|
Microseism
In seismology, a microseism is defined as a faint earth tremor caused by natural phenomena. Sometimes referred to as a "hum", it should not be confused with the anomalous acoustic phenomenon of the The Hum, same name. The term is most commonly used to refer to the dominant background seismic and electromagnetic noise signals on Earth, which are caused by water waves in the oceans and lakes. Characteristics of microseism are discussed by Bhatt. Because the ocean wave oscillations are statistically homogeneous over several hours, the microseism signal is a long-continuing oscillation of the ground. The most energetic seismic waves that make up the microseismic field are Rayleigh waves, but Love waves can make up a significant fraction of the wave field, and body waves are also easily detected with arrays. Because the conversion from the ocean waves to the seismic waves is very weak, the amplitude of ground motions associated to microseisms does not generally exceed 10 micrometers. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbarom
In acoustics, microbaroms, also known as the "voice of the sea", are a class of Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric infrasonic waves generated in marine storms by a non-linear interaction of ocean surface waves with the atmosphere. They typically have narrow-band, nearly sinusoidal waveforms with amplitudes up to a few microbars, and wave periods near 5 seconds (0.2 hertz). Due to low atmospheric Absorption (acoustics), absorption at these low frequency, frequencies, microbaroms can Wave propagation, propagate thousands of kilometers in the atmosphere, and can be readily detected by widely separated instruments on the Earth's surface. History The reason for the discovery of this phenomenon was an accident: the aerologists working at the marine hydrometeorological, Hydrometeorology stations and watercraft drew attention to the strange pain that a person experiences when approaching the surface of a standard meteorological probe (a balloon filled with hydrogen). During one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the '' fetch''. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples to waves over high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth. When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch and no longer being affected by the local wind, wind waves are called '' swells'' and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy example of this is waves generated south of Tasmania during heavy wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Waves
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of Body of water, bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the wind direction, direction of the wind is known as the ''Wind fetch, fetch''. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small capillary wave, ripples to waves over high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth. When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch and no longer being affected by the local wind, wind waves are called ''swell (ocean), swells'' and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Noise
In geophysics, geology, civil engineering, and related disciplines, seismic noise is a generic name for a relatively persistent vibration of the ground, due to a multitude of causes, that is often a non-interpretable or unwanted component of signals recorded by seismometers. Physically, seismic noise arises primarily due to surface or near surface sources and thus consists mostly of elastic surface waves. Low frequency waves (below 1 Hz) are commonly called microseisms and high frequency waves (above 1 Hz) are called microtremors. Primary sources of seismic waves include human activities (such as transportation or industrial activities), winds and other atmospheric phenomena, rivers, and ocean waves. Seismic noise is relevant to any discipline that depends on seismology, including geology, oil exploration, hydrology, and earthquake engineering, and structural health monitoring. It is often called the ambient wavefield or ambient vibrations in those disciplines (however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clapotis
In hydrodynamics, a clapotis (from French for "lapping of water") is a non-breaking standing wave pattern, caused for example, by the reflection of a traveling surface wave train from a near vertical shoreline like a breakwater, seawall or steep cliff. The resulting ''clapotic'' wave does not travel horizontally, but has a fixed pattern of nodes and antinodes. These waves promote erosion at the toe of the wall, and can cause severe damage to shore structures. The term was coined in 1877 by French mathematician and physicist Joseph Valentin Boussinesq who called these waves 'le clapotis' meaning "the lapping". In the idealized case of "full clapotis" where a purely monotonic incoming wave is completely reflected normal to a solid vertical wall, the standing wave height is twice the height of the incoming waves at a distance of one half wavelength from the wall. In this case, the circular orbits of the water particles in the deep-water wave are converted to purely linear moti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
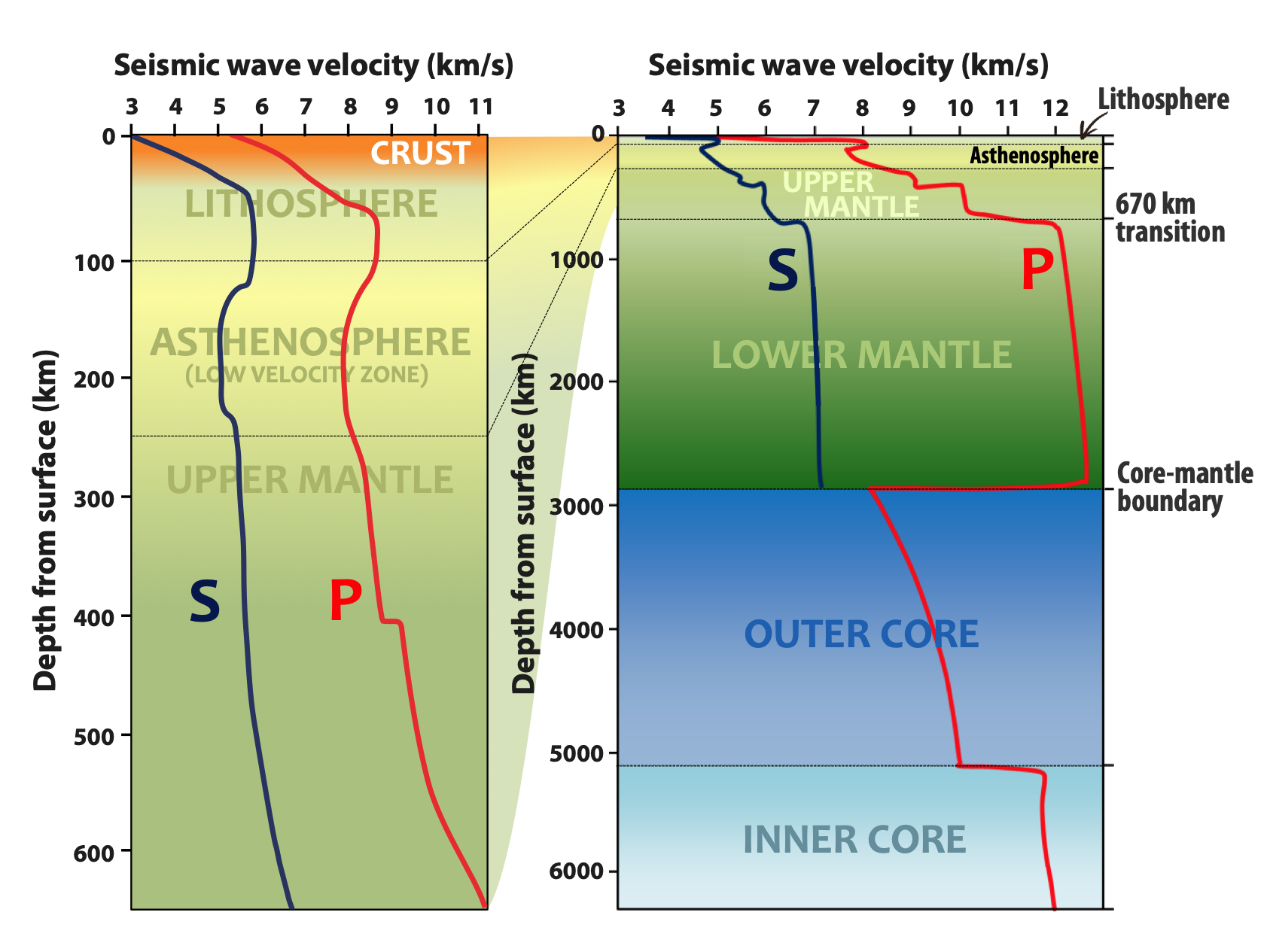
Seismic Wave
A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake), volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Group
In physics, a wave packet (also known as a wave train or wave group) is a short burst of localized wave action that travels as a unit, outlined by an envelope. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, a potentially-infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Any signal of a limited width in time or space requires many frequency components around a center frequency within a bandwidth inversely proportional to that width; even a gaussian function is considered a wave packet because its Fourier transform is a "packet" of waves of frequencies clustered around a central frequency. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion) or it may change ( dispersion) while propagat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hum
The Hum is persistent and invasive low-frequency humming, rumbling, or droning noise audible to many but not all people. Hums have been reported in many countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Canada. They are sometimes named according to the locality where the problem has been particularly publicized, such as the " Taos Hum" in New Mexico and the " Windsor Hum" in Ontario. The Hum does not appear to be a single phenomenon. Different causes have been attributed, including local mechanical sources, often from industrial plants, as well as manifestations of tinnitus or other biological auditory effects. Description A 1973 report cites a university study of fifty cases of people complaining about a "low throbbing background noise" that others were unable to hear. The sound, always peaking between 30 and 40 Hz (hertz), was found to only be heard during cool weather with a light breeze, and often early in the morning. These noises were often con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropogenic Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'' is a fortnightly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society. It publishes original research and review content in a wide range of physical scientific disciplines. Articles can be accessed online a few months prior to the printed journal. All articles become freely accessible two years after their publication date. The current editor-in-chief is John Dainton. Overview ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A'' publishes themed journal issues on topics of current scientific importance and general interest within the physical, mathematical and engineering sciences, edited by leading authorities and comprising original research, reviews and opinions from prominent researchers. Past issue titles include "Supercritical fluids - green solvents for green chemistry?", "Tsunamis: Bridging science, engineering and society", "Spatial transformations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |