|
Military Revolution
The Military Revolution is the theory that a series of radical changes in military strategy and tactics during the 16th and 17th centuries resulted in major lasting changes in governments and society. The theory was introduced by Michael Roberts (historian), Michael Roberts in the 1950s as he focused on Swedish Empire, Sweden (1560–1660) searching for major changes in the European way of war caused by the introduction of portable firearms. Roberts linked military technology with larger historical consequences, arguing that innovations in tactics, drill and doctrine by the Dutch and Swedes (1560–1660), which maximized the utility of firearms, led to a need for more trained troops and thus for permanent forces (Standing army, standing armies). Armies grew much larger and more expensive. These changes in turn had major political consequences in the level of administrative support and the supply of money, men and provisions, producing new financial demands and the creation of new g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Halmyros
The Battle of Halmyros, known by earlier scholars as the Battle of the Cephissus or Battle of Orchomenos, was fought on 15 March 1311, between the forces of the Frankish Greece, Frankish Duchy of Athens and its vassals under Walter V of Brienne, Walter of Brienne against the mercenaries of the Catalan Company, resulting in a decisive victory for the mercenaries. Engaged in conflict with their original employers, the Byzantine Empire, the Catalan Company had traversed the southern Balkans and arrived in southern Greece in 1309. The new Duke of Athens, Walter of Brienne, hired them to attack the Greek ruler of neighbouring Thessaly. Although the Catalans conquered much of the region for him, Walter refused to pay them and prepared to forcibly expel them from their gains. The two armies met at Halmyros in southern Thessaly (or at the Boeotic Cephissus, near Orchomenus (Boeotia), Orchomenos, according to an earlier interpretation). On the Athenian side, many of the most important l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Roberts (historian)
Michael Roberts (1908–1996) was an English historian specializing in the early modern period. He was particularly known for his studies of Swedish history, and his introduction of the concept of a Military Revolution in early modern Europe. Biography Roberts was born in Lytham St Annes, Lancashire and educated at Brighton College, and Worcester College, Oxford. He taught at Rhodes University College in Grahamstown, South Africa from 1935, served in the army in East Africa during World War II, and headed the British Council in Stockholm 1944–46. From 1954 until his retirement in 1973, he was professor of modern history at the Queen's University of Belfast. He also held guest professorships in U.S. universities. He was a member of the British Academy and the Royal Irish Academy. Roberts is chiefly known as the originator of the theory of a " Revolution in Military Affairs" or RMA, which he first presented in a paper entitled "The Military Revolution: 1560-1660" in a lect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
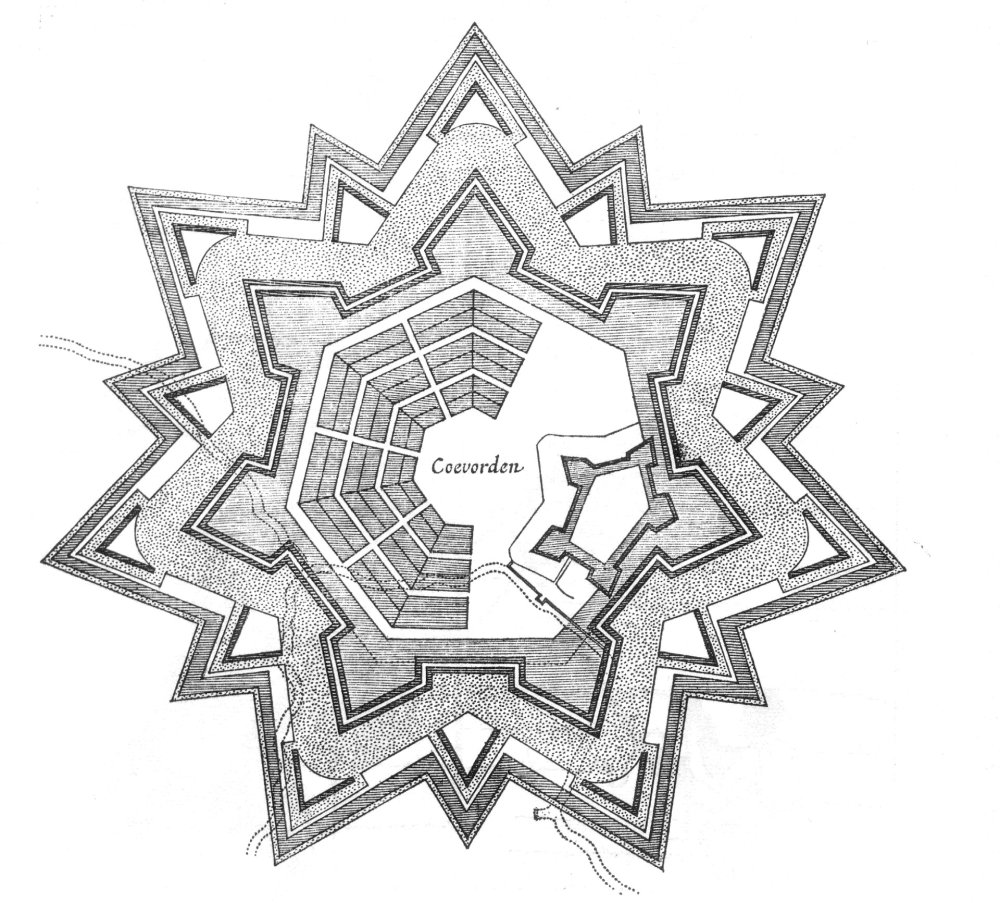
Trace Italienne
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, meaning 'Italian outline') is a fortification in a style developed during the early modern period in response to the ascendancy of gunpowder weapons such as cannon, which rendered earlier medieval approaches to fortification obsolete. It appeared in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era. The design of the fort is normally a polygon with bastions at the corners of the walls. These outcroppings eliminated protected blind spots, called "dead zones", and allowed fire along the curtain wall (fortification), curtain wall from positions protected from direct fire. Many bastion forts also feature Cavalier (fortification), cavaliers, which are raised secondary structures based entirely inside the primary structure. Origins Their predecessors, Medieval fortification, medieval fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years War, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles VIII Of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable (; 30 June 1470 – 7 April 1498), was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. He succeeded his father Louis XI at the age of 13. His elder sister Anne acted as regent jointly with her husband Peter II, Duke of Bourbon until 1491, when the young king turned 21 years of age. During Anne's regency, the great lords rebelled against royal centralisation efforts in a conflict known as the Mad War (1485–1488), which resulted in a victory for the royal government. In a remarkable stroke of audacity, Charles married Anne of Brittany in 1491 after she had already been married by proxy to the Habsburg Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I in a ceremony of questionable validity. Preoccupied by the problematic succession in the Kingdom of Hungary, Maximilian failed to press his claim. Upon his marriage, Charles became administrator of Brittany and established a personal union that enabled France to avoid total encirclement by Habsburg territories. To se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Contamine
Philippe Contamine (7 May 1932 – 26 January 2022) was a French historian of the Middle Ages who specialised in military history and the history of the nobility. Life Contamine was a president of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, the Société de l'histoire de France, and the Societé des Antiquaires de France. He taught at the Université de Nancy, the Paris Nanterre University at Nanterre and Paris-Sorbonne University (Paris-Sorbonne). He was an officer of the Legion of Honour and a fellow of the Royal Historical Society The Royal Historical Society (RHS), founded in 1868, is a learned society of the United Kingdom which advances scholarly studies of history. Origins The society was founded and received its royal charter in 1868. Until 1872 it was known as the H .... He died on 26 January 2022, at the age of 89. Select bibliography * ''Guerre, État et Société à la Fin du Moyen Âge. Études sur les armées des rois de France, 1337-1494 (doctora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lance Rest
A lance rest ( French: ''arrêt de cuirasse'' or ''arrêt'') is a metal flange or hook that is typically attached to the right side of a breastplate, just under the armpit. The lance rest appeared in the late 14th century, remaining in use until the use of full plate armour and heavy lance The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...s became obsolete for general use in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. The lance rest was used to stop the rearward movement of the weapon upon impact. This allowed the wielder of the lance to created an unyielding platform from which to couch the weapon so that the rider's strong armour absorbed the shock of the impact, thus delivering a more solid blow to his target while lessening the chance of injury to himself. The lance rest achieves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Armour
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, especially in the context of the Hundred Years' War, from the coat of plates (popular in late 13th and early 14th century) worn over mail (armour), mail suits during the 14th century, a century famous for the Transitional armour, in that plate gradually replaced mail. In Europe, full plate armour reached its peak in the 15th and 16th centuries. The full suit of armour, also referred to as a panoply, is thus a feature of the very end of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance period. Its popular association with the "Middle Ages in popular culture, medieval knight” is due to the specialised jousting armour which developed in the 16th century. Full suits of Gothic plate armour and Milanese plate armour were worn on the battlefields of the Burgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Formigny
The Battle of Formigny, fought on 15 April 1450, took place towards the end of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. It was a decisive French victory that destroyed the last significant English field army in Normandy, and paved the way for the recapture of their remaining strongholds. Although cannon had been employed in siege warfare since the early 14th century, Formigny is notable as one of the first recorded uses of field artillery on a European battlefield. Background Charles VII of France used the time afforded by the 1444 Treaty of Tours to reorganise and reinvigorate his armies. In contrast, the English were divided by the internal struggle for power that would lead to the Wars of the Roses in 1455. Inability to agree a coherent strategy left their forces in Normandy scattered and dangerously weak. As a result, the French were in a much stronger position when they broke the truce in June 1449. By August, they had taken Pont-Audemer, Pont-L'Evêque and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Patay
The Battle of Patay, fought on 18 June 1429 during the Hundred Years' War, was the culmination of the Loire Campaign between the French and English in north-central France. In this engagement, the horsemen of the French vanguard inflicted heavy casualties on an English army; most of them sustained by the longbowmen as the English cavalry fled. In addition, all but one of the senior English commanders were captured. A victory often credited to Joan of Arc, she was in fact not present for the battle as she had remained with the main body of the French army. The vanguard at Patay was led by La Hire and Jean Poton de Xaintrailles. The battle was a disastrous blow to English aspirations in France. For the French, it cemented the turn of fortune which had begun at Orléans and concluded a highly successful campaign. The latter was followed by a march to Reims which saw the Dauphin Charles be crowned King of France. The Hundred Years' War, however, would continue until 1453. Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Legnano
The battle of Legnano was a battle between the imperial army of Frederick Barbarossa and the troops of the Lombard League on 29 May 1176, near the town of Legnano, in present-day Lombardy, Italy. Although the presence of the enemy nearby was already known to both sides, they suddenly met without having time to plan any strategy. The battle was crucial in the long war waged by the Holy Roman Empire in an attempt to assert its power over the municipalities of northern Italy, which decided to set aside their mutual rivalries and join in a military alliance symbolically led by Pope Alexander III, the Lombard League. The battle ended the fifth and last descent into Italy of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, who after the defeat tried to resolve the Italian question by adopting a diplomatic approach. This resulted a few years later in the Peace of Constance (25 June 1183), with which the Emperor recognized the Lombard League and made administrative, political, and judicial concessions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bannockburn
The Battle of Bannockburn ( or ) was fought on 23–24 June 1314, between the army of Robert the Bruce, King of Scots, and the army of King Edward II of England, during the First War of Scottish Independence. It was a decisive victory for Robert Bruce and formed a major turning point in the war, which ended 14 years later with the ''de jure'' restoration of Scottish independence under the Treaty of Edinburgh–Northampton. For this reason, the Battle of Bannockburn is widely considered a landmark moment in Scottish history. King Edward II invaded Scotland after Bruce demanded in 1313 that all supporters still loyal to ousted Scottish king John Balliol acknowledge Bruce as their king or lose their lands. Stirling Castle, a Scots royal fortress occupied by the English, was under siege by the Scottish army. King Edward assembled a formidable force of soldiers to relieve it—the largest army ever to invade Scotland. The English summoned 25,000 infantry soldiers and 2,000 horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |