|
Metal–semiconductor Junction
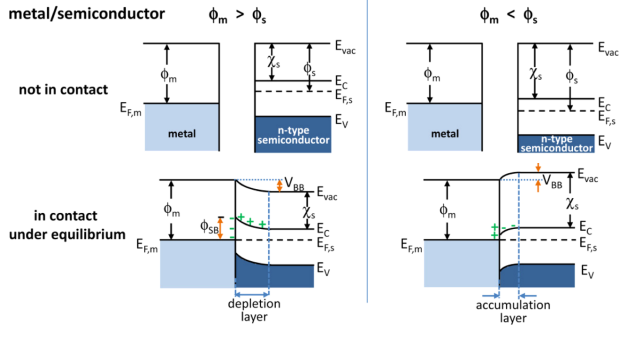
In solid-state physics, a metal–semiconductor (M–S) junction is a type of electrical junction in which a metal comes in close contact with a semiconductor material. It is the oldest type of practical semiconductor device. M–S junctions can either be rectifying or non-rectifying. The rectifying metal–semiconductor junction forms a Schottky barrier, making a device known as a Schottky diode, while the non-rectifying junction is called an ohmic contact. (In contrast, a rectifying semiconductor–semiconductor junction, the most common semiconductor device today, is known as a p–n junction.) Metal–semiconductor junctions are crucial to the operation of all semiconductor devices. Usually, an ohmic contact is desired so that electrical charge can be conducted easily between the active region of a transistor and the external circuitry. Occasionally, however, a Schottky barrier is useful, as in Schottky diodes, Schottky transistors, and metal–semiconductor fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. Along with solid-state chemistry, it also has direct applications in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and Elasticity (physics), elasticity), Heat conduction, thermal, Electrical conduction, electrical, Magnetism, magnetic and Crystal optics, optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelled workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" means that the final electron position is far from the surface on the atomic scale, but still too close to the solid to be influenced by ambient electric fields in the vacuum. The work function is not a characteristic of a bulk material, but rather a property of the surface of the material (depending on crystal face and contamination). Definition The work function for a given surface is defined by the difference :W = -e\phi - E_, where is the charge of an electron, is the electrostatic potential in the vacuum nearby the surface, and is the Fermi level (electrochemical potential of electrons) inside the material. The term is the energy of an electron at rest in the vacuum nearby the surface. In practice, one directly controls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface State
Surface states are electronic states found at the Surface (topology), surface of materials. They are formed due to the sharp transition from solid material that ends with a surface and are found only at the atom layers closest to the surface. The termination of a material with a surface leads to a change of the electronic band structure from the bulk material to the vacuum. In the weakened potential at the surface, new electronic states can be formed, so called surface states. Origin at condensed matter interfaces As stated by Bloch wave, Bloch's theorem, eigenstates of the single-electron Schrödinger equation with a perfectly periodic potential, a crystal, are Bloch waves : \begin \Psi_ &=\mathrm^u_(\boldsymbol). \end Here u_(\boldsymbol) is a function with the same periodicity as the crystal, ''n'' is the band index and k is the wave number. The allowed wave numbers for a given potential are found by applying the usual Born–von Karman cyclic boundary conditions. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American solid-state physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Houser Brattain for their invention of the transistor; and again in 1972 with Leon Cooper and John Robert Schrieffer for their fundamental theory of superconductivity, known as the BCS theory. Born and raised in Wisconsin, Bardeen received a Ph.D. in physics from Princeton University. After serving in World War II, he was a researcher at Bell Labs and a professor at the University of Illinois. The transistor revolutionized the electronics industry, making possible the development of almost every modern electronic device, from telephones to computers, and ushering in the Information Age. Bardeen's developments in superconductivity—for which he was awarded his second Nobel Prize—are used in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), medical magnetic resonance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Of States
In condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of allowed modes or quantum state, states per unit energy range. The density of states is defined as where N(E)\delta E is the number of states in the system of volume V whose energies lie in the range from E to E+\delta E. It is mathematically represented as a distribution by a probability density function, and it is generally an average over the space and time domains of the various states occupied by the system. The density of states is directly related to the dispersion relations of the properties of the system. High DOS at a specific energy level means that many states are available for occupation. Generally, the density of states of matter is continuous. In isolated systems however, such as atoms or molecules in the gas phase, the density distribution is Discrete distribution, discrete, like a spectral density. Local variations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Bending
In solid-state physics, band bending refers to the process in which the electronic band structure in a material curves up or down near a junction or interface. It does not involve any physical (spatial) bending. When the electrochemical potential of the free charge carriers around an interface of a semiconductor is dissimilar, charge carriers are transferred between the two materials until an equilibrium state is reached whereby the potential difference vanishes. The band bending concept was first developed in 1938 when Nevill Francis Mott, Mott, Alexander Davydov (physicist), Davydov and Walter H. Schottky, Schottky all published theories of the rectifying effect of Metal–semiconductor junction, metal-semiconductor contacts. The use of semiconductor junctions sparked the computer revolution in the second half of the 20th century. Devices such as the diode, the transistor, the Photoelectric sensor, photocell and many more play crucial roles in technology. Qualitative description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor-semiconductor Junction
A heterojunction is an interface between two layers or regions of dissimilar semiconductors. These semiconducting materials have unequal band gaps as opposed to a homojunction. It is often advantageous to engineer the electronic energy bands in many solid-state device applications, including semiconductor lasers, solar cells and transistors. The combination of multiple heterojunctions together in a device is called a heterostructure, although the two terms are commonly used interchangeably. The requirement that each material be a semiconductor with unequal band gaps is somewhat loose, especially on small length scales, where electronic properties depend on spatial properties. A more modern definition of heterojunction is the interface between any two solid-state materials, including crystalline and amorphous structures of metallic, insulating, fast ion conductor and semiconducting materials. Manufacture and applications Heterojunction manufacturing generally requires the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson's Rule
Anderson's rule is used for the construction of energy band diagrams of the heterojunction between two semiconductor materials. Anderson's rule states that when constructing an energy band diagram, the vacuum levels of the two semiconductors on either side of the heterojunction should be aligned (at the same energy). It is also referred to as the electron affinity rule, and is closely related to the Schottky–Mott rule for metal–semiconductor junctions. Anderson's rule was first described by R. L. Anderson in 1960. Constructing energy band diagrams Once the vacuum levels are aligned it is possible to use the electron affinity and band gap values for each semiconductor to calculate the conduction band and valence band offsets. The electron affinity (usually given by the symbol \chi in solid state physics) gives the energy difference between the lower edge of the conduction band and the vacuum level of the semiconductor. The band gap (usually given the symbol E_) gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Energy
In physics and chemistry, ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, Ion, positive ion, or molecule. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as :X(g) + energy ⟶ X+(g) + e− where X is any atom or molecule, X+ is the resultant ion when the original atom was stripped of a single electron, and e− is the removed electron. Ionization energy is positive for neutral atoms, meaning that the ionization is an endothermic process. Roughly speaking, the closer the outermost electrons are to the atomic nucleus, nucleus of the atom, the higher the atom's ionization energy. In physics, ionization energy (IE) is usually expressed in electronvolts (eV) or joules (J). In chemistry, it is expressed as the energy to ionize a Mole (unit), mole of atoms or molecules, usually as Joule per mole, kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or Kilocalorie per mole, kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Comparison of ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Affinity
The electron affinity (''E''ea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion. ::X(g) + e− → X−(g) + energy This differs by sign from the energy change of electron capture ionization. The electron affinity is positive when energy is released on electron capture. In solid state physics, the electron affinity for a surface is defined somewhat differently ( see below). Measurement and use of electron affinity This property is used to measure atoms and molecules in the gaseous state only, since in a solid or liquid state their energy levels would be changed by contact with other atoms or molecules. A list of the electron affinities was used by Robert S. Mulliken to develop an electronegativity scale for atoms, equal to the average of the electrons affinity and ionization potential. Other theoretical concepts that use electron affinity include electronic chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevill Mott
Sir Nevill Francis Mott (30 September 1905 – 8 August 1996) was a British physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1977 for his work on the electronic structure of magnetic and disordered systems, especially amorphous semiconductors. The award was shared with Philip W. Anderson and J. H. Van Vleck. The three had conducted loosely related research. Mott and Anderson clarified the reasons why magnetic or amorphous materials can sometimes be metallic and sometimes insulating. Education and early life Mott was born in Leeds to Charles Francis Mott and Lilian Mary Reynolds, a granddaughter of Sir John Richardson, and great granddaughter of Sir John Henry Pelly, 1st Baronet. Miss Reynolds was a Cambridge Mathematics Tripos graduate and at Cambridge was the best woman mathematician of her year. His parents met in the Cavendish Laboratory, when both were engaged in physics research under J.J. Thomson. Nevill grew up first in the village of Giggleswick, in the West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter H
Walter may refer to: People and fictional characters * Walter (name), including a list of people and fictional and mythical characters with the given name or surname * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–1968) * Gunther (wrestler), Austrian professional wrestler and trainer Walter Hahn (born 1987), who previously wrestled as "Walter" * Walter, standard author abbreviation for Thomas Walter (botanist) ( – 1789) * "Agent Walter", an early codename of Josip Broz Tito * Walter, pseudonym of the anonymous writer of '' My Secret Life'' * Walter Plinge, British theatre pseudonym used when the original actor's name is unknown or not wished to be included * John Walter (businessman), Canadian business entrepreneur Companies * American Chocolate, later called Walter, an American automobile manufactured from 1902 to 1906 * Walter Energy, a metallurgical coal producer for the global steel industry * Walter Aircraft Engines, Czech manufacturer of aero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |