|
Metropolitan Green Belt
The Metropolitan Green Belt is a statutory green belt around London, England. It comprises parts of Greater London, Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, Essex, Hertfordshire, Kent and Surrey, parts of two of the three districts of Bedfordshire and a small area in Copthorne, Sussex. Government statistics show the planning designation covered of land. History For some years after 1580 Elizabeth I of England banned new building in a three-mile wide belt around the City of London, in an attempt to stop the spread of plague. However, this was not widely enforced, relatively short-lived and it was possible to buy dispensations which reduced the effect. The concept was also inspired by those elsewhere in Europe, one being inner buffer zones and broad boulevards to separate non-ancient parts. One re-used extensive ramparts more like protective fields to serve old city walls, the , in inner Vienna before 1900 in which numerous parks have been laid out. The first major proposals for a gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Metropolitan Green Belt Among The Green Belts Of England
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
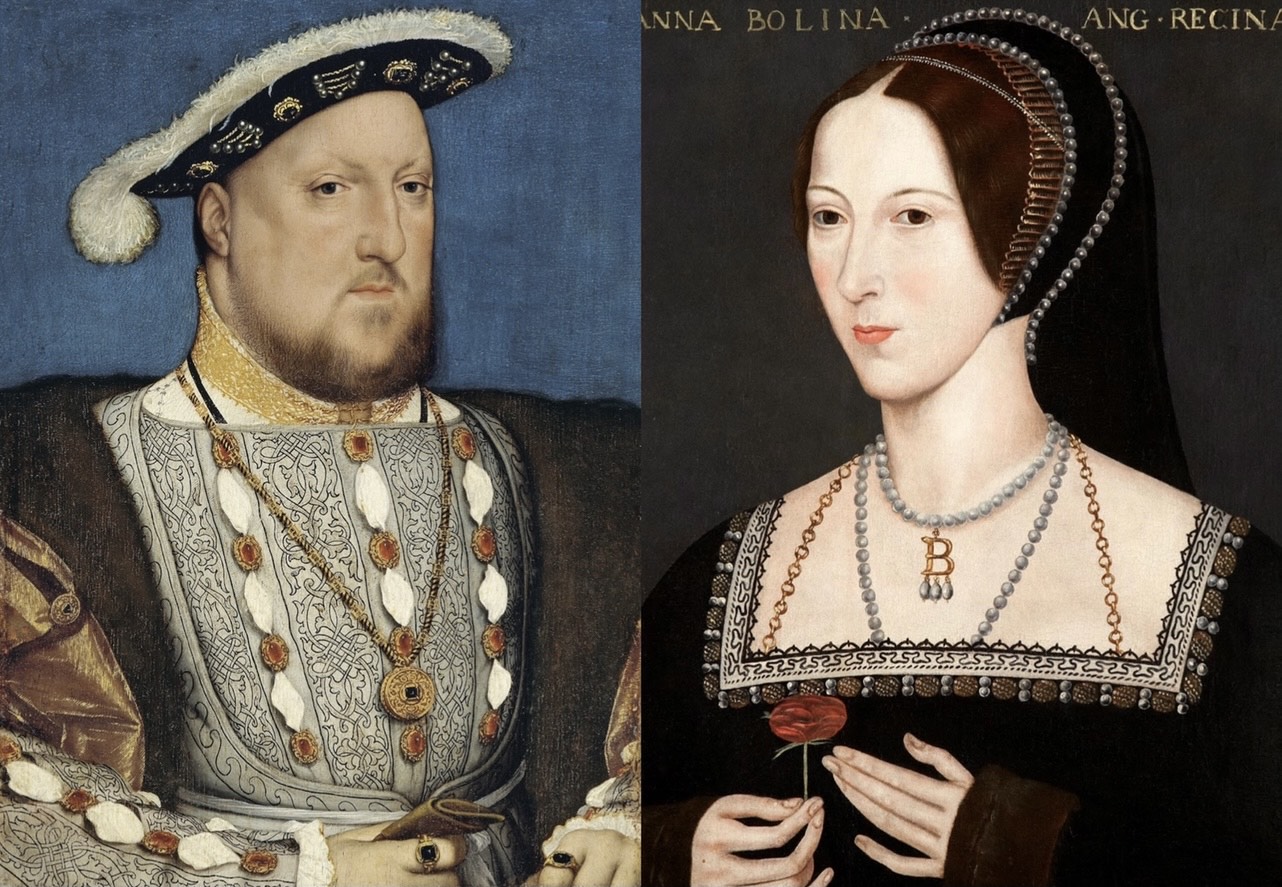
Elizabeth I Of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history and culture, gave name to the Elizabethan era. Elizabeth was the only surviving child of Henry VIII and his second wife, Anne Boleyn. When Elizabeth was two years old, her parents' marriage was annulled, her mother was executed, and Elizabeth was declared illegitimate. Henry restored her to the line of succession when she was 10. After Henry's death in 1547, Elizabeth's younger half-brother Edward VI ruled until his own death in 1553, bequeathing the crown to a Protestant cousin, Lady Jane Grey, and ignoring the claims of his two half-sisters, Mary and Elizabeth, despite statutes to the contrary. Edward's will was quickly set aside and the Catholic Mary became queen, deposing Jane. During Mary's reign, Elizabeth was imprisoned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9 & 10 Geo
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an Ascender (typography), ascender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Towns Act 1946
The New Towns Acts were a series of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to found new settlements or to expand substantially existing ones, to establish Development Corporations to deliver them, and to create a Commission to wind up the Corporations and take over their assets and liabilities. Of these, the more substantive acts were the New Towns Act 1946 and the Town Development Act 1952. "The New Towns Act 946was intended to pre-emptively direct urban growth and infrastructural development into new towns, thereby decentralising population and economic opportunity while inhibiting urban sprawl." New Towns were developed in three generations. *The first generation set up in the late 1940s concentrated predominantly on housing development with provision for rail and seldom for cars; eight were in a ring around London. *The second generation in the early 1960s included a wider mix of uses and used more innovative architecture. *The third generation towns were larger and te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attlee Ministry
Clement Attlee was invited by King George VI to form the first Attlee ministry in the United Kingdom on 26 July 1945, succeeding Winston Churchill as prime minister of the United Kingdom. The Labour Party (UK), Labour Party had won a landslide victory at the 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945 general election, and went on to enact policies of what became known as the post-war consensus, including the establishment of the welfare state and the nationalisation of 20 per cent of the entire economy. The government's spell in office was marked by post-war austerity measures; the crushing of pro-independence and communist movements Malayan Emergency, in Malaya; the grant of Indian Independence Act 1947, independence to India, Pakistan, Ceylon, and Burma; the engagement in the Cold War against Soviet Communism; and the creation of the country's National Health Service (NHS). Attlee went on to win a narrow majority at the 1950 United Kingdom general election, 1950 general electi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Gravier
Jean-François Gravier () was a French geographer famous for his work ''Paris and the French Desert'' published in 1947, and republished in 1953 and 1972. He denounces the extreme concentration of France in Paris, and the monopoly of that city over French resources. Quotation Bibliography * Gravier (J. - F.). Paris and the French desert, Portulan, Paris, 1947, 418 p. * Gravier (J. - F.). Paris and the French desert in 1972, Flammarion, Paris, 1972, 284 p. See also * Empty diagonal * Regional planning * Decentralization Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those related to planning and decision-making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group and gi ... French geographers {{Geographer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Town
A satellite city or satellite town is a smaller municipality or settlement that is part of (or on the edge of) a larger metropolitan area and serves as a regional population and employment center. It differs from mere suburbs, subdivisions and especially bedroom communities in that it has employment bases sufficient to support its residential population, and conceptually, could be a self-sufficient community outside of its larger metropolitan area. However, it functions as part of a metropolis and experiences high levels of cross-commuting (that is, residents commuting out of and employees commuting into the city). Satellite cities versus other types of settlement Satellite cities are different from and are sometimes confused with the following related patterns of development. Suburbs Satellite cities differ from suburbs in that they have distinct employment bases, commuter sheds, and cultural offerings from the central metropolis, as well as an independent municipal gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, opening on 10 January 1863 as the world's first underground passenger railway. The Metropolitan is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines with of track. However, the Underground does not cover most southern parts of Greater London; there are only 33 Underground stations south of the River Thames. The system's List of London Underground stations, 272 stations collectively accommodate up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interwar Britain
In the United Kingdom, the interwar period (1918–1939) entered a period of relative stability after the Partition of Ireland, although it was also characterised by economic stagnation. In politics, the Liberal Party collapsed and the Labour Party became the main challenger to the dominant Conservative Party throughout the period. The Great Depression affected Britain less severely economically and politically than other major nations, although some areas still suffered from severe long-term unemployment and hardship, especially mining districts and in Scotland and North West England. Historian Arthur Marwick sees a radical transformation of British society resulting from the Great War, a deluge that swept away many old attitudes and brought in a more egalitarian society. He sees the famous literary pessimism of the 1920s as misplaced, arguing there were major positive long-term consequences of the war for British society. He points to an energised self-consciousness a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaign To Protect Rural England
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to: Types of campaigns * Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beet A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with ...s are harvested and processed * Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme * Blitz campaign, a short, intensive, and focused marketing campaign for a product or business * Civil society campaign, a project intended to mobilize public support in order to instigate social change * Military campaign, large scale, long duration, significant military strategy plans incorporating a series of inter-related military operations or battles * Political campaign, an organized effort which seeks to influence the decision making process within a specific group * Project, an underta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Society (organisation)
The London Society is a British membership organisation established to encourage public interest and participation in urban planning and transport matters in London as well as to study and celebrate the capital's unique history and character. It is among the oldest civic societies in the United Kingdom. Purpose The society advertises itself as being "for all those who love London". Its original motto was ''"Antiqua Tegenda, Pulchra Petenda, Futura Colenda”'', Latin for "look after the old, seek the beautiful, cultivate the future". It was agreed at the society's annual general meeting in 2018 that a new motto would be adopted: ''"Valuing the past; looking to the future"'', which came into effect in 2019. The society's journal states that "the aim of the society is to stimulate a wider concern for the beauty of the capital city, for the preservation of its charms and the careful consideration of its developments". History The London Society was founded on the back of the tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringstraße
The Ringstrasse or Ringstraße (pronounced Help:IPA/Standard German, [ʁɪŋˌʃtʁaːsə] :File:De-Ringstraße.ogg, ⓘ, lit. ''ring road'') is a 5.3 km (3.3 mi) circular grand boulevard that serves as a ring road around the historic city centre, the Innere Stadt, of Vienna, Austria. The road is built where the city walls once stood. The Ring, as it is colloquially known, was built, along with grand buildings on either side of the road, in the second half of the 19th century. The road runs clockwise, from the Urania to the Schottenring, and is divided into nine parts. Because of its architectural beauty and history, the Ringstrasse is designated by UNESCO as part of the Historic Centre of Vienna World Heritage Site. History The grand boulevard was constructed to replace the Defensive wall, city walls, which had originally been erected during the 13th century. These walls were initially funded by the ransom payment obtained from the release of Richard I of England, Richard the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |