|
Military Fiat
Military fiat is a process whereby a decision is made and enforced by military means without the participation of other political elements. The Latin term ''fiat'', translated as "let it be," suggests the autocratic attitude ascribed to such a process. For example, many coups involve the imposition of a new government by military fiat. See also * Ecoregional democracy * Fiat money Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ... References External links Goldsmith and his Gaian hierarchy Political terminology Civil–military relations Autocracy {{poli-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocracy
Autocracy is a form of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state and Head of government, government, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with democracy and feudalism. Various definitions of autocracy exist. They may restrict autocracy to cases where power is held by a single individual, or they may define autocracy in a way that includes a group of rulers who wield absolute power. The autocrat has total control over the exercise of civil liberties within the autocracy, choosing under what circumstances they may be exercised, if at all. Governments may also blend elements of autocracy and democracy, forming a mixed type of regime sometimes referred to as anocracy, hybrid regime, or electoral autocracy. The concept of autocracy has been recognized in political philosophy since ancient history. Autocrats maintain power through political repression of any opposition and Co-option, co-op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coup D'état
A coup d'état (; ; ), or simply a coup , is typically an illegal and overt attempt by a military organization or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership. A self-coup is said to take place when a leader, having come to power through legal means, tries to stay in power through illegal means. By one estimate, there were 457 coup attempts from 1950 to 2010, half of which were successful. Most coup attempts occurred in the mid-1960s, but there were also large numbers of coup attempts in the mid-1970s and the early 1990s. Coups occurring in the post-Cold War period have been more likely to result in democratic systems than Cold War coups, though coups still mostly perpetuate authoritarianism. Many factors may lead to the occurrence of a coup, as well as determine the success or failure of a coup. Once a coup is underway, coup success is driven by coup-makers' ability to get others to believe that the coup attempt will be successful. The number of successful cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 list of sovereign states, independent national governments and government agency, subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracy, democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarianism, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
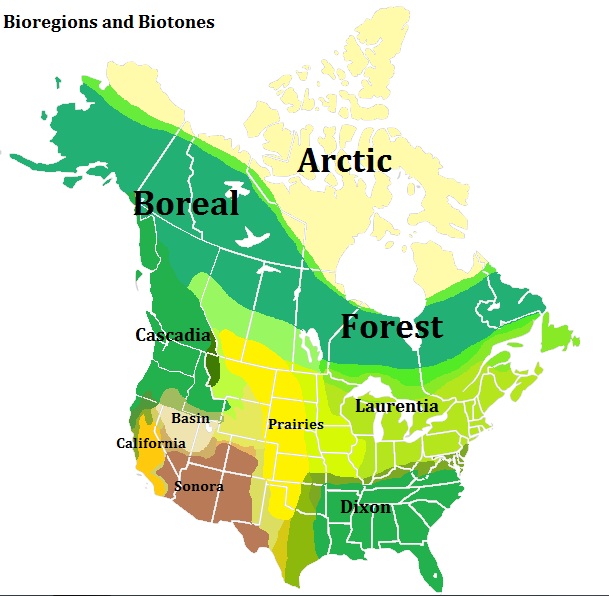
Ecoregional Democracy
Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called ''bioregions'' (similar to ''ecoregions''). Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions. Bioregionalism is a concept that goes beyond national boundaries—an example is the concept of Cascadia, a region that is sometimes considered to consist of most of Oregon and Washington, the Alaska Panhandle, the far north of California and the West Coast of Canada, sometimes also including some or all of Idaho and western Montana. Another example of a bioregion, which does not cross national boundaries, but does overlap state lines, is the Ozarks, a bioregion also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiat Money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender, and is authorized by government regulation. Since the end of the Bretton Woods system in 1976 by the Jamaica Accords, the major currencies in the world are fiat money. Fiat money generally does not have intrinsic value and does not have use value. It has value only because the individuals who use it as a unit of account or, in the case of currency, a medium of exchange agree on its value. They trust that it will be accepted by merchants and other people as a means of payment for liabilities. Fiat money is an alternative to commodity money, which is a currency that has intrinsic value because it contains, for example, a precious metal such as gold or silver which is embedded in the coin. Fiat also differs from representative mone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Terminology
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social status, status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil–military Relations
Civil–military relations (Civ-Mil or CMR) describes the relationship between military organizations and civil society, military organizations and other government bureaucracies, and leaders and the military. CMR incorporates a diverse, often normative field, which moves within and across management, social science and policy scales. More narrowly, it describes the relationship between the civil authority of a given society and its military authority. "The goal of any state is to harness military professional power to serve vital national security interests, while guarding against the misuse of power that can threaten the well-being of its people." Studies of civil-military relations often rest on a normative assumption that it is preferable to have the ultimate responsibility for a country's strategic decision-making to lie in the hands of the civilian political leadership (i.e. civilian control of the military) rather than a military (a military dictatorship). A paradox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |