|
Metamorphopsia
Metamorphopsia (from , ) is a type of distorted vision in which a grid of straight lines appears wavy or partially blank. In addition, metamorphopsia can result in misperceptions of an object's size, shape, or distance to the viewer. People can first notice they suffer from the condition when looking at mini blinds in their home. Initially characterized in the 1800s, metamorphopsia was described as one of the primary and most notable indications of myopic and senile maculopathies. Metamorphopsia can present itself as unbalanced vision, resulting from small unintentional movements of the eye as it tries to stabilize the field of vision. It is mainly associated with macular degeneration, particularly age-related macular degeneration with choroidal neovascularization.Page 45 in: Other conditions that can present with complain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preferential Hyperacuity Perimetry
Preferential hyperacuity perimetry (PHP) is a psychophysical test used to identify and quantify visual abnormalities such as metamorphopsia and scotoma. It is a type of perimetry. Background Vision abnormalities such as metamorphopsia (distortions) and scotoma are symptoms of retinal diseases such as macular degeneration. In advanced stages of the disease, photoreceptor cells may be irreversibly damaged. Hence, if not treated, macular degeneration may lead to blindness. Awareness to early changes in vision, especially in high risk patients, leads to early treatment (such as intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF factors, e.g. bevacizumab or ranibizumab) and prevents loss of vision. Because of complex brain mechanisms such as filling-in, patients with small and peripheral defects in their vision are often unaware of such changes until late stages in the disease. Another problem is that minute visual aberrations can be normal and therefore should be distinguished from genuine visual ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
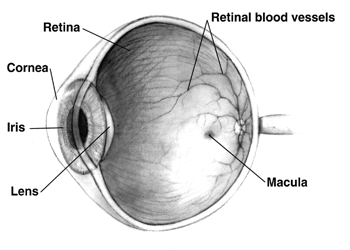
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between the two forms is categorized by the change in the macula. Those with dry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmorphopsia
Dysmorphopsia, in a broad sense, is a condition in which a person is unable to correctly perceive objects. It is a visual distortion, used to denote a variant of metamorphopsia in which lines appear wavy. These illusions may be restricted to certain visuals areas, or may affect the entire visual field. It has been associated with meningioma tumors and bilateral lateral occipital cortical damage, e.g. after carbon monoxide poisoning or drug abuse. Etymology The term ''dysmorphopsia'' comes from the Greek words ''dus'' (bad), ''morphè'' (form) and ''opsis'' (seeing). See also * Hallucination * Macropsia * Metamorphopsia * Micropsia * Occipital lobe * Visual perception Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ... References Visual disturbances and blindness Neurologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual release hallucinations, Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of retina, macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between the two forms is categorized by the change in the macula. Those with dry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amsler Grid - Distorted Vision (metamorphopsia)
Amsler is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Guy Amsler (1895–1986), associate justice of the Arkansas Supreme Court * Marc Amsler (1891–1968), Swiss ophthalmologist ** Amsler grid ** Amsler sign, a medical sign * Margaret Harris Amsler (1908–2002), American lawyer and academic * Marty Amsler (born 1942), American football player * Samuel Amsler (1791–1849), Swiss engraver See also * Jakob Amsler-Laffon (1823–1912), Swiss mathematician, physicist and engineer *Amsler Island Amsler Island is a small island off the south coast of Anvers Island in the Palmer Archipelago of Antarctica. It sits between Loudwater Cove and Arthur Harbour. The island is a roughly triangular rocky plot of granite land approximately long ..., an island of the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica {{surname German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies. Associated with the natural, applied, formal, and social sciences this research strategy promotes the objective empirical investigation of observable phenomena to test and understand relationships. This is done through a range of quantifying methods and techniques, reflecting on its broad utilization as a research strategy across differing academic disciplines. There are several situations where quantitative research may not be the most appropriate or effective method to use: 1. When exploring in-depth or complex topics. 2. When studying subjective experiences and personal opinions. 3. When conducting exploratory research. 4. When studying sensitive or controversial topics The objective of quantitative research is to deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and of the interpretative faculty of the brain. The most commonly referred-to visual acuity is ''distance acuity'' or ''far acuity'' (e.g., "20/20 vision"), which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a far distance. This ability is compromised in people with myopia, also known as short-sightedness or near-sightedness. Another visual acuity is ''Near visual acuity, near acuity'', which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a near distance. This ability is compromised in people with hyperopia, also known as long-sightedness or far-sightedness. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a condition where the retina pulls away from the tissue underneath it. It may start in a small area, but without quick treatment, it can spread across the entire retina, leading to serious vision loss and possibly blindness. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that requires surgery. The retina is a thin layer at the back of the eye that processes visual information and sends it to the brain. When the retina detaches, common symptoms include seeing floaters, flashing lights, a dark shadow in vision, and sudden blurry vision. The most common type of retinal detachment is rhegmatogenous, which occurs when a tear or hole in the retina lets fluid from the center of the eye get behind it, causing the retina to pull away. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most commonly caused by posterior vitreous detachment, a condition where the gel inside the eye breaks down and pulls on the retina. Risk factors include older age, nearsightedness ( myopia), eye injury, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Hole
A macular hole is a small break in the macula, located in the center of the eye's light-sensitive tissue called the retina. Symptoms If the vitreous is firmly attached to the retina when it pulls away, it can tear the retina and create a macular hole. Also, once the vitreous has pulled away from the surface of the retina, some of the fibers can remain on the retinal surface and can contract. This increases tension (physics), tension on the retina and can lead to a macular hole. In either case, the fluid that has replaced the shrunken vitreous can then seep through the hole onto the macula, blurring and distorting central vision. Causes The eye contains a Gelatin dessert, jelly-like substance called the vitreous. Shrinking of the vitreous usually causes the hole. As a person ages, the vitreous becomes watery and begins to pull away from the retina. If the vitreous is firmly attached to the retina when it pulls away, a hole can result. Diagnosis Macular degeneration is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiretinal Membrane
Epiretinal membrane or macular pucker is a disease of the eye in response to changes in the vitreous humor or more rarely, diabetes. Sometimes, as a result of immune system response to protect the retina, cells converge in the macular area as the vitreous ages and pulls away in posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). PVD can create minor damage to the retina, stimulating exudate, inflammation, and leucocyte response. These cells can form a transparent layer gradually and, like all scar tissue, tighten to create tension on the retina which may bulge and pucker, or even cause swelling or macular edema. Often this results in distortions of vision that are clearly visible as bowing and blurring when looking at lines on chart paper (or an Amsler grid) within the macular area, or central 1.0 degree of visual arc. Usually it occurs in one eye first, and may cause binocular diplopia or double vision if the image from one eye is too different from the image of the other eye. The dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally covers specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications, such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |