|
Mid-Cenomanian Event
The Mid-Cenomanian Event (MCE) was an oceanic anoxic event that took place during the middle Cenomanian, as its name suggests, around 96.5 Ma. Timing Approximately 400 kyr before the MCE occurred a major negative δ13C excursion. Geochronological analysis of the Iona-1 core from the Eagle Ford Group of Texas shows the MCE lasted from 96.57 ± 0.12 Ma to 96.36 ± 0.12 Ma. A positive δ13C excursion of a rather small magnitude (1%) defines the MCE. The MCE δ13C excursion had two pulses, designated MCE Ia and MCE Ib, respectively. The magnitude of MCE Ib's δ13C shift was greater than MCE Ia's. Causes Orbital forcing is considered the chief cause of the MCE by many scientists. It is believed that the MCE occurred during the simultaneous occurrence of nodes in the obliquity, orbital eccentricity, and axial precession Milankovitch cycles. A coincidence in all three nodes would occur once every 2.45 Myr, a timeframe consistent with the occurrence of the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Anoxic Event
An anoxic event describes a period wherein large expanses of Earth's oceans were depleted of dissolved Oxygen, oxygen (O2), creating toxic, Euxinia, euxinic (anoxic waters, anoxic and wikt:sulfidic, sulfidic) waters. Although anoxic events have not happened for millions of years, the geologic record shows that they happened many times in the past. Anoxic events coincided with several mass extinctions and may have contributed to them. These mass extinctions include some that geobiology, geobiologists use as Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, time markers in biostratigraphy, biostratigraphic dating. On the other hand, there are widespread, various Shale, black-shale beds from the mid-Cretaceous which indicate anoxic events but are not associated with mass extinctions. Many geologists believe oceanic anoxic events are strongly linked to the slowing of ocean circulation, climatic warming, and elevated levels of greenhouse gases. Researchers have proposed enhanced volcanism (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene is an interglacial period within the ongoing Ice age, glacial cycles of the Quaternary, and is equivalent to Marine isotope stages, Marine Isotope Stage 1. The Holocene correlates with the last maximum axial tilt towards the Sun of the Earth#Axial tilt and seasons, Earth's obliquity. The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth, and impacts of the human species worldwide, including Recorded history, all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban culture, urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global significance for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonoidea
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family Nautilidae). The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Emsian stage of the Early Devonian (410.62 million years ago), with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (66 million years ago). They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, the only remaining group of ammonoids from the Jurassic up until their extinction. Ammonoids exhibited considerable diversity over their evolutionary history, with over 10,000 species having been described. Ammonoids are excellent index fossils, and they have been frequently used to link rock layers in which a particular species or genus is found to specific Geologic time scale, geologic time periods. Their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Benthos from the Census of Antarctic Marine Life website This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from tidal pools along the , out to the continental shelf, and then down to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction Event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is a part of the biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration (storage) to and release from carbon sinks. To describe the dynamics of the carbon cycle, a distinction can be made between the ''fast'' and ''slow'' carbon cycle. The fast cycle is also referred to as the ''biological carbon cycle''. Fast cycles can complete within years, moving substances from atmosphere to biosphere, then back to the atmosphere. Slow or geological cycles (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemical Perspectives Letters
''Geochemical Perspectives Letters'' is a peer-reviewed open access scholarly journal publishing original research in geochemistry Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the e .... It is published by the European Association for Geochemistry. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: References External links * Open access journals Academic journals established in 2015 English-language journals Geochemistry journals {{geochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
''Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal covering research in Earth and planetary processes with a focus on understanding the Earth as a system. The journal is published by Wiley on behalf of the American Geophysical Union. As of May 2022 the editor-in-chief is Claudio Faccenna (Roma Tre University and University of Texas at Austin). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 4.480. References External links *{{Official website, https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15252027 English-language journals Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals Earth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontong-Java Plateau
The Ontong Java Plateau (OJP) is a massive oceanic plateau located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, north of the Solomon Islands. The OJP was formed around (Ma), with a much smaller volcanic event around 90 Ma. Two other southwestern Pacific plateaus, Manihiki and Hikurangi, now separated from the OJP by Cretaceous oceanic basins, are of similar age and composition and probably formed as a single plateau and a contiguous large igneous province together with the OJP. When eruption of lava had finished, the Ontong Java–Manihiki–Hikurangi plateau covered 1% of Earth's surface and represented a volume of of basaltic magma. This "Ontong Java event", first proposed in 1991, represents the largest volcanic event of the past 200 million years, with a magma eruption rate estimated at up to per year over 3 million years, for a total several times larger than the Deccan Traps. The smooth surface of the OJP is punctuated by seamounts such as the Ontong Java Atoll, one of the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar Flood Basalt
The Madagascar flood basalt, also known as the Madagascar large igneous province (LIP), is one of the major magmatic events of the Late Cretaceous. They cover a large area of basaltic and rhyolitic lava flows that erupted during an episode of widespread basaltic volcanism during the Cretaceous period. The flood basalts are characterized by lava flows, Dike (geology), dykes, sill (geology), sills, and intrusive rock, intrusions, and other volcanic features include Volcanic plug, plugs, scoria, and spatter cones. Tholeiitic basalt constitutes the primary rock type.Mahoney, J. J., Saunders, A. D., Storey, M., & Randriamanantenasoa, A. (2008). Geochemistry of the Volcan de l’ Androy Basalt–Rhyolite Complex, Madagascar Cretaceous Igneous Province. Journal of Petrology, 49(6), 1069–1096. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egn018Melluso, L., Morra, V., Brotzu, P., Franciosi, L., Lieberknecht, A., & Bennio, L. (2003). Geochemical provinciality in the Cretaceous basaltic magmatism of Northern Madag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
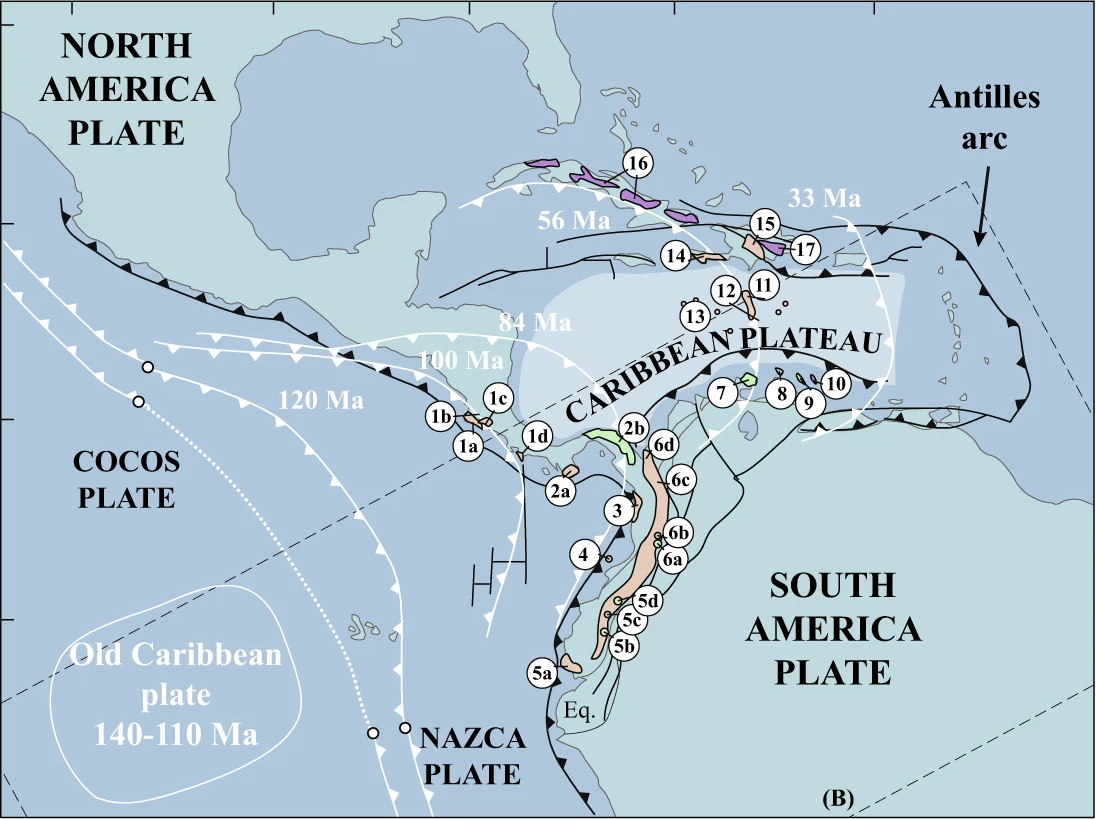
Caribbean Large Igneous Province
The Caribbean large igneous province (CLIP) consists of a major flood basalt, which created this large igneous province (LIP). It is the source of the current large eastern Pacific oceanic plateau, of which the Caribbean-Colombian oceanic plateau is the tectonized remnant. The deeper levels of the plateau have been exposed on its margins at the North American and South American plates. The volcanism took place between 139 and 69 million years ago ( Ma), with the majority of activity appearing to lie between 95 and 88 Ma. The plateau volume has been estimated as on the order of . It has been linked to the Galápagos hotspot. Proto-Caribbean Seaway Divergence between the North American and South American Plates began to create oceanic crust off Colombia's Pacific coast by the end of the Jurassic (150 Ma). This divergence, which continued until at least 66 Ma, first resulted in a " proto-Caribbean spreading ridge" between these plates flanked by a perpendicular transform zone on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |