|
Methodology Of Econometrics
The methodology of econometrics is the study of the range of differing approaches to undertaking econometric analysis. The econometric approaches can be broadly classified into nonstructural and structural. The nonstructural models are based primarily on statistics (although not necessarily on formal statistical models), their reliance on economics is limited (usually the economic models are used only to distinguish the inputs (observable "explanatory" or " exogenous" variables, sometimes designated as ) and outputs (observable "endogenous" variables, ). Nonstructural methods have a long history (cf. Ernst Engel, 1857). Structural models use mathematical equations derived from economic models and thus the statistical analysis can estimate also ''unobservable'' variables, like elasticity of demand. Structural models allow to perform calculations for the situations that are not covered in the data being analyzed, so called counterfactual analysis (for example, the analysis of a monop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometrics
Econometrics is an application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships. M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8–22 Reprinted in J. Eatwell ''et al.'', eds. (1990). ''Econometrics: The New Palgrave''p. 1 p. 1–34Abstract ( 2008 revision by J. Geweke, J. Horowitz, and H. P. Pesaran). More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on the concurrent development of theory and observation, related by appropriate methods of inference." An introductory economics textbook describes econometrics as allowing economists "to sift through mountains of data to extract simple relationships." Jan Tinbergen is one of the two founding fathers of econometrics. The other, Ragnar Frisch, also coined the term in the sense in which it is used today. A basic tool for econometrics is the multiple linear regression model. ''Econome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katarina Juselius
Katarina Juselius (born 25 September 1943) is professor Emeritus of econometrics and empirical economics at the University of Copenhagen. Her work has been on empirical macro models and associated issues. She obtained her Lic.Econ.Sc. and PhD from the Swedish School of Economics and Business Administration in Helsinki. Research She is the 271st most quoted economist in the world according to IDEAS and her research has been quoted 27000 times. She is also the on the editorial board of Journal of Economic Methodology. Her most quoted paper, "Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—with applications to the demand for money" has been quoted over 16000 times. Personal life She is married to Søren Johansen Søren Johansen (born 6 November 1939) is a Danish statistician and econometrician who is known for his contributions to the theory of cointegration. He is currently a professor at the Department of Economics, University of Copenhagen and in the . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
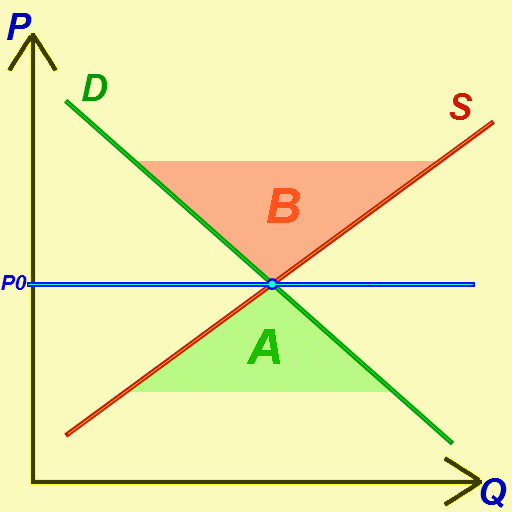
Equilibrium (economics)
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris_paribus#Applications, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good or other traded item in a perfect competition, perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market clearing, market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In situations where a firm has market power, its decision on how much output to bring to market influences the market price, in violation of perfect competition. There, a more complicated model should be used; for example, an oligopoly or product differentiation, differentiated-product model. Likewise, where a buyer has market power, models such as monopsony will be more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Wold
Herman Ole Andreas Wold (25 December 1908 – 16 February 1992) was a Norwegian-born econometrician and statistician who had a long career in Sweden. Wold was known for his work in mathematical economics, in time series analysis, and in econometric statistics. In mathematical statistics, Wold contributed the Cramér–Wold theorem characterizing the normal distribution and developed the Wold decomposition in time series analysis. In microeconomics, Wold advanced utility theory and the theory of consumer demand. In multivariate statistics, Wold contributed the methods of partial least squares (PLS) and graphical models. Wold's work on causal inference from observational studies was decades ahead of its time, according to Judea Pearl. Early life Herman Wold was born in Skien, southern Norway. He was the youngest in a family of six brothers and sisters. In 1912 the family moved to Sweden and became Swedish citizens. Herman's father had a small fur and hide business. Scientific ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploratory Data Analysis
In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of data analysis, analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell beyond the formal modeling and thereby contrasts with traditional hypothesis testing, in which a model is supposed to be selected before the data is seen. Exploratory data analysis has been promoted by John Tukey since 1970 to encourage statisticians to explore the data, and possibly formulate hypotheses that could lead to new data collection and experiments. EDA is different from Data analysis#Initial data analysis, initial data analysis (IDA), which focuses more narrowly on checking assumptions required for model fitting and hypothesis testing, and handling missing values and making transformations of variables as needed. EDA encompasses IDA. Overview Tukey defined data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observational Study
In fields such as epidemiology, social sciences, psychology and statistics, an observational study draws inferences from a sample (statistics), sample to a statistical population, population where the dependent and independent variables, independent variable is not under the Scientific control, control of the researcher because of ethical concerns or logistical constraints. One common observational study is about the possible effect of a treatment on subjects, where the assignment of subjects into a treated group versus a control group is outside the control of the investigator. This is in contrast with experiments, such as randomized controlled trials, where each subject is Random assignment, randomly assigned to a treated group or a control group. Observational studies, for lacking an assignment mechanism, naturally present difficulties for inferential analysis. Motivation The independent variable may be beyond the control of the investigator for a variety of reasons: * A rand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevin Hoover
Kevin Douglas Hoover (born May 3, 1955) is Professor of Economics and Philosophy and a Senior Fellow at the Center for the History of Political Economy at Duke University. He has previously held positions at the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, University of Oxford (Balliol College, Nuffield College, and Lady Margaret Hall), and the University of California, Davis, where he served eight years as chair of the Economics Department. He is a former president of the History of Economics Society and chaired the International Network for Economic Method. He is a former editor of the ''Journal of Economic Methodology'' and the current editor of the ''History of Political Economy.'' Hoover is most noted for his work in the history and methodology of macroeconomics, the philosophy of causation and empirical methods of causal inference applicable to macroeconomics, as well as to search methods in econometrics more generally. He has also made substantial contributions to the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jörn-Steffen Pischke
Jörn-Steffen Pischke is a professor of economics at the London School of Economics. He is known for his work on Applied Econometrics. Selected publications * Angrist, J. D., & Pischke, J. S. (2009). ''Mostly harmless econometrics: An empiricist's companion''. Princeton University Press. * Angrist, J. D., & Pischke, J. S. (2014). ''Mastering 'metrics': The path from cause to effect''. Princeton University Press. * Acemoglu, D., & Pischke, J. S. (1998). Why do firms train? Theory and evidence. ''The Quarterly Journal of Economics ''The Quarterly Journal of Economics'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Oxford University Press for the Harvard University Department of Economics. Its current editors-in-chief are Robert J. Barro, Lawrence F. Kat ...'', 113(1), 79–119. References External links Jörn-Steffen Pischke Microeconometricians Year of birth missing (living people) Living people Academics of the London School of Economics {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Angrist
Joshua David Angrist (; born September 18, 1960) is an Israeli American economist and Ford Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Angrist, together with Guido Imbens, was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 2021 "for their methodological contributions to the analysis of causal relationships". He ranks among the world's top economists in labor economics, urban economics, econometrics, and the economics of education, and is known for his use of quasi-experimental research designs (such as instrumental variables) to study the effects of public policies and changes in economic or social circumstances. He is a co-founder and co-director of MIT's Blueprint Labs, which researches the relationship between human capital and income inequality in the U.S. He also cofounded Avela, an ed-tech startup that provides application and enrollment-related software and services to school districts, schools of all kinds, organizations like Teach f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference In Differences
Difference in differences (DID or DD) is a statistical technique used in econometrics and quantitative research in the social sciences that attempts to mimic an experimental research design using observational study data, by studying the differential effect of a treatment on a 'treatment group' versus a 'control group' in a natural experiment. It calculates the effect of a treatment (i.e., an explanatory variable or an independent variable) on an outcome (i.e., a response variable or dependent variable) by comparing the average change over time in the outcome variable for the treatment group to the average change over time for the control group. Although it is intended to mitigate the effects of extraneous factors and selection bias, depending on how the treatment group is chosen, this method may still be subject to certain biases (e.g., mean regression, reverse causality and omitted variable bias). In contrast to a time-series estimate of the treatment effect on subjects (wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |