revolutionary Military Council (Revvoyensoviet) on 25 October 1919. The initial aim was to publish literature for the needs of the Ministry of Defence. It later published both fiction and non-fiction literature, technical manuals and dictionaries A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically (or by Semitic root, consonantal root for Semitic languages or radical-and-stroke sorting, radical an .... The company was absorbed into the joint stock company Red Star in 2009. References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Supremacy
Air supremacy (as well as air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of command of the sea. Air power has increasingly become a powerful element of military campaigns; military planners view having an environment of at least air superiority as a necessity. Air supremacy allows increased bombing efforts, tactical air support for ground forces, paratroop assaults, airdrops and simple cargo plane transfers, which can move ground forces and supplies. Air power is a function of the degree of air superiority and numbers or types of aircraft, but it represents a situation that defies black-and-white characterization. The degree of a force's air control is a zero-sum game with its opponent's; increasing control by one corresponds to decreasing control by the other. Air forces unable to contest for air superiori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Command
A combat command was a Combined arms, combined-arms military organization of comparable size to a brigade or regiment employed by armored forces of the United States Army from 1942 until 1963. The structure of combat commands was task-organized and so the forces assigned to a combat command often varied from mission to mission. Abbreviations Combat command is most often abbreviated by one of the related derivative notations: * CCA, or CC-A or CC A * CCB, or CC-B or CC B * CCC, or CC-C or CC C (an older convention for "reserve formation") * CCR, or CC-R or CC R (for Combat Command Reserve) History The concept of the combat command was developed by General Adna R. Chaffee Jr., Adna Chaffee during the 1930s. Chaffee's concept envisaged combined arms mechanized units with no formal structure. When the first U.S. armored divisions were organized a few years later, Chaffee's concepts for the combat command were incorporated into the divisional structure. The combat command was a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce C
The English language name Bruce arrived in Scotland with the Normans, from the place name Brix, Manche in Normandy, France, meaning "the willowlands". Initially promulgated via the descendants of king Robert the Bruce (1274−1329), it has been a Scottish surname since medieval times; it is now a common male given name. The variant ''Lebrix'' and ''Le Brix'' are French variations of the surname. Note: A few people are notable in more than one field, and therefore appear in more than one section. Arts and entertainment Film and television * Bruce Altman (born 1955), American actor * Bruce Baillie (1931–2020), American filmmaker * Bruce Bennett (1906–2007), American actor and athlete * Bruce Berman (born 1952), American film producer * Bruce Boa (1930–2004), Canadian actor * Bruce Boxleitner (born 1950), American actor * Bruce Campbell (born 1958), American actor, director, writer, producer and author * Bruce Conner (1933–2008), American artist and filmmaker * Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |